 On an elementary foundation, computers can be classified into three categories – analog, digital and hybrid computers. These computers can be categorised according to the working principle they follow. For example, analog computers use some certain physical properties such as the electrical and mechanical characteristics for solving or simplifying a problem. On the other hand, digital computers utilize discrete electrical and voltage levels in order to encode a real-life scenario. The computers developed in the first generation were the analog computers where the major components used were vacuum tubes, resistors, capacitors, etcetera.
On an elementary foundation, computers can be classified into three categories – analog, digital and hybrid computers. These computers can be categorised according to the working principle they follow. For example, analog computers use some certain physical properties such as the electrical and mechanical characteristics for solving or simplifying a problem. On the other hand, digital computers utilize discrete electrical and voltage levels in order to encode a real-life scenario. The computers developed in the first generation were the analog computers where the major components used were vacuum tubes, resistors, capacitors, etcetera.
In this content, we are going to discuss the difference between the above given two types of computers that are analog and digital. When it comes to accuracy the digital computers are more accurate than an analog computer. The reason behind accuracy is that in analog computers, the overall accuracy of the system depends on the individual internal components of the devices.
Content: Analog Computer Vs Digital Computer
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Analog Computers | Digital Computers |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Computations are carried out employing continuous variations of physical properties. | Discrete electrical voltage levels are used to encode the input. |
| Computation | Performed in real-time | Large delays can occur |
| Accuracy | Low | High |
| Circuitry | Made up of electrical and mechanical components. | Consists of a large number of tiny electrical switches. |
| Mechanism | Uses variation of different physical quantities. | Uses binary numbers and binary arithmetic. |
| Examples | Speedometers, energy meters and traditional washing machine, etc | Digital cameras and watches, thermometers, scanners, modern computers, etc. |
Definition of Analog Computer
Analog computer, not many people, seem to be aware of this term. At present, we barely use the term analog computers as these are losing its existence. However, analog computers are the initial devices produced to solve complicated problems. It employs the physical properties of the object to gain the outcome or solve a problem.
An analog device measures the continuous variation of a particular process with the help of computing the continuous variation in a physical quantity (i.e., voltage, current, pressure, torque, etcetera). Thereafter, the calculations are performed according to the measured value of the physical quantity and the output is produced in the form of another pneumatic signal.
Example
Let’s take an example of analog device which is used to indicate the level of the water in a tank. So, this water level indicating device must be pressure-sensitive, where piezo-electric crystal or a strain gauge can be utilized to transform water pressure, that is proportional to the level of water in the tank, into a corresponding voltage signal. 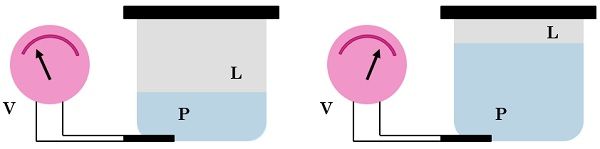 We can use a voltmeter to display the variation in voltage produced due to the change in the water level.
We can use a voltmeter to display the variation in voltage produced due to the change in the water level.
Implementation
There are several fields where analog computers can be implemented, let’s see some of the examples where it can be implemented. The computing devices such as voltmeters, energy meters, speedometers of automobiles, analogue square root extractors, slide rules, are the analog computing devices. Analog devices were very popular in Chemical Process Plants, Flight Simulators, Power Plants, etc.
Definition of Digital Computer
As the advancement in technology, every technology is digitizing because it provides more accuracy. Unlike an analog computer, the digital computer works with discrete signals, rather than the physical quantity. It encodes the continuous processes and variables into discrete states which are further expressed as a group of numbers. However, these digital systems use binary numbers to express the states, and all the calculations are also performed using binary numbers.
In digital computers the circuitry comprises of several numbers of small electrical switches, which can exist in two possible states – ON (1, or high voltage) or OFF (0, low voltage) and this represents the binary numbers. For example, to represent the colours in binary a set of 8-bit binary numbers are used such as red = 10101111 (175), blue = 11100000 (224) and green = 00110110 (54) (the three primary colours binary representation). Therefore, in this way, the physical property, like colour with numerous shades, are quantised and represented in a finite numbers.
Example
Let’s take our previous example of the water level indicator. So, in a digital device, there can be 4 different sensors used rather than an analog pressure sensor. The sensors are placed one after the other from bottom to top, so when the water level increases, the sensors will get activated from the bottom to the top.
The 4 distinct levels of the water in the tank where the sensors are placed can be expressed in 4 sets of binary numbers (00, 01, 10, 11). In the circuit diagram, ‘C’ computes the level, and ‘D’ displays the output. 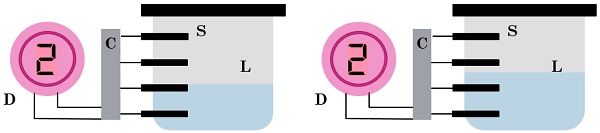 If two distinct water level generates the same number of activated sensors, then the output generated would be same. In order to increase the accuracy of these devices, the number of discrete states can be increased, which is used to show particular measurements.
If two distinct water level generates the same number of activated sensors, then the output generated would be same. In order to increase the accuracy of these devices, the number of discrete states can be increased, which is used to show particular measurements.
Implementation
The digital computers are widely used in most of the modern technologies from watches to the washing machines. Some of the examples of it are digital cameras, clocks, scanners, security devices, thermometers, etcetera.
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Computer
- Continuous variations of physical properties such as voltage, frequency, electrical resistance, pressure are applied to perform computations in an analog computer. As against, in digital computers, the discrete electrical voltage levels are used to deal with real-world problems.
- An analog system carry out the calculations in real-time concomitantly making the process faster. In contrast, digital computers generate large delays due to the sequential form of calculations is followed.
- As the analog computers involve different individual components on which the overall accuracy depends and it could also involve visual observation of the output where accuracy can be affected by the various factors. On the other hand, digital computing systems uses fixed voltage levels to represent binary numbers and the accuracy of the complete system is not affected by the individual components of the device. This is the reason digital computers are more accurate and precise as compared to analog computers.
- The analog computers contain electrical and mechanical components such as inductors, resistors, capacitors to build an analog device. Conversely, digital computers circuitry comprised of the electrical switches, transistors, IC’s etcetera.
Conclusion
The analog computers take some physical property as the input. On the contrary, digital computers convert input into the digital form to solve the problem.
Leave a Reply