 In Computer Networks, the term unicast and multicast are the information transmission methods. In unicast, one station transfers the information to only one receiver station. In multicast, the sender transfers the information to a group of interested receiver stations.
In Computer Networks, the term unicast and multicast are the information transmission methods. In unicast, one station transfers the information to only one receiver station. In multicast, the sender transfers the information to a group of interested receiver stations.
The fundamental difference between unicast and multicast is that unicast is one-to-one communication and multicast is a one-to-many communication process.
Let us study in brief the difference between unicast and multicast using the comparison chart.
Content: Unicast Vs Multicast
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Unicast | Multicast |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | One sender and one receiver. | One sender and multiple receivers. |
| Bandwidth | Multiple unicasting utilizes more bandwidth as compared to multicast. | Multicasting utilizes bandwidth efficiently. |
| Scale | It does not scale well for streaming media. | It does not scale well across large networks. |
| Mapping | One-to-one. | One-to-many. |
| Examples | Web surfing, file transfer. | Multimedia delivery, stock exchange. |
Definition of Unicast
In Computer Networks, the term unicast is a transmission method where one station sends information to another station. It is a one-to-one communication. Unicast transmission is used, where one station transmits some private or unique information to another station.
Examples of the unicast transmission are web surfing, file transfer as here the there is a single service requestor and a single service provider.
If one station needs to send packets to multiple stations, it has to send multiple unicast packets, each packet containing the address of the specific station and it is called “multiple unicasting“. Multiple unicasting utilizes the maximum bandwidth of the network. TCP protocol supports unicasting.
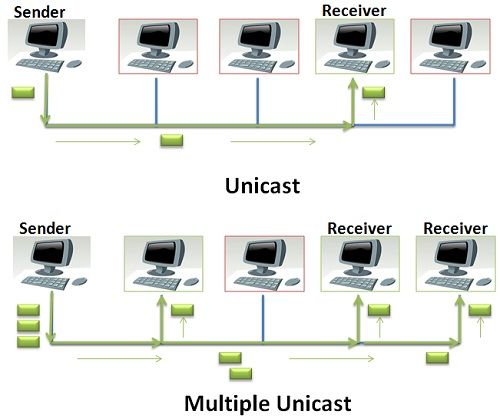 In the above figure, I had shown both the unicasting and multiple unicasting. In unicast clearly shows that the sender is sending the packet to only one receiver station which s highlighted by green color and rest station highlighted by green color are non-receiving stations.
In the above figure, I had shown both the unicasting and multiple unicasting. In unicast clearly shows that the sender is sending the packet to only one receiver station which s highlighted by green color and rest station highlighted by green color are non-receiving stations.
Now look at the figure of multiple unicasting, The sender is needed to send the packet to three receiving stations so, it has created three separate packets, containing the address of three separate receiving stations and each packet is delivered to address on it.
Definition of Multicast
Multicast is an information transmission method where one station transmits the information packet to the interested stations only. It is a one-to-many communication method. It is a mixture between unicast and broadcast, where unicasting sends the packet to only one station, and broadcasting sends the packet to all the stations, their multicasting sends the packet to only some selected stations in the network.
Examples of multicasting are forwarding emails, multimedia delivery, etc.
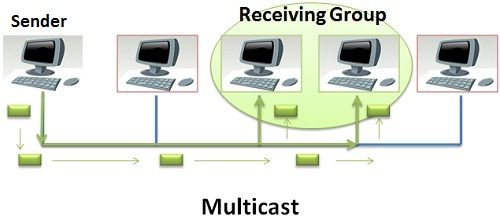 In the figure of multicast, you can clearly see that the sender station has created a single packet only which now will be delivered to the group of interested stations only. A single packet is forwarded to the group of receiving stations.
In the figure of multicast, you can clearly see that the sender station has created a single packet only which now will be delivered to the group of interested stations only. A single packet is forwarded to the group of receiving stations.
It’s hard to use multicasting across a large network because only small sections of the internet are multicast-enabled. Multicast utilizes the bandwidth of the network very efficiently. The group of the receiving stations is decided dynamically. Multicast uses a UDP transport protocol.
Key Differences Between Unicast and Multicast
- The basic difference that distinguishes unicast from multicast is that in unicast, there is only one sender and only one receiver. But, in multicast there is a single sender but, multiple receivers.
- When we want to send the data to multiple people then using unicast will waste lots of bandwidth but, multicasting will utilize the bandwidth more efficiently.
- Unicast does not perform well while streaming media whereas, multicast does not perform well across large networks.
- Unicast is one to one mapping whereas, multicast is one to many mapping.
- Examples of unicast is surfing the web or transferring a file whereas, multicast examples are multimedia delivery, stock exchange.
Conclusion
If some private or unique information is being shared between two stations, a unicast method must be used. When the same information is to be shared with multiple stations, the multicast method must be used.
Leave a Reply