 When the multimedia is transferred across the network, it needs the variable bandwidth and distinct traffic types which is known as the heterogeneous service. To deliver these services the high transmission rate is required, and different bit rates must be combined. These characteristics are achieved by distinct techniques known as frame relay and ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode). The difference between frame relay and ATM lies in the speed of transmission, efficiency, accurate delivery of the packets, etcetera. The frame relay provides 1.544 Mbps or 44.736 Mbps. On the other hand, ATM provides 51 Mbps or 155 Mbps.
When the multimedia is transferred across the network, it needs the variable bandwidth and distinct traffic types which is known as the heterogeneous service. To deliver these services the high transmission rate is required, and different bit rates must be combined. These characteristics are achieved by distinct techniques known as frame relay and ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode). The difference between frame relay and ATM lies in the speed of transmission, efficiency, accurate delivery of the packets, etcetera. The frame relay provides 1.544 Mbps or 44.736 Mbps. On the other hand, ATM provides 51 Mbps or 155 Mbps.
Content: Frame Relay Vs ATM
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Frame Relay | ATM |
|---|---|---|
| Packet size | Variable | Fixed |
| Processing overhead | Increased | Decreased |
| Data transfer | Implemented in more than one area network. | Takes place within a LAN |
| Cost | Inexpensive | Cost is higher |
| Speed | Low | High |
| QoS | Quantifiable QoS is not provided. | Offers quantifiable QoS. |
| Error control | No support is provided for error and flow control | Error and flow control is provided. |
| Data rate | 64 Kbps up to 45 Mbps. | 155.5 Mbps or 622 Mbps. |
| Reliability | Low | Good |
| Throughput | Medium | High |
| Delay | High | Less |
Definition of Frame Relay
The Frame relay is a packet mode transmission service devised to handle the upgraded type of WAN. X.25 was the earlier technology used in place of frame relay, but there are some demerits of using it such as low data rate, an unnecessary increase in the rate of the flow and error control.
The frame relay service uses either a permanent or switched virtual circuit to set the connection and enable the transfer of bit from source to the destination at a fair speed in an affordable cost. Before the advent of frame relay and X.25, the slow telephone lines were used for the intended purpose. In the older technology, the network delays, protocol overheads and equipment cost were the major drawbacks.
Features of Frame Relay
- Frame relay works in the speed of 1.544 Mbps and 44.376 Mbps.
- It involves only two layers – physical and data link layers. Therefore, it could be used as a backbone network with the protocols having network layer protocol to deliver the services.
- Bursty data does not have any adverse effect on frame relay.
- The frame size permitted in the frame relay is of 9000 bytes to carry entire local area network frame sizes.
- Frame relay lowers the cost of the WAN technology.
- It only supports error detection at the data link layer but not the flow control and error control mechanism. Therefore, if a frame is damaged, there is no retransmission policy, and the frame is silently discarded.
Working of Frame Relay
Frame relay is used to transfer the data in the form of packets, with the help of the data link layer. Here, a unique identifier DLCI (Data link connection identifier) identifies the virtual connection which is referred to as ports. The frame relay basically connects two DTE devices by using a DCE device. The DTE devices connected to the frame relay is assigned with a port to make each remote connection unique. It can create two types of circuits, PVC (Permanent virtual circuit) and SVC (Switched virtual circuit).
The former type of virtual circuit, PVC comprised of two operational states, data transfer and idle. In the data transfer state, the transferring of data occurs within the DTE devices across the virtual circuit. In the idle state, the data transfer does not occur even if the connection within the DTE devices is active.
The latter SVC type establishes the transient connection which could prevail until the data transfer takes place. It includes various operations such as call set up, data transfer, idle and call termination. In the call set up, termination operation the connection is established and terminated between the two DTE devices, and other operations are similar to PVC operation.
Layers of the Frame Relay
There are only two layers in the frame relay that are the physical layer and data link layer.
Definition of ATM
ATM stands for Asynchronous Transmission Mode; it is a switching technique developed by integrating the features of the telecommunication and computer networks. ATM make use of cells in order to transfer information of many service forms such as voice, data and video. These cells are encoded by using asynchronous time division multiplexing. It also enables the communication between the devices works at the variable speed by combining the multiplexing and switching, and it is appropriate for the bursty traffic. These cells are nothing but the collection of fixed size packets.
ATM Devices
The ATM networks need ATM switches and ATM endpoints for its functioning. ATM switch transit a cell transmitted from an ATM endpoint to an ATM network. Before transmitting the cell, it first scans the header of the frame and update it if needed then switch it to output interface to deliver it to the destination. The ATM endpoints also include the network interface adapter.
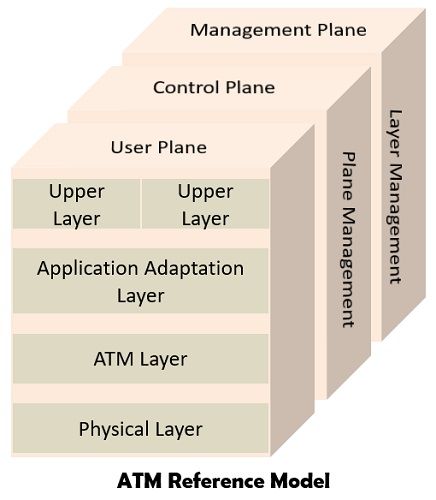
Architecture of ATM
The ATM reference model consists of layers and planes as shown in the diagram. There are three basic layers in the ATM- physical, ATM and ATM AAL layer.
- Physical Layer: This layer of the ATM handles the medium dependent transmissions.
- ATM Layer: The ATM layer is similar to data link layer which enables the sharing of virtual circuits between the different users and transmission of the cells over the virtual circuit.
- Application Adaptation Layer (AAL): The AAL is responsible for hiding the ATM implementation details form the higher layers. It also transforms the data into 48 bit cell payloads.
The different planes included in the ATM reference model are control, user and management.
- Control: The main function of this plane is to produce and manage the signalling request.
- User: This plane handles the transfer of the data.
- Management: Layer related functions such as failure detection, problems regarding protocols are governed by this plane. It also involves the functions related to the complete system.
Working of ATM
The ATM header comprised of two types of format UNI (User network interface) and NNI (Network network interface). These formats contain two fields in the ATM header named as VPI (Virtual path identifier) and VCI (Virtual circuit identifier).
Now lets first understand the concept of virtual channel connection and virtual path connection. The virtual channel is the most fundamental unit in the ATM network, while the virtual path connection is a collection of virtual channel connections. Further, a set of virtual path connection makes up a transmission path.
The VPI field employs the virtual values to switch the cells between the ATM networks such as the routing. The UNI interface contains 8 bits for the VPI field which allows 256 virtual path identifiers. While NNI interface format can have 12 bits in the VPI fields and that allow 4,095 virtual path identifiers. On the other hand, the VCI field is used to perform switching for the end users and has a 16-bit value for both UNI and NNI interface formats. This field permits to get 65,536 virtual channels.
Key Differences Between Frame Relay and ATM
- The packet size in the frame relay varies while ATM uses a fixed size packet known as a cell.
- ATM produces fewer overheads as compared to the frame relay technology.
- Frame relay is less expensive respective to the ATM.
- ATM is faster than the frame relay.
- ATM provides error and flow control mechanism, whereas the frame relay does not provide it.
- Frame relay is less reliable than the ATM.
- Throughput generated by frame relay is medium. In contrast, ATM has a higher throughput.
- The delay in the frame relay is more. As against, it is less in case of ATM.
Advantages of the Frame Relay
- Efficient communication process.
- It performs fewer functions at the user-network interface.
- Delay is also lowered.
- Produces higher throughput.
- It is cost effective.
- It is faster than its predecessor X.25.
Advantages of the ATM
- It can easily interface with the existing network such as PSTN, ISDN. It can be used over SONET/SDH.
- Seamless integration with the different types of networks (LAN, MAN and WAN).
- Effective utilization of the network resources.
- It is less susceptible to the noise degradation.
- Provides large bandwidth.
Disadvantages of the Frame Relay
- Unreliable service.
- The order of the arriving packets may not be maintained.
- The erroneous packets are directly dropped.
- The frame relay does not offer any flow control.
- There is no provision of the acknowledgement of the received packets and retransmission control for the frames.
Disadvantages of the ATM
- Cost of switching devices is higher.
- Overhead generated by the cell header is more.
- ATM QoS mechanism is quite complex.
Conclusion
The frame relay is controlled through the software while ATM is implemented for hardware which makes it more costly and fast. ATM can achieve higher processing and switching speed by providing flow and error control.
Leave a Reply