 The GPS and DGPS are the satellite-based navigation systems. The basic difference between GPS and DGPS lies on their accuracy, DGPS is more accurate than GPS. DGPS was intentionally designed to reduce the signal degradation.
The GPS and DGPS are the satellite-based navigation systems. The basic difference between GPS and DGPS lies on their accuracy, DGPS is more accurate than GPS. DGPS was intentionally designed to reduce the signal degradation.
GPS provides the accuracy about 10 meters, but DGPS can provide accuracy around 1 meter, even beyond that 10 cm.
Content: GPS Vs DGPS
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | GPS | DGPS |
|---|---|---|
| Number of receivers used | Only one, i.e., Stand-alone GPS receiver | Two, Rover and stationary receivers |
| Accuracy | 15-10 m | 10 cm |
| Range of the instruments | Global | Local (within 100 km) |
| Cost | Affordable as compared to DGPS | Expensive |
| Frequency range | 1.1 - 1.5 GHz | Varies according to agency |
| Factors affecting the Accuracy | Selective availability, satellite timing, atmospheric conditions, ionosphere, troposphere and multipath. | Distance between the transmitter and rover, ionosphere, troposphere and multipath. |
| Time coordinate system used | WGS84 | Local coordinate system |
Definition of GPS
Global Positioning System (GPS) provides the accurate position of an object to the earth. It uses timely signals generated by satellites revolving around the earth. GPS includes a constellation of 24 satellites and extra for backup purpose. Four satellites are used for getting the precise position, this process is known as trilateration.
GPS technology uses standalone receivers, where the location is directly calculated. This technique is prone to errors such as uncorrected satellite clock errors, orbital parameter satellite error, ionospheric and tropospheric delays, multipath errors, geometric errors and datum selection errors. To reduce these errors new technologies are evolved. GPS can gain nominal accuracy of 10-15 meters.
Definition of DGPS
Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) is an improvement to GPS. DGPS technology can achieve accuracy up to 10 cm. It reduces or eliminates the signal degradation, resulting in improving the accuracy. The goal of differential GPS is not to go directly for the location; rather it finds the location relative to a fixed reference point. DGPS relies on two receivers rover and reference receiver, rover is the user, and reference receiver is also known as the stationary receiver.
A stationary receiver is fixed, and its position is known to the system. The satellite information is continuously beamed towards the rover and the base station tower. Base station tower uses its known position to calculate the accurate timing. The stationary receiver sends the information to the rover receiver to rectify the measurements with the help of stationary receiver’s relative position.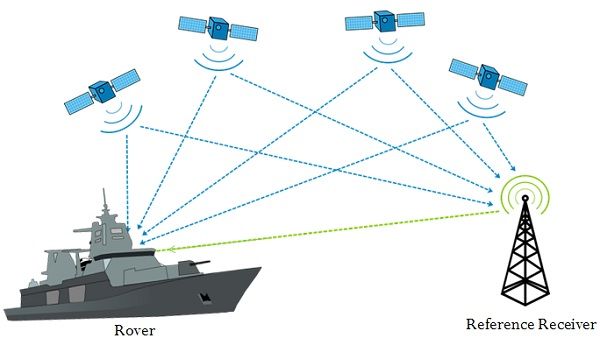
Key Differences Between GPS and DGPS
- In GPS, there is a standalone receiver which receives signals from the satellite whereas in DGPS there are two receivers, reference receiver and rover (user) where rover receives a calibrated signal from the reference receiver (fixed base station).
- The accuracy of GPS system is around 15 meters. On the other hand, DGPS is more accurate and can achieve accuracy up to 10 cm.
- GPS instruments cover the wide range and can be used globally while DGPS instruments cover a short range up to 100 km, but this range could change according to the frequency band.
- GPS system is less expensive as compared to DGPS system.
- The signal frequency transmitted by satellites in GPS ranges between 1.1 to 1.5 GHz. On the contrary, in DGPS the satellites do not transmit fixed range of frequency, the transmitted frequency depends on the agencies.
- The factors that affect the accuracy of the GPS system are selective availability, satellite timing, atmospheric conditions, ionosphere, troposphere and multipath. In contrast, the DGPS system is affected by the distance between the transmitter and rover, ionosphere, troposphere and multipath but at less extent.
- The GPS uses WGS84 time coordinate system which is an earth-fixed terrestrial system, earth-centred, and geodetic datum. As against DGPS uses a local coordinate system.
Conclusion
The Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) is more accurate technology than its antecedent Global Positioning system (GPS). The accuracy in DGPS is improved by using two receivers instead of using one, which finds the precise location using relative positions.
TAREK ALAKDHER says
VERY GOOD INFORMATION