 The Magnetic disk and Optical disk are the storage devices provides a way to store data for a long duration. These disks differ in many characteristics; firstly magnetic disk works by using magnetising material over the disk whereas in optical disk polycarbonate plastic is used in its construction and laser is used to store and retrieve the data.
The Magnetic disk and Optical disk are the storage devices provides a way to store data for a long duration. These disks differ in many characteristics; firstly magnetic disk works by using magnetising material over the disk whereas in optical disk polycarbonate plastic is used in its construction and laser is used to store and retrieve the data.
The magnetic and optical disk comes under the category of secondary storage devices. The need to devise these devices has emerged because the previous semiconductor storage devices have very limited capabilities, for example, the cost of storing the information in such devices is very high.
Content: Magnetic disk and Optical disk
Comparison Chart
| Basis For Comparison | Magnetic Disk | Optical Disk |
|---|---|---|
| Media type | Muiltiple fixed disk | Single removable disk |
| Position error signals | Intermediate signal to noise ratio | Excellent signal to noise ratio |
| Sample rate | Low | High |
| Implementation | Used mostly where data is randomly accessed. | Used in streaming files. |
| Tracks | Circular | Spiral or circular |
| Usage | Only one disk can be used at a time | Mass replication is possible |
| Access time | Shorter comparatively | Longer |
Definition of Magnetic disk
The Magnetic disk is made of a set of circular platters. These platters are initially build up of non-magnetic material i.e., aluminium or aluminium alloy referred to as substrate then the substrate is coated with a magnetic film and mounted on a common spindle. The disks are placed inside a rotary drive where the magnetised surface rotates close to the read and write heads. Every head is comprised of a magnetising coil and a magnetic yoke. It stores the digital information on the concentric tracks by applying the current pulse of appropriate polarity to the magnetic coil.
The number of bits stored on each track does not change by using simplest constant angular velocity. Multiple zoned recording is used to increase the density in which the surface is partitioned into a number of zones and the zones located near the centre contain fewer bits than the zones farther from the centre. However, this strategy is not optimal.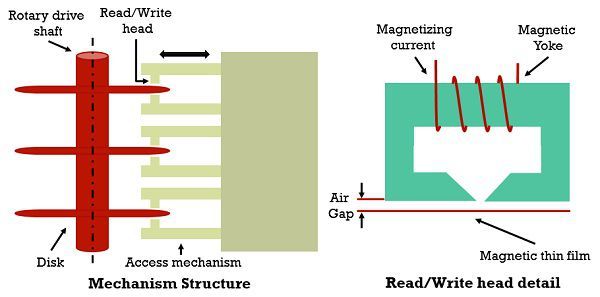
In the read operation, the alteration in a magnetic field is sensed. So, the two opposite states of magnetisation represent 0 and 1; it produces the voltage in the head when 0-1 and 1-0 transition takes place in the bit stream.
Definition of Optical disk
The Optical disk is a storage device in which optical (light) energy is used. In the initial stages, the designers created a compact disk in the mid- 1980s which use the digital representation for the analog sound signals. The CD was capable of providing great quality sound recording by taking 16-bit samples of analog signals at the speed of 44,100 samples per second and also it can detain up to 75 minutes where a total amount of stored bits needed is approx 3 x 109 (3 gigabits). These optical disks use the optical technology in which a laser light is centred to the spinning disks.
Optical disk Construction
The optical disk is constructed from a resin like polycarbonate, and the surface of this polycarbonate contains the digital information impressed on it as the sequence of microscopic pits. A microscopic pitted surface is then glazed by a highly reflective surface such as aluminium or gold. To make the disk scratch resistant it is coated by acrylic and silkscreened label on it. Finally, a concentrated high-intensity laser is utilized in the creation of the master disk.
The information retrieval from a CD is done through housing a low powered laser in an optical disk player. The laser is radiated through the clear polycarbonate while the disk is spinning by the motor. As the laser falls on the pit (usually having the rough surface), the magnitude of the reflected laser light changes. The vacant smooth area between the pits is known as the land from which the light reflects back at a higher magnitude. 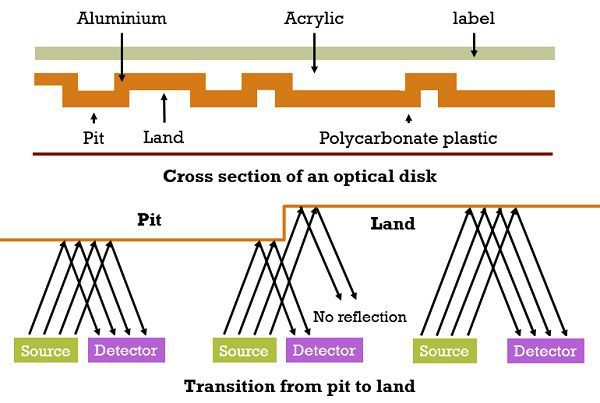 A photosensor is used to identify the alteration between the pits and lands and translate it into a digital signal. The pit area represents a ‘1’ while no change is observed between intervals a ‘0’ is recorded. There are numerous optical disk products are available in the market such as CD, CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD, DVD-R, DVD-RW.
A photosensor is used to identify the alteration between the pits and lands and translate it into a digital signal. The pit area represents a ‘1’ while no change is observed between intervals a ‘0’ is recorded. There are numerous optical disk products are available in the market such as CD, CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD, DVD-R, DVD-RW.
Key Differences Between Magnetic disk and Optical disk
- The magnetic disk is a fixed storage device whereas optical disk is transportable storage media which is removable.
- Optical disk generates better signal-to-noise ratio as compared to magnetic disk.
- The sample rate used in the magnetic disk is lower than used in the optical disk.
- In the optical disk, the data is sequentially accessed. In contrast, the data in the magnetic disk is randomly accessed.
- Tracks in the magnetic disk are generally circular while in optical disk the tracks are constructed spirally.
- Optical disk allows mass replication. On the contrary, in the magnetic disk, only one disk is accessed at a time.
- The access time of the magnetic disk is lesser than the optical disk.
Conclusion
The magnetic disk works on electromagnetic technology while optical disk functions by using optical means (laser light). Although, the speed of the magnetic disk is higher than that of the optical disk.
CJ says
This was a really helpful source for my studies. I loved the diagrams. Thank you.