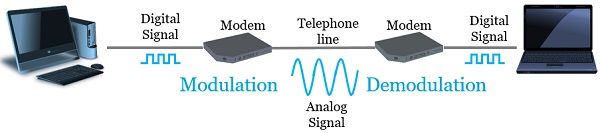
 Modulation and demodulation are the techniques important for establishing communication between the devices. Modulation superimposes a weak signal (information) onto a strong carrier signal to get a modulated signal. The modulated signal is further transmitted over a longer distance. Demodulation processes the modulated signal to retrieve the original information.
Modulation and demodulation are the techniques important for establishing communication between the devices. Modulation superimposes a weak signal (information) onto a strong carrier signal to get a modulated signal. The modulated signal is further transmitted over a longer distance. Demodulation processes the modulated signal to retrieve the original information.
Modulation and demodulation are complementary processes to each other. Thus, modulation is being conducted at the senders’ side whereas, demodulation is being conducted at the receivers’ side.
Let’s get into the details of modulation and demodulation and figure out more differences between these two techniques.
Content: Modulation Vs Demodulation
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Modulation | Demodulation |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Modifies low frequency information signal to high frequency carrier signal. | Remodifies high frequency carrier signal into low frequency information signal. |
| Device Required | Modulator | Demodulator |
| Conducted | It is conducted at the transmitter end. | It is conducted into receiver end. |
| Purpose | Required to transmit data to longer distance. | Required to retrieve the original signal from the carrier signal. |
| Complexity | Modulation is quite simple. | Demodulation is complex. |
| Frequency | Transforms low frequency to high frequency. | Transforms high frequency to low frequency. |
What is Modulation?
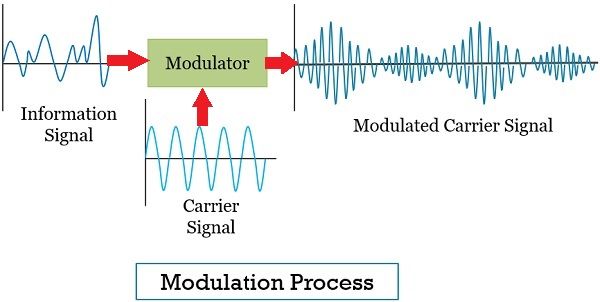
Modulation imposes the information signal onto a carrier signal. In this process, the modulator modified some of the parameters of the carrier signal. These parameters can be amplitude, frequency or phase.
The modulation intakes the information signal and carrier wave. and then outputs the modulated signal. This modulated signal is strong enough to be easily transmitted over a longer distance.
Why Modulation is Necessary?
Now you must be thinking about why do we require modulation?
Well, the information signal we need to transmit is low-frequency. The low-frequency signal is weak and cannot be transmitted over a longer distance. Because they are not immune to parameters such as:
- Light
- Noise
- Temperature
- Distance
- Pressure
- Other physical phenomena.
Due to these parameters, the low-frequency signal faces distortion. Thus we need to transform the low-frequency signal into a high-frequency signal. Because the high-frequency signals are immune to the parameters discussed above.
Thus the low-frequency information signal is imposed on the high-frequency carrier. And the obtained modulated signal is a high-frequency signal.
Modulation Block Diagram
Types of Modulation
Based on the types of signal we classify modulation into two types:
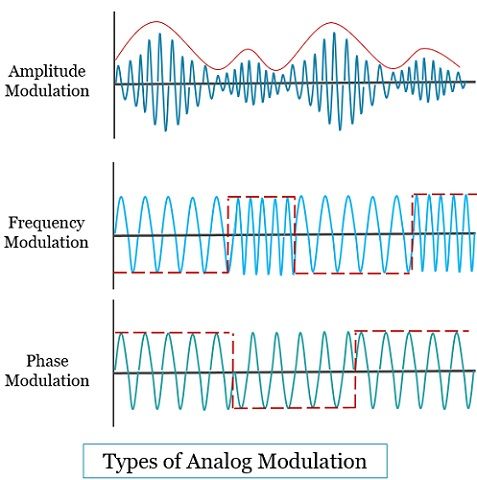
Analog Modulation
The carrier signal used for modulating the information signal is an analog signal. In an analog signal, there are three parameters that can be altered to obtain modulation – amplitude, frequency, and phase.
- Amplitude Modulation
Here, the modulator varies the amplitude of the carrier signal in accordance with the information signal. However, the carrier signal’s remaining parameters, i.e. frequency and phase, remain constant. - Frequency Modulation
In this technique, the modulator varies the frequency of the carrier signal in accordance with the information signal. However, the remaining parameters such as amplitude and phase remain constant. - Phase Modulation
Here, the phase of the carrier signal is varied in accordance with the information signal. The change in the signal’s phase also affects the signal frequency of the signal. So we count this modulation under the frequency modulation.
You can notice these three kinds of analog modulations in the figure below:
Digital Modulation
The digital modulation technique provides effective and better-quality communication. In digital modulation, if the information signal is analog it is first transformed into the digital signal. The digital information signal is then modulated using the carrier wave.
The reasons behind opting the digital modulation is:
- It is more immune to noise.
- It is easy to remove redundant information from the digital signal.
- We can easily implement multiplexing techniques on digital signals.
Even a digital signal has three parameters to alter in order to achieve modulation.
- Amplitude Shift Keying
The modulator modifies the amplitude of the carrier signal. The modification is in accordance with the digital information signal. - Frequency Shift Keying
The carrier signal frequency varies in accordance with the digital signal with information. - Phase Shift Keying
The carrier signal’s phase varies according to the digital signal with information.
What is Demodulation?
Now as we all know demodulation is a process that the demodulator performs at the receiver end. This process separates the original information signal from the modulated signal.
Demodulation is the reverse process of modulation. It transforms the high-frequency signal into a low-frequency signal.
Why Do We Require Demodulation?
As far as modulation is important to let the information signal travel a longer distance. Equally, demodulation is important to retrieve the original information from the modulated signal.
This is because the receiver cannot understand the modulated signal. Thus, demodulation is essential to separate the information signal from the modulated signal.
Key Differences Between Modulation and Demodulation
- Modulation imposes a low-frequency information signal on a high-frequency carrier signal. However, demodulation retrieves the original information signal from the high-frequency modulated signal.
- To perform modulation, we require a modulator. However, to perform demodulation we require a demodulator.
- Modulation is always performed on the sender or the transmitter end. On the other hand, the demodulation is always performed at the receiver end.
- Modulated signals can travel a longer distance. However, demodulated signals travel a shorter distance only.
- Modulation is a simple task to perform whereas, demodulation is a complex task to perform.
- Modulation technique transforms low-frequency signal to high-frequency carrier signal. However, the demodulation technique transforms high-frequency carrier signals into low-frequency signals.
Conclusion
Basically, the modulation transforms a weak signal that cannot be transmitted over a long distance into a stronger signal that can be transmitted in a better way. However, the demodulation is just the reverse of modulation that processes the received strong signal to retrieve the original information.
Modulation and demodulation are the technique that leverages wireless communication. You must be familiar with the device ‘modem’ that is important for communication between analog and digital devices.
we have to install modem at both the end i.e. sender and receiver end. At the sender, it modulates the digital signal to anlaog signal and at the receiver end, it demodulates the analog signal into the digital signal. The modem allows a computer to connect to the internet over a telephone line.
Leave a Reply