 The baseband and broadband are the types of signalling techniques. These terminologies were developed to categorise different types of signals depending on particular kind of signal formats or modulation technique.
The baseband and broadband are the types of signalling techniques. These terminologies were developed to categorise different types of signals depending on particular kind of signal formats or modulation technique.
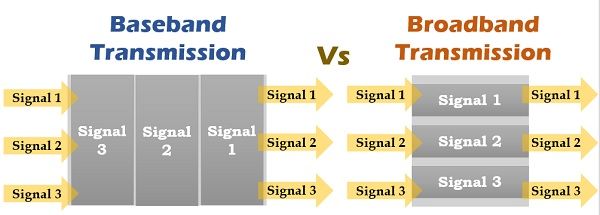
The prior difference between baseband transmission and broadband transmission is that in the baseband transmission the whole bandwidth of the cable is utilized by a single signal. Conversely, in the broadband transmission, multiple signals are sent on multiple frequencies simultaneously using a single channel.
Content: Baseband and Broadband Transmission
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Baseband Transmission | Broadband Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Type of signalling used | Digital | Analog |
| Application | Work well with bus topology. | Used with a bus as well as tree topology. |
| Encoding Used | Manchester and Differential Manchester encoding. | PSK encoding. |
| Transmission | Bidirectional | Unidirectional |
| Signal range | Signals can be travelled over short distances | Signals can be travelled over long distances without being attenuated. |
Definition of Baseband Transmission
Baseband transmission uses whole frequency spectrum of the medium for the transmission. That is the reason frequency division multiplexing cannot be used in the transmission but time division multiplexing is used in this transmission as in TDM the link is not divided into multiple channels instead it provides each input signal with a time slot, in which the signal utilize whole bandwidth for a given time slot. The signals are carried by wires in the form of electrical pulse.
Signals transmitted at point propagated in both the directions hence it is bidirectional. The expansion of baseband signal is limited to shorter distances because at high frequency the attenuation of the signal is most strong and the pulse blur out, causing the large distance communication completely impractical.
Definition of Broadband Transmission
The Broadband transmission employs analog signals which include optical or electromagnetic wave form of signal. The signals are sent into multiple frequencies permitting multiple signals to be sent simultaneously. Frequency division multiplexing is possible in which the frequency spectrum is divided into multiple sections of bandwidth. The distinct channels can support different types of signals of varying frequency ranges to travel simultaneously (at the same instance).
The signals propagated at any point are unidirectional in nature, in simple words the signal can be travelled at only one direction, unlike baseband transmission. It requires two data path that are connected at a point in the network refer to as headend. The first path is used for signal transmission from the station to the headend. And the other path is used for receiving propagated signals.
Key Differences Between Baseband and Broadband Transmission
- Baseband transmission utilizes digital signalling while broadband transmission uses analog signalling.
- Bus and tree topologies, both work well with the broadband transmission. On the other hand, for the baseband transmission bus topology is suitable.
- Baseband involves manchester and differential manchester encoding. In contrast, broadband does not make use of any digital encoding instead it uses PSK (Phase shift keying) encoding.
- The signals can be travelled in both the direction in baseband transmission whereas in broadband transmission the signals can travel in only one direction.
- In baseband transmission, the signals cover shorter distances because at higher frequencies the attenuation is most pronounced which make a signal to travel short distances without reducing its power. As against, in broadband signals, the signals can be travelled at longer distances.
Conclusion
The baseband and broadband transmissions are the types of signalling. Baseband transmission uses digital signalling and involves digital signal or electrical impulse that can be carried in a physical media such as wires. The broadband transmission uses analog signalling which involves optical signals or signals in the form of an electromagnetic wave. Baseband transmission utilizes the whole bandwidth of the channel to transmit a signal whereas in broadband transmission the bandwidth is divided into variable frequency ranges to transmit the different signals at the same instant.
Yash says
Thank you very much for such a better explanation.
Rahul kumar says
A better explanation, when I have to differentiate anything in IT, I always use to visit this site.
Huda says
Thank you for good explanation mam.
yumin says
wow amazing article,
love this article…
Ayman Metwally says
Thank you very much for such a better explanation but please send the reference of this article to me