 FDM and OFDM are the multiplexing techniques used mainly in the analog system. These techniques are distinguished depending upon the spacing between the various subchannels (in the form of the composite signal) transmitted through a single channel. So, in FDM the message signals prevent noise by separating the signals with the help of the guard bands. On the contrary, the OFDM technique does not use guard band, in fact, it allows the overlapping of the signals. Thus, enabling the better utilization of the provided bandwidth.
FDM and OFDM are the multiplexing techniques used mainly in the analog system. These techniques are distinguished depending upon the spacing between the various subchannels (in the form of the composite signal) transmitted through a single channel. So, in FDM the message signals prevent noise by separating the signals with the help of the guard bands. On the contrary, the OFDM technique does not use guard band, in fact, it allows the overlapping of the signals. Thus, enabling the better utilization of the provided bandwidth.
Multiplexing is the technique which permits the transmission of the numerous signals through a single channel. There are various types of multiplexing methods such as TDM, FDM, CDM, WDM, OFDM, etcetera.
Content: FDM Vs OFDM
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | FDM | OFDM |
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Frequency Division Multiplexing | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing |
| Basic | Bandwidth dedicated to several sources. | All the sub-channels are assigned to a single data source. |
| Relationship between the carriers | No relationship exists | Addition of the number of orthogonal carriers |
| Use of Guard band | Necessary | Not required |
| Spectral efficiency | Low | High |
| Effect of interference | Prone to interference. | Negligible susceptance to interferece. |
Definition of FDM
FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) is the partitioning of the spectrum in several individual frequency channels. It works on analog systems unlike other multiplexing techniques such as TDM. The independent message signals are converted into frequency bands within a common bandwidth by implying the modulation technique. These modulated signals use different carrier known as sub-carriers and merged in a linear summing circuit to form a composite signal for transmission. The resulting signal can be transported over the single channel through electromagnetic means.
At the receiver, the signals are surpassed by band-pass filters to isolate the individual frequency channels. At last, the output of the band-pass filter is demodulated and distributed at the different destination.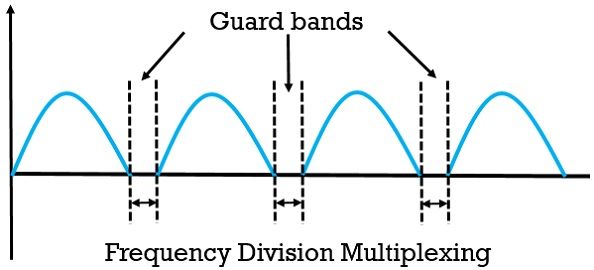
FDM is implemented only in the case when the usable bandwidth of the channel is greater than the needed channel bandwidth. The channels are separated with each other by unused bandwidth called as guard bands to prevent the inter-channel crosstalk and overlapping of the channel.
Definition of OFDM
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) is a spread spectrum technique which divides the data over a large number of carrier separately located at precise frequencies. The spacing between these carrier provides the orthogonality feature to assist the demodulator for detecting the correct frequencies. However, the subchannels are closely spaced and overlap each other.
Prior understanding orthogonality feature, we must clear out the meaning of the orthogonal, which means more than one object is acting independently. Therefore, in OFDM the neighbour signals do not interfere with each other. So, how does orthogonality works? Let’s consider the example given below when a signal reaching its peak (the highest point) its two neighbouring signals are at null or zero. 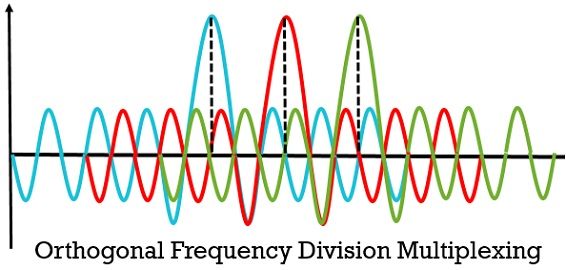 Similarly, with the other two signals, the peak of one signal occurs at the null of the other two signals. In the receiver end, the multiplexer strengthens the signal according to the orthogonal characteristics of the signal.
Similarly, with the other two signals, the peak of one signal occurs at the null of the other two signals. In the receiver end, the multiplexer strengthens the signal according to the orthogonal characteristics of the signal.
OFDM is a prevalent multiplexing technique mostly implemented in the latest wireless methods and telecommunication standards, like Wi-Fi 802.11 ac, WiMAX, 4G and 5G cellular phone technologies, satellite and other.
Key Differences Between FDM and OFDM
- In FDM the entire bandwidth is divided by several sources. On the contrary, in OFDM all the subchannels are dedicated to the single data source.
- The carriers do not rely on each other in case of FDM while OFDM sums up the number of orthogonal carriers for the particular point.
- FDM makes use of guard band, whereas OFDM eliminated the use of guard band.
- The spectral efficiency of OFDM is better than FDM.
- FDM is easily affected by other RF resources, causing it vulnerable to interference. As against, OFDM is not affected by interference.
Conclusion
The OFDM technique is advantageous over FDM because it is more spectrally efficient by placing the subchannels closely until they generate an overlapping effect. Multipath distortion and RF interference are the major issues in the FDM technique while OFDM is immune to these problems.
Leave a Reply