 TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) and FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) are the two techniques of multiplexing. The common difference between TDM and FDM is that TDM share the timescale for the different signals; Whereas FDM shares the frequency scale for the different signals.
TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) and FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) are the two techniques of multiplexing. The common difference between TDM and FDM is that TDM share the timescale for the different signals; Whereas FDM shares the frequency scale for the different signals.
Before understanding both terms in deep let’s understand the term multiplexing. Multiplexing is a technique through which several signals are concurrently transmitted over a single data link. Multiplexed system involves n number of devices which share the capacity of one link that’s how a link (path) can have multiple channels.
Multiple devices fed their transmission streams to a Multiplexer (MUX) which merges them into a single stream. At the receiver, the single stream is directed to the Demultiplexer (DEMUX), which is again translated into its component transmission and sent to their intended receivers.
Content: TDM Vs FDM
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | TDM | FDM |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Times scale is shared. | Frequency is shared. |
| Used with | Digital signals and analog signals | Analog signals |
| Necessary requirement | Sync Pulse | Guard Band |
| Interference | Low or negligible | High |
| Circuitry | Simpler | Complex |
| Utilization | Efficiently used | Ineffective |
Definition of TDM
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is considered to be a digital procedure which can be employed when the transmission medium data rate quantity is higher than the data rate requisite of the transmitting and receiving devices. In TDM, corresponding frames carry data to be transmitted from the different sources. Each frame consists of a set of time slots, and portions of each source is assigned a time slot per frame.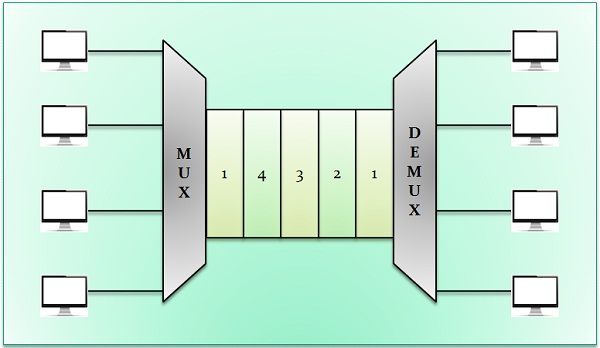
Types of TDM
- Synchronous Time-Division Multiplexing: In this type the synchronous term signifies that the multiplexer is going to assign precisely the same slot to each device at every time even if a device has anything to send or not. If it doesn’t have something, the time slot would be empty. TDM uses frames to group time slots which covers a complete cycle of time slots. Synchronous TDM uses a concept, i.e., interleaving for building a frame in which a multiplexer can take one data unit at a time from each device, then another data unit from each device and so on.
The order of the receipt notifies the demultiplexer where to direct each time slot, which eliminates the need of addressing. To recover from timing inconsistencies Framing bits are used which are usually appended to the beginning of each frame. Bit stuffing is used to force speed relationships to equalize the speed between several devices into an integer multiple of each other. In bit stuffing, the multiplexer appends additional bits to device’s source stream. - Asynchronous Time-Division Multiplexing: Synchronous TDM waste the unused space in the link hence it does not assure the efficient use of the full capacity of the link. This gave rise to Asynchronous TDM. Here Asynchronous means flexible not fixed. In Asynchronous TDM several low rate input lines are multiplexed to a single higher speed line. In Asynchronous TDM, the number of slots in a frame is less than the number of data lines. On the contrary, In Synchronous TDM the number of slots must be equal to the number of data lines. That’s why it, avoids the wastage of the link capacity.
Definition of FDM
Frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is an analog technique which is implemented only when the bandwidth of the link is higher than the merged bandwidth of the signals to be transmitted. Each sending device produces signals which modulate at distinct carrier frequencies. To hold the modulated signal, the carrier frequencies are isolated by adequate bandwidth. 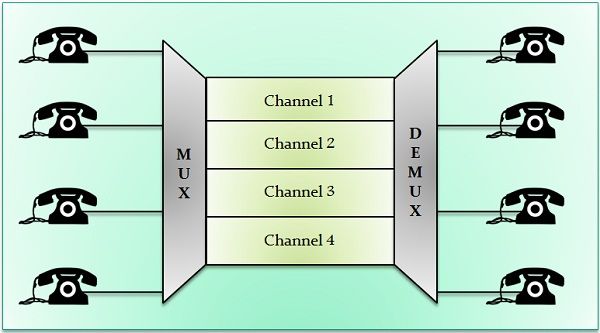 The modulated signals are then merged into one compound signal that can be transferred by the link. The signals travel through the bandwidth ranges referred to as channels.
The modulated signals are then merged into one compound signal that can be transferred by the link. The signals travel through the bandwidth ranges referred to as channels.
Signals overlapping can be controlled by using unutilized bandwidth strips for segregating the channels, these are known as guard bands. Also, carrier frequencies should not interrupt with the original data frequencies. If any condition fails to adhere, the original signals cannot be recovered.
Key Differences Between TDM and FDM
- The time-division multiplexing (TDM) includes sharing of the time through utilizing time slots for the signals. On the other hand, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) involves the distribution of the frequencies, where the channel is divided into various bandwidth ranges (channels).
- Analog signal or Digital signal any could be utilized for the TDM while FDM works with Analog signals only.
- Framing bits (Sync Pulses) are used in TDM at the start of a frame in order to enable synchronization. As against, FDM uses Guard bands to separate the signals and prevent its overlapping.
- FDM system generates different carriers for the different channels, and also each occupies a distinct frequency band. In addition, different bandpass filters are required. Conversely, the TDM system requires identical circuits. As a result, the circuitry needed in FDM is more complex than needed in TDM.
- The non–linear character of the various amplifier in the FDM system produces harmonic distortion, and this introduces the interference. In contrast, in TDM system time slots are allotted to various signals; as the multiple signals are not inserted simultaneously in a link. Although, the non-linear requirements of both the systems are same, but TDM is immune to interference (crosstalk).
- The utilization of physical link in case of TDM is more efficient than in FDM. The reason behind this is that the FDM system divides the link in multiple channels which does not make use of full channel capacity.
Conclusion
TDM and FDM, both are the techniques used for multiplexing. FDM uses analog signals, and TDM uses Analog and digital both types of signals. However, the efficiency of TDM is much greater than FDM.
Rajat says
Nice article
Dhanu says
good information.
Hayat khan says
Thanks for this information helping in my computer networking assignment
Aryan says
Best result, i love to learn from here.
Preethi says
Using to answer the questions during online class 😂 nice