 TCP/IP and OSI are the two most widely used networking models for communication. There are some similarities and dissimilarities between them. One of the major differences is that OSI is a conceptual model which is not practically used for communication. On the other hand, TCP/IP is a model used for establishing a connection over the network.
TCP/IP and OSI are the two most widely used networking models for communication. There are some similarities and dissimilarities between them. One of the major differences is that OSI is a conceptual model which is not practically used for communication. On the other hand, TCP/IP is a model used for establishing a connection over the network.
The OSI model mainly emphasises the services, interfaces and protocols. Conversely, the TCP model is not able to distinctly describe these concepts.
However OSI model supports connectionless and connection-oriented communication over the network layer. But in the transport layer, connection-oriented communication is merely allowed. Refer to the article difference between connectionless and connection-oriented services, for a better understanding.
We will discuss some more differences in the content ahead.
Content: TCP/IP Model Vs OSI Model
- Comparison Chart
- What is TCP/IP Model?
- What is OSI Model?
- Key Differences
- Diagrammatic Comparison
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | TCP/IP Model | OSI Model |
|---|---|---|
| Expands To | Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol | Open system Interconnect |
| Meaning | It is a client server model used for transmission of data over the internet. | It is a theoretical model which is used for computing system. |
| Number Of Layers | 4 Layers | 7 Layers |
| Developed by | Department of Defense (DoD) | ISO (International Standard Organization) |
| Tangible | Yes | No |
| Usage | Mostly used | Never used |
| Obeys | Horizontal approach | Vertical approach |
What is TCP/IP MODEL?
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)/IP (Internet Protocol) was developed by the Department of Defense (DoD) project agency. Unlike OSI Model, it consists of four layers each having its own protocols. Internet Protocols are the set of rules defined for communication over the network.
We consider TCP/IP as the standard protocol model for networking. TCP handles data transmission and IP handles addresses. The TCP/IP protocol suite has a set of protocols that includes
- TCP
- UDP
- ARP
- DNS
- HTTP
- ICMP, etc.
It is a robust and flexible model. The TCP/IP model is mostly used for interconnecting computers over the internet.
Layers of TCP/IP Model
Network Interface Layer
The layer act as an interface between the host and the network hardware. It specifies what operation must links (such as serial links) and classic ethernet perform? So that they can satisfy the requirements of a connectionless internet layer.
Internet Layer
The layer enables the host to transmit the packet over the network independently. The packets may arrive to their destination in a different order. It is the responsibility of the higher layer to rearrange them in proper order. The layer defines a packet format and the protocol such as:
- IP (Internet Protocol)
- A companion protocol such as ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol).
Transport Layer
It enables a fault-free end-to-end delivery of the data between the source and destination. The data is in the form of datagrams. The protocols defined by this layer are:
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
Application Layer
The layer permits users to access the services of global or private internet. The various protocols described in this layer are:
- Virtual terminal (TELNET)
- Electronic mail (SMTP)
- File transfer (FTP)
It also describes some additional protocols like:
- DNS (Domain Name System)
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol)
The working of the application layer is a combination of the application, presentation and session layer of the OSI.
Advantages of Disadvantages of TCP/IP Model
Advantages
- With TCP/IP, we can establish connections between two computers in different kinds of networks.
- TCP/IP is a scalable client-server architecture.
- The model has flow control, error control, and congestion control mechanism.
- TCP/IP supports several routing protocols at each of its layers.
Disadvantages
- Difficult to set up and maintain when compared to IPX/SPX.
- It is quite slower than IPX/SPX.
- The model does not provide a clear separation between its services, interfaces and protocols.
What is of OSI Model?
OSI (Open System Interconnection) model was introduced by ISO (International Standard Organization). The model relies on the concept of layering and has a vertical set of layers, each having different functions. It follows a bottom-up approach to transferring the data. It is robust and flexible, but not tangible.
The main intent of the OSI reference model is to conduct the design and development of digital communication hardware. It also defines the designing of software in a way that it can efficiently interoperate.
Layers of OSI Model
OSI model consists of seven layers as described below:
Application Layer
The layer enables users to access the network by using interfaces and services. Such as electronic mail, shared database management, file access/transfer and other services.
Presentation Layer
The layer focuses on the syntax and semantics of the transmitting information. It performs tasks such as translation, encryption and compression. The layer encodes the actual information into bit streams. It is then converted into another form and compressed.
Session Layer
The layer establishes the session between different machines. It is also responsible to synchronize and maintain the interaction between them. The services provided by the layer are dialog control, token management and synchronization.
Transport Layer
The layer accepts the data from its preceding layer in the form of independent packets. Then it transmits that data to the succeeding layer. The other function carried out by this layer are:
- Service point addressing
- Connection control
- Segmentation and reassembly
- Flow control and error control
Network Layer
Logical addressing and routing are the major operations performed by the network layer. It translates the network logical address into a physical MAC address. So that, the two systems residing in the different networks could also communicate efficiently. A packet also requires a path that it can follow to reach the destination avoiding congestion and failed components. Thus, it also facilitates the automatic updation of the routes.
Data Link Layer
It is responsible for transforming the raw transmission service (Physical layer) into a reliable link. It makes the physical layer free from error by masking them so that the network layer does not notice them. The layer splits input data into frames. The tasks carried out in the data link layer are:
- Framing
- Access control
- Physical addressing
- Error and flow control
Physical Layer
It transmits the individual bits over the transmission channel. The physical layer deals with the description of:
The characteristics of the interface between the devices.
- Transmission media
- Representation of bits
- Synchronization of the bits
- Data rate
- Physical topology
- Line configuration
- Transmission mode
Advantages and Disadvantages of OSI Model
Advantages
- The OSI model is a generic model and it provides full guidance to develop any network model.
- Being a layered model it provides a clear separation between the layers, services and protocol.
- Supports both connection-oriented and connectionless services.
Disadvantages
- It is a theoretical model.
- The model is quite complex and hard to manage.
- It has addressed similar functions in different layers that make it even more complicated.
Key Differences Between TCP/IP and OSI Model
- TCP/IP is a client-server model, i.e. when the client requests for service it is provided by the server. On the other hand, OSI is a conceptual model.
- TCP/IP is a standard protocol used for every network including the Internet. However, OSI is not a protocol but a reference model used for understanding and designing the system architecture.
- TCP/IP is a four-layered model. Although OSI has seven layers.
- TCP/IP follows a horizontal approach. On the other hand, the OSI Model supports the Vertical approach.
- TCP/IP is tangible, whereas, OSI is not.
- TCP/IP follows top to bottom approach, However, OSI Model follows a bottom-up approach.
Diagrammatic Comparison
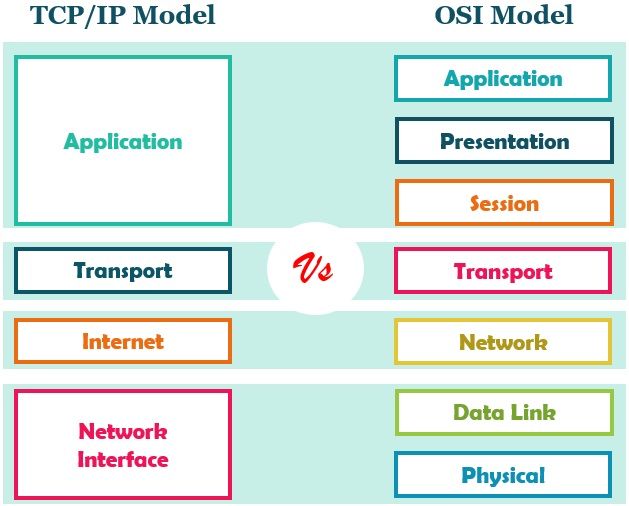
The TCP/IP Model was developed before OSI Model, and hence, the layers differ. Concerning the diagram, we can clearly see that TCP/IP Model has four layers namely, Network Interface, Internet, Transport and Application Layer.
On the other hand, the OSI model has seven layers. The model has merged data link and physical layers to make the network interface layer of the TCP/IP model. The Application layer of TCP/IP is a combination of the Session, Presentation and Application Layer of the OSI Model.
Conclusion
Concerning the above article, we can conclude that the TCP/IP Model is more reliable than OSI Model.
We use TCP/IP for end-to-end connection so as to transmit the data over the internet. Subsequently, TCP/IP is robust, flexible, and tangible and also suggests how data should be sent over the web. The transport layer of the TCP/IP Model checks whether the data has arrived in order, it has an error or not, whether lost packets are resent or not, acknowledgement is received or not, etc.
In contrast, the OSI model is just a conceptual framework to interpret how applications communicate over a network.
Mohammad Chaudry says
Well done!
Great help for students.
Please continue the good work.
Thank you very much
billy says
agreed my friend thank you 🙂
Networking Signal says
An interviewer asks mostly that question. You provide a useful matter to people. Thanks for sharing this article with me and whole people.
Anurag says
Nice
Zulkaif says
Great Job
Akech andrew says
Great work.
Dave Shanny says
Splendid work. I am very pleased and it is of a great help to me.
Thank you and Big ups for the good work.
luqman zulkifli says
thanks!
billy says
very epic thank you
Ryan Newton says
Outstanding! This is the clearest explanation I have heard. Thank you!
Deadbone says
Wow! Impressive and clear.
Adolf says
that’s Good 🙂
Mohammed may there be peace says
very good and clear
sirajunnisa says
nice work……… a clear understanding
Akash says
Awesome.
That was really helpful.
Stephen says
This is the easiest way to understand the difference between OSI setup compared to the TCP/IP setup. Thanks a lot
Kasuni Kuruppuarachchi says
This article helped me lot for my studies.
Thank you.
Shyam Sundar says
Very nice article Billy.
Thanks,
Shyam.
Sukrala says
Thanks For Sharing it Is Very Helpful.
Azhar says
Good Article.
Shubham says
Great work.
Rahul Prajapat says
All topics are clear in simple
GOOD WORK
THANK YOU
Ankit says
Can you more elaborate top to bottom and bottom to top approach and follow horizontal and vertical approach
Saira gulzar says
It’s really clear and out standing
Chrispine says
This information is really helpful thank you.
FEWBEX says
IMPRESSIVE………OKIE
mark estep says
very helpful