 PCM and DPCM are the procedures used for transforming analog signal into digital. These methods are different as the PCM represents sample value by code words whereas in DPCM the original and sample values depend on previous samples.
PCM and DPCM are the procedures used for transforming analog signal into digital. These methods are different as the PCM represents sample value by code words whereas in DPCM the original and sample values depend on previous samples.
The conversion of analog-to-digital signal is beneficial for many applications because the digital signals are less susceptible to noise. The digital communication system provides better performance, reliability, security, efficiency and system integration. PCM and DPCM are the distinct source encoding techniques, let’s understand the difference between them with the comparison chart.
Content: PCM Vs DPCM
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | PCM | DPCM |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Bits involved | 4, 8 or 16 bits per sample. | More than one but less than PCM. |
| Quantization error and distortion | Depends on number of levels. | Slope overload distortion and quantization noise could present. |
| Bandwidth of transmission channel | Require high bandwidth. | Need less bandwidth as compared to PCM. |
| Feedback | Doesn't provide any feedback. | Feedback is provided. |
| Complexity of notation | Complex | Simple |
| Signal to noise-ratio | Good | Average |
| Area of application | Audio, video and telephony. | Speech and video. |
| Bits/sample | 7/8 | 4/6 |
| Bits rate | 56-64 | 32-48 |
Definition of PCM
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) is a source encoding strategy where the sequence of the coded pulse is used to represent the message signal with the help plotting the signal into time and amplitude in the discrete form. It involves two basic operations – time discretization and amplitude discretization. The time discretization is accomplished by sampling, and amplitude discretization is achieved quantization. It also includes an additional step that is encoding where the quantized amplitudes generate simple pulse patterns.
The PCM process is divided into three parts, first is the transmission at the source end, secondly regeneration at the transmission path and the receiving end.
The operations performed at source transmitting end –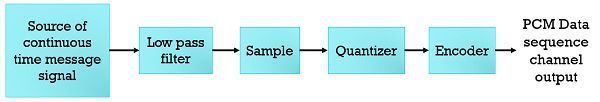
- Sampling – Sampling is a process of measuring the signal at equal intervals in which the message (baseband) signal is sampled with the line of rectangular pulses. These pulses are extremely narrowed down to extract the instantaneous sampling process closely. The accurate reconstruction of the baseband signal is obtained when sampling rate should be greater than twice the highest frequency component which is known as Nyquist rate.
- Quantization – After sampling the message signal undergoes quantization which provides discrete representation in both time and amplitude. In the quantization process, the sampled instances are alotted integral values in particular range.
- Encoding – The transmitted signal is made more strong against the interference and noise the quantized signal by translating it into a more suitable form of signal and this translation is known as encoding.
Operations performed at the time of regeneration along the transmission path –
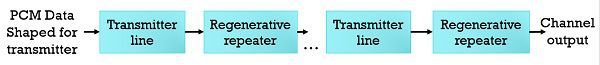 The signals are regenerated by placing the regenerative repeaters at the transmission route. It performs operations such as equalization, decision making and timing.
The signals are regenerated by placing the regenerative repeaters at the transmission route. It performs operations such as equalization, decision making and timing.
Operations performed at receiving end –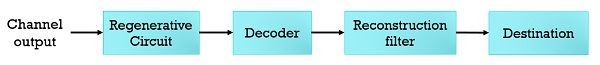
- Decoding and expanding – After the regeneration, the clean pulses of the signal are then combined in a code word. Then the code word is decoded into quantized PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation) signal. These decoded signals represent the projected sequence of compressed samples.
- Reconstruction – In this operation, the original signal is recovered at the receiving end.
Definition of DPCM
DPCM (Differential Pulse Code Modulation) is nothing but a variant of PCM. PCM is not efficient as it generates a lot of bits and consumes more bandwidth. So, to overcome the above-given problem the DPCM was devised. Similar to PCM, DPCM is comprised of sampling, quantization and coding processes. But DPCM differs from PCM because it quantizes the difference of the actual sample and predicted value. That is the reason it is called as differential PCM.
The DPCM uses the common property of PCM in which the high degree of correlation between adjacent samples is used. This correlation is generated when the signal is sampled at the rate greater than the Nyquist rate. Correlation means that the signal does not adapt change quickly from one sample to another. 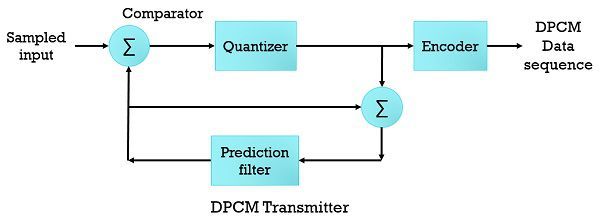 As an outcome, the difference between adjacent samples is consist of an average power which is smaller than the average power of the original signal.
As an outcome, the difference between adjacent samples is consist of an average power which is smaller than the average power of the original signal.
The encoding of extremely correlated signal in the standard PCM system produces redundant information. Through eliminating redundancy more efficient signal can be produced. 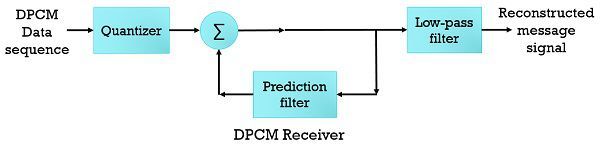 The redundant signal future value is inferred by analysing the past behaviour of the signal. This prediction of future value gives rise to differential quantization technique. When the quantizer output is encoded, the Differential Pulse Code Modulation is obtained.
The redundant signal future value is inferred by analysing the past behaviour of the signal. This prediction of future value gives rise to differential quantization technique. When the quantizer output is encoded, the Differential Pulse Code Modulation is obtained.
Key Differences Between PCM and DPCM
- The number of bits included in PCM is 4, 8 or 16 bits per sample. On the other hand, DPCM involves bits more than one, but less than the number of bits used in PCM
- Both PCM and DPCM techniques suffer quantization error and distortion but in different extent.
- DPCM requires less bandwidth while PCM works on higher bandwidth.
- PCM does not provide any feedback. In contrast, DPCM provides feedback.
- PCM is comprised of complex notation. As against, DPCM has a simple notation.
- DPCM has an average signal-to-noise ratio. On the contrary, PCM has a better signal-to-noise ratio.
- PCM is used in audio, video and telephony applications. Conversely, DPCM is used in speech and video application.
- If we talk about efficiency DPCM is a step ahead of PCM.
Conclusion
The PCM procedure samples and convert the analog waveform into digital code directly with the help of an Analog to digital converter. On the other hand, the DPCM does the similar work but uses multibit difference value.
Pidikiti says
Very useful and good information in a lucid way.
Youvanesh says
Excellent very easy to understand