 AM and FM are the modulation techniques. The prior difference between AM and FM is that in AM the frequency is kept constant and amplitude of the signal changes while in FM the amplitude of the signal is not allowed to change and frequency of the signal changes. Fundamentally, there are two types of continuous wave modulation/analog modulation, amplitude modulation and angle modulation. FM is categorized under angle modulation.
AM and FM are the modulation techniques. The prior difference between AM and FM is that in AM the frequency is kept constant and amplitude of the signal changes while in FM the amplitude of the signal is not allowed to change and frequency of the signal changes. Fundamentally, there are two types of continuous wave modulation/analog modulation, amplitude modulation and angle modulation. FM is categorized under angle modulation.
Modulation is a method of changing some particular properties of a carrier signal according to the message signal and modulating signal. The signal that bears the information and required to be transmitted is called as modulating signal, message signal or baseband signal. It is so called baseband because it represents a band of frequencies that is transmitted by the source of information. The prior goal of the continuous wave modulation is the translation of the frequency to employ the practical design of the antenna, narrow banding and frequency division multiplexing.
Content: AM Vs FM
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | AM | FM |
|---|---|---|
| Expands to | Amplitude Modulation | Frequency Modulation |
| Basic | Carrier wave amplitude is altered. | Changes carrier wave frequency. |
| Frequency range | 535 - 1705 Kilo hertz or at max 1200 bits/sec. | 88 - 108 Mega hertz or 1200 - 2400 bits/sec. |
| Bandwidth consumption | Takes up to 30 KHz. | Consumes up to 80 KHz per signal. |
| Complexity of the circuit | Simple | Transmitter and receiver are complex. |
| Affect of noise | Prone to noise. | Less susceptible. |
| Distance coverage | AM waves cover a large distance. | FM covers less distance as compared AM. |
| Affect of obstruction | Can resist obstruction such as buildings. | Obstructions can degrade the signal strength. |
| Property | AM waves reflect from the upper layer of the atmosphere. | FM waves can penetrate the atmosphere. |
Definition of AM
Amplitude Modulation is a process in which the amplitude of the carrier signal is altered in accordance with the baseband signal. In other words, the maximum value of the amplitude of the carrier wave is set proportional to the instantaneous value of the baseband signal. In amplitude modulation the amplitude of the baseband signal changes as represented in the diagram below.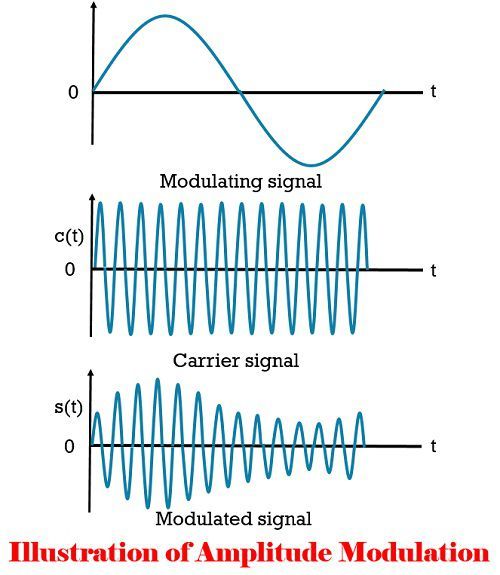
The sinusoidal carrier wave c(t) represented as –![]() Where A shows the maximum amplitude of the carrier wave. The carrier frequency is denoted as wc. Let’s assume the phase of the carrier wave is set to 0 in the following equation. Suppose x(t) represents the baseband and modulating signal then, the amplitude of the carrier signal is made proportional to the intensity of the baseband signal x(t).
Where A shows the maximum amplitude of the carrier wave. The carrier frequency is denoted as wc. Let’s assume the phase of the carrier wave is set to 0 in the following equation. Suppose x(t) represents the baseband and modulating signal then, the amplitude of the carrier signal is made proportional to the intensity of the baseband signal x(t).
The amplitude modulated wave is expressed with the following given standard equation.![]()
![]() The time-varying amplitude of the AM wave is known as the envelope which varies in linear proportion with the message signal.
The time-varying amplitude of the AM wave is known as the envelope which varies in linear proportion with the message signal.
Definition of FM
Frequency Modulation is a category of angle modulation. In the angle modulation either of the two properties, frequency or phase of the carrier can change in accordance with the baseband or modulated signal. Frequency modulation is a modulation technique which linearly changes the instantaneous frequency fi(t) proportional to the magnitude of modulated signal x(t).
The equation used to express frequency modulation is as follows:![]() In the above equation, fc is the carrier frequency of the unmodulated wave, frequency sensitivity of the modulator is indicated by kf and fi(t) is the instantaneous frequency. The unit fo frequency modulation is hertz/volt, where the message signal is assumed to be voltage signal.
In the above equation, fc is the carrier frequency of the unmodulated wave, frequency sensitivity of the modulator is indicated by kf and fi(t) is the instantaneous frequency. The unit fo frequency modulation is hertz/volt, where the message signal is assumed to be voltage signal.
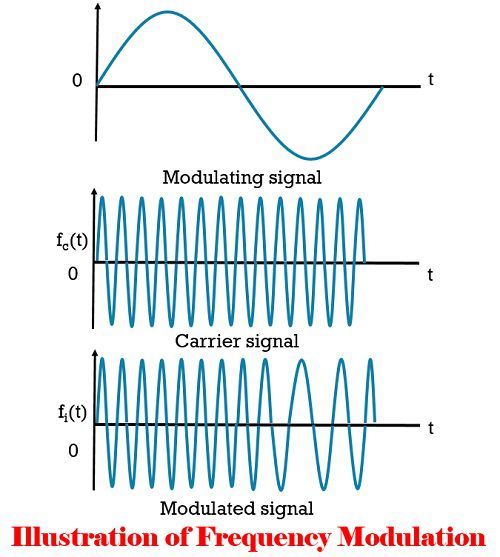
As the instantaneous frequency fi(t) of FM is continuously changing along with time, we have to take the integration of x(t) over the duration of 0 to t. The resultant value is expressed by Θ(t), which is given as follows.![]() The FM envelope does not rely upon message (modulating) signal and remains constant. The diagram below illustrates the Frequency modulation.
The FM envelope does not rely upon message (modulating) signal and remains constant. The diagram below illustrates the Frequency modulation.
Key Differences Between AM and FM
- The amplitude modulation alters the carrier amplitude of the signal. As against, in frequency modulation, the frequency of the carrier signal is altered in accordance with the modulated signal.
- In amplitude modulation, the frequency ranges from 535 – 1705 Kilohertz whereas in frequency modulation the frequency range is 88 to 108 megahertz.
- AM usually consumes less bandwidth, i.e. 30 kHz while FM takes a maximum of 80 kHz bandwidth.
- AM circuitry is simple as compared to FM as AM is the older technology.
- FM can resist noise while AM is susceptible to noise and disturbance.
- AM covers a large distance such as a country. Conversely, FM has a limited range.
- The physical barriers such as buildings, vehicles could not hinder the performance of the AM wave. On the other hand, these obstructions could significantly affect the FM wave.
- AM waves are propagated by experiencing reflection from the upper layer of the atmosphere. In contrast, FM waves propagate by penetrating the atmosphere.
Conclusion
The AM and FM are techniques to transmit data through modifying carrier signal. In AM the phase and frequency of the signal, remain constant and amplitude changes while in FM the amplitude and phase do not change the only frequency of the carrier is altered according to the instantaneous value of the information signal. The AM and FM are mostly used in radio broadcasting but for distinct applications.
Leave a Reply