 Transmission is the process of forwarding a packet from one host to other connections in a network. In this article, I have discussed the two transmission methods, broadcast and multicast. In both cases, address aggregation is performed, which reduces the size of the prefix that defines the network to which destination hosts are connected.
Transmission is the process of forwarding a packet from one host to other connections in a network. In this article, I have discussed the two transmission methods, broadcast and multicast. In both cases, address aggregation is performed, which reduces the size of the prefix that defines the network to which destination hosts are connected.
Address aggregation combines the packets and deliver them to ISP (Internet Service Provider), which holds some network together. Further, the packets are separated to be delivered to their final destination.
The transmission technologies broadcast and multicast are different from each other in the context that in the broadcast, the packet is forwarded to all the hosts connected to the network, whereas, in multicast, the packet is forwarded only to the intended recipients. I have discussed some more differences between broadcast and multicast in the comparison chart shown below.
Content: Broadcast Vs Multicast
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Broadcast | Multicast |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | The packet is transmitted to all the hosts connected to the network. | The packet is transmitted only to intended recipients in the network. |
| Transmission | One-to-all. | One-to-many. |
| Management | Broadcasting does not require any group management. | Multicasting requires group management to define the group of hosts/stations which will receive packets. |
| Bandwidth | Bandwidth is wasted. | Bandwidth is utilized efficiently. |
| Traffic | Unnecessarily huge amount traffic is generated in the network. | Traffic is under control. |
| Process | Slow. | Fast. |
Definition of Broadcast
Broadcast is a transmission technology which allows all hosts connected to a network to share the same communication channel. In broadcast, a packet sent by a host is received by all the other hosts in the network.
When a host broadcasts a packet, it specifies the address of the intended recipient in the address field of the packet. Now, as the packet is broadcasted, it is received by all the other hosts in the network. After receiving the packet, each host checks the address field of the packet. If the packet has the address of receiving host, it is processed by the receiving host. Else the packet is ignored.
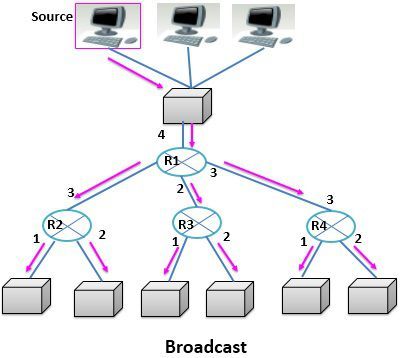 The broadcast has the possibility to address packets to all the hosts on the network. For this, the host broadcasting the packet specifies a special code in the address field of the packet. When the packet with the special code in the address field is transmitted, the packet is received and processed by all the hosts in the network.
The broadcast has the possibility to address packets to all the hosts on the network. For this, the host broadcasting the packet specifies a special code in the address field of the packet. When the packet with the special code in the address field is transmitted, the packet is received and processed by all the hosts in the network.
Broadcasting can be explained with the help of an example. Suppose you are delivering a lecture in a classroom of 50 students. In between, you call out to a student, “James, stand up”. Though it is listened to by all the students in the classroom, only James will respond; others will just ignore this message.
The wireless network is a common example of broadcasting.
Definition Multicast
Broadcasting allows the transmission of the packet to the group of hosts in the network, and this is called multicasting. Multicasting is a transmission method in which copies of a single packet are transmitted to the group of hosts in the network interested in receiving the packet.
The relationship between source and destination is one-to-many. There is only one source and multiple destinations. In multicasting, the source address is a unicast address, whereas the destination address is a group address. The group address is an address of one or more destination networks which has at least one member in the group interested in receiving the packet.
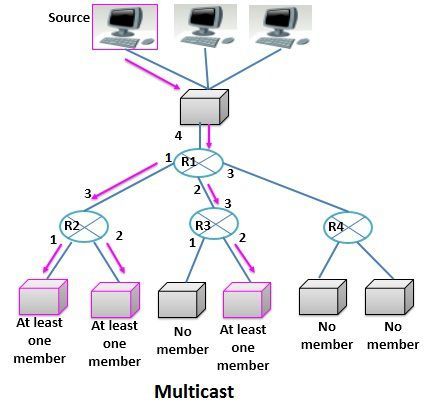 The routers in the network forward the received packet through several of its interfaces. As in the figure, you can see that the router R1 sends the received packet through interfaces 1 and 2. Further, you can see that the router R2 forwards the received packet through interface 1 and 2 as the network connected to both interfaces have at least one member interested in receiving the packet. Similarly, router R3 forwards the received packet through interface 2.
The routers in the network forward the received packet through several of its interfaces. As in the figure, you can see that the router R1 sends the received packet through interfaces 1 and 2. Further, you can see that the router R2 forwards the received packet through interface 1 and 2 as the network connected to both interfaces have at least one member interested in receiving the packet. Similarly, router R3 forwards the received packet through interface 2.
Multicasting has several applications nowadays. Like assessing distributed databases requires multicasting. In a distributed database, the information is stored in more than one location. So the user’s request for information is multicasted to all the database locations, and the location with intended information responds.
Similarly, the distribution of similar information to several customers in business, distribution of news, teleconferencing, and distance learning.
Key Differences Between Broadcast and Multicast
- The key difference between broadcast and multicast is that in the broadcast, the packet is delivered to all the hosts connected to the network, whereas, in the multicast packet is delivered to intended recipients only.
- In broadcast, the transmission of a packet is one-to-all, whereas, in multicast, the transmission of a packet is one-to-many.
- No group management is required in broadcasting, whereas; group management is required in multicasting to define the networks in which at least one host is interested in receiving the packet.
- Bandwidth is wasted in broadcasting as the packet is delivered even to those hosts who are not interested in receiving the packet. However, the bandwidth is effectively utilized in multicasting as the packet is delivered only to those hosts who are interested in receiving the packet.
- Broadcasting creates a huge amount of traffic on the network as it delivers each packet to all the hosts on the network. The traffic is under control in multicasting as packets are delivered to interested hosts only, thereby reducing the traffic on the network.
- Broadcasts create a huge amount of traffic, thereby slowing down the system. However, multicast creates less traffic which fastens the system in comparison to broadcasting.
Conclusion
Broadcasting sends a packet to all the hosts connected to the system. It is not worth it if there are thousands of machines connected to each network. Multicasting is useful as it delivers the packet to the hosts that are interested in receiving the packet.
Kris maussen says
Is another advantage/disadvantage … broadcast is only in the LAN, NOT passed by the router. And multicast can be passed by the router(s).