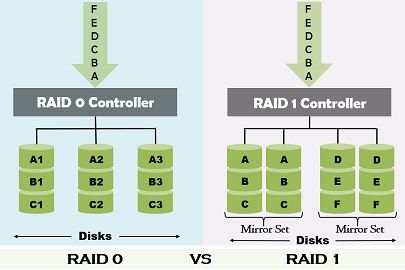
 RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disk) are the group of disk organisation techniques evolved to deal with the reliability and performance. The fundamental difference between the RAID 0 and RAID 1 is that the RAID level 0 does not contain redundant data, in fact, it uses striping. On the other hand, RAID level 1 uses mirroring and contain redundant data.
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disk) are the group of disk organisation techniques evolved to deal with the reliability and performance. The fundamental difference between the RAID 0 and RAID 1 is that the RAID level 0 does not contain redundant data, in fact, it uses striping. On the other hand, RAID level 1 uses mirroring and contain redundant data.
The RAID was initially abbreviated as redundant disks of inexpensive disks because it was devised for providing large disk capacities at a low cost by using numerous inexpensive disks. Although, today this technology it provides not only large disk volume but also offers high data rates, fast access and reliability. The technology works by dividing the data implied in an I/O operation across multiple disks and performs the task on these disks in parallel. It employs redundancy to enhance the reliability.
Content: RAID 0 Vs RAID 1
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | RAID 0 | RAID 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Striped array with no fault tolerance | Disk mirroring |
| Cost | Inexpensive | Expensive comparatively |
| Relative storage efficiency (in %) | 100% | 50% |
| Read performance | Perform well in both random and sequential read. | Moderate but better than a single disk. |
| Write performance | Better than RAID 1. | Slower than a single disk. |
| Write penalty | No | Moderate |
| Appropriate | When the data accessing speed is the main concern. | When emphasis is on Data availability. |
Definition of RAID 0
RAID 0 or RAID level 0 organises data by interleaving it on multiple disks. So, the disk is accessed in parallel at the time of performing an I/O operation. Ideally, RAID level O is not considered as RAID organisation because it does not contain any redundant data. It uses disk striping technique. Disk striping is a technique of partitioning a drive storage space into stripes having varying sizes from 8KB to 1024 KB. These stripes are inserted in a repeated serial manner.
Strips from each drive construct an integrated storage space. The data can be written over multiple drives in spite of only one in RAID 0. The part of a stripe that resides on a single drive is known as strip size. For example, a stripe holds the disk space of 48 KB and has 16 KB of data remaining on each disk in the stripe. So, the stripe size is 48 KB, and the strip size is 16 KB.
The RAID level 0 provides ‘n’ time increase in transfer rates when n number of the disks are used and placed under a separate disk controller. However, it also has demerits such as data cannot be accessed even if a single disk stops functioning. Additionally, the lack of redundancy can cause data loss.
Definition of RAID 1
RAID 1 (level 1) configuration involves data mirroring where the identical data is stored on the two separate disks. During the read operation, the data among the identical data which can be accessed in less time is used and parallel reads can also be performed when no errors are occurred. Every time when a record is updated or written by a process, one copy of the record is written on each disk. Thereby RAID level 1 experiences 100 % overhead. In case of disk failure, one copy of the record is assured to be accessible. The use of mirroring technique improve fault tolerance.
Key Differences Between RAID 0 and RAID 1
- The RAID 0 technology uses disk stripping while RAID 1 uses the concept of disk mirroring.
- When it comes to cost RAID 0 is cheap whereas RAID 1 is quite expensive.
- Storage efficiency of RAID level 0 is very good. In contrast, the RAID level 1 can attain just half of the storage efficiency as it copies data in the different disks.
- The read operation is performed effectively in RAID 0. As against, read performance is moderate in RAID 1 but is still better than using a single disk.
- Write performance of the RAID 0 is superior to RAID 1 because each write to a disk is performed two times which significantly degrades the write performance of the RAID 1.
- There is no write penalty in RAID 0 while it present in the RAID 1.
Advantages of RAID 0
- The data is read and written fastly.
- No overheads are generated for parity calculation.
- The disk is utilized completely.
Advantages of RAID 1
- Performance is good.
- Provision for fault tolerance.
- Ease of recovery.
Disadvantages of RAID 0
- No fault tolerance is provided.
- The failure of one drive causes loss of data.
- Redundant data does not present.
Disadvantages of RAID 1
- Reduced storage efficiency.
- Data cannot be accessed during the recovering process as it needs shutting the RAID.
Conclusion
The RAID level 0 is not contemplated as the RAID as there is no redundant information is stored. RAID 0 is suitable when faster access to the data is the priority. On the other hand, RAID 1 contain the redundant information and is suitable when the emphasis is on the data availability.
TTR Data Recovery says
Nice Blog for Difference Between RAID 0 and RAID 1