 Communication can be established in two ways between two or more devices that are connection-oriented and connection-less. Network layers can offer these two different types of services to its predecessor layer for transferring data. Connection-oriented services involve the establishment and termination of the connection while connection-less services don’t require any connection creation and termination processes for transferring data.
Communication can be established in two ways between two or more devices that are connection-oriented and connection-less. Network layers can offer these two different types of services to its predecessor layer for transferring data. Connection-oriented services involve the establishment and termination of the connection while connection-less services don’t require any connection creation and termination processes for transferring data.
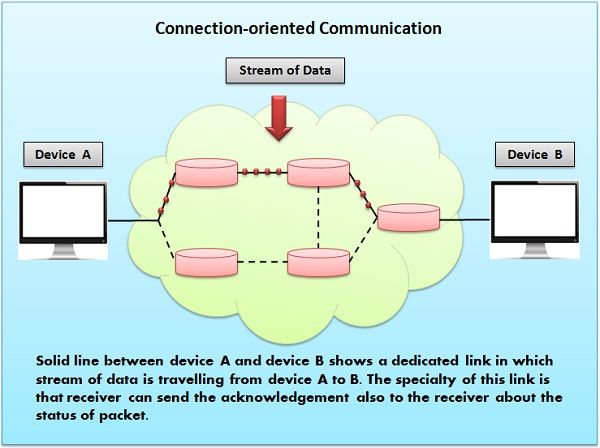
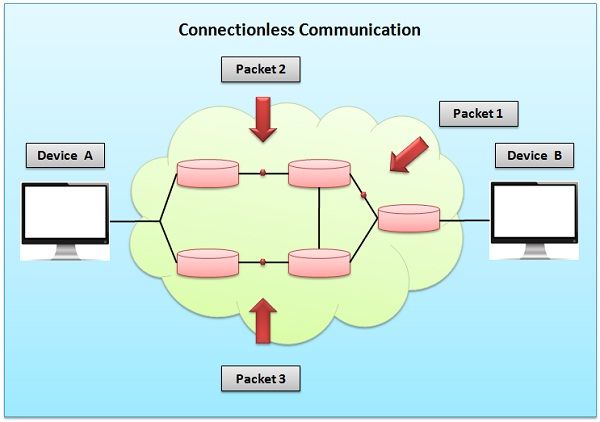
Another difference between connection-oriented and connection-less services is connection-oriented communication uses a stream of data and is vulnerable to router failure while connection-less communication uses messages and is robust to router failure.
Content: Connection-oriented Vs Connection-less Services
Comparison Chart
| Basis of Comparison | Connection-oriented service | Connection-less service |
|---|---|---|
| Prior Connection Requirement | Necessary | Not required |
| Reliability | Ensures reliable transfer of data. | Not guaranteed. |
| Congestion | Unlikely | Occur likely. |
| Transferring mode | It can be implemented using circuit switching and virtual circuit. | It is implemented using packet switching. |
| Lost data retransmission | Feasible | Practically, not possible. |
| Suitability | Suitable for long and steady communication. | Suitable for bursty Transmission. |
| Signalling | Used for connection establishment. | There is no concept of signalling. |
| Packet forwarding | Packets sequentially travel to their destination node and follows the same route. | Packets reach the destination randomly without following the same route. |
| Delay | There is a delay in transfer of information, but once the connection is established faster delivery can be achieved. | Because to the absence of connection establishment phase, the transmission is faster. |
| Resource Allocation | Need to be allocated. | No prior allocation of the resource is required. |
Definition of Connection-oriented Service
Connection-oriented service is analogous to the telephone system that requires communication entities to establish a connection before sending data. TCP provides Connection-oriented services as does ATM, Frame Relay and MPLS hardware. It uses handshake process to establish the connection between the sender and receiver.
A handshake process includes some steps which are:
- Client requests server to set up a connection for transfer of data.
- Server program notifies its TCP that connection can be accepted.
- The client transmits a SYN segment to the server.
- The server sends SYN+ACK to the client.
- Client transmits 3rd segment i.e. just ACK segment.
- Then server terminates the connection.
More precisely, it sets up a connection uses that connection then terminates the connection.
Reliability is achieved by having recipient acknowledge each message. There are sequencing and flow control, that’s the reason packets received at the receiving end are always in order. It uses circuit switching for transmission of data.
Connection-oriented transport service priorly constructs a virtual circuit between two remote devices. To this end, COTS makes four different kinds of services available to the upper layers:
| T-CONNECT | This service enables a full duplex transport connection on a remote device with a peer function. |
| T-DATA | This service is used to transfer data, it could provide uncertain service and restricted amount of data but still, it is reliable. |
| T-EXPEDITED-DATA | This service is also used for transferring data, but it carries a limited amount expedited data up to 16 octets (bytes). |
| T-DISCONNECT | It is used to terminate the Transport connection and to reject a connection request also. |
where, T stands for Transfer.
Definition of Connection-less Service
Connection-less service is analogous to the postal system. In which packets of data (usually known as a datagram) is transmitted from source to destination directly. Each packet is treated as an individual entity, which allows communication entities to send data before establishing communication. Each packet carries a destination address to identify the intended recipient.
Packets don’t follow a fixed path that is the reason the packets received at receiver end can be out of order. It uses packet switching for transmission of data.
Most network hardware, the Internet Protocol (IP), and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) provides connection-less service.
Connection-less Transport services offer only one type of service to its upper layer that is T-UNIT-DATA. It provides a single solitary data unit for all transmission. Each unit contains all of the protocol control information necessary for delivery but does not include provision for sequencing and flow control.
Key Differences Between Connection-oriented and Connection-less Services
The points given below explains the difference between connection-oriented and connection-less services:
- There is a requirement for prior connection for communication in connection-oriented services, in contrast, it is not needed in connection-less services.
- Reliability is more in connection-oriented as compared to connection-less services.
- Traffic congestion is greater in connection-less services whereas its occurrence is rare in connection-oriented services.
- In connection-oriented services order of packets received at the destination is same as sent from the source. On the contrary, the order might change in connection-less services.
- All packets follow the same path in connection-oriented services while packets follow a random path to reach the destination in connection-less services.
- Connection-oriented service is appropriate for long and steady communication whereas connection-less service is fit for bursty transmission.
- In connection-oriented services, sender and receiver are synchronized with each other while it is not the case of connection-less services.
- Connection-oriented services use circuit switching on the other hand packet switching is used in connection-less services.
- Bandwidth requirement is higher in Connection-oriented services whereas its low in connection-less services.
Conclusion
Both connection-oriented and connection-less services have their merits and demerits. Connection-oriented service is reliable and appropriate for long distance communication, but it’s slow and requires higher bandwidth. Similarly, connection-less service is fast, needs minor bandwidth and adequate for bursty communication, but is not always reliable.
So, we conclude that both services have their equal importance and are necessary for data transmission and communication.
BHAMIDIPATI NARASIMHA SARMA says
Well informed about the difference between connection oriented network and connection less network. Very useful for ICAI IPCC-INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY paper.
Laecon says
Hopefully, just got to understand the difference between connection-oriented and connectionless oriented, thank you it’s useful…
INGAMULE SIRAJI says
This work has helped me a lot in differentiating connection-oriented and connectionless services. Thank you