 The CD and DVD are the versions of an optical disk which mainly differ in size and manufacturing method. Generally, a DVD can store more data than a CD, its one of the reason is that CD contain the polycarbonate substrate on only a single side while in DVDs it present on both of the sides. We have already discussed the construction and working principle of the optical disk in our previous article difference between Magnetic Disk and Optical disk.
The CD and DVD are the versions of an optical disk which mainly differ in size and manufacturing method. Generally, a DVD can store more data than a CD, its one of the reason is that CD contain the polycarbonate substrate on only a single side while in DVDs it present on both of the sides. We have already discussed the construction and working principle of the optical disk in our previous article difference between Magnetic Disk and Optical disk.
The CD and DVD work on optical technology where the data retrieved by using light specifically lasers. A laser beam is concentrated into the CD or DVD in order to read the content (data) stored in the disc in the form of the bits and to write the content.
Content: CD Vs DVD
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | CD | DVD |
|---|---|---|
| Expands to | Compact disk | Digital Versatile Disk |
| Acquired size | 700 MB | 4.7 to 17 GB |
| Usage | Less as compared to DVDs. | More |
| Metal layer (recording layer) position on the disk | Top | Middle of the disk. |
| Layers of the pits | Single | Double (two-sided) |
| Spacing between the loops of the spiral | 1.6 micrometre | 0.74 micrometre |
| Spacing between the pits | 0.834 micrometre | 0.4 micrometre |
| Error correction codes | CIRC and EFMP | RS-PC and EFMplus |
| Removal of the adhesive labels | Result in damage of metal layer. | Can cause an imbalance in spin. |
Definition of CD
The CD (Compact Disc) was the first step towards the idea of digital encoding of the data. It uses a unique method of encoding in which a 14-bit code indicates a byte and this encoding technique also helps in error detection. It was a suitable replacement for the magnetic disk as it offered the low-cost solution for storing a significant amount of data.
The CDs first layer is constructed by the polycarbonate plastic which stores the data in the indented pits. This layer also provides a clear glass base. The flat or unindented area is known as the land. The thin aluminium material covers the programmed disk, and a protective acrylic then coats this aluminium layer. In the last part, the disk is stamped by a label. The pits are organised into the spiral track, in the outward direction from the middle of the disk, though decreasing the risk of damage by storing the index information at the start of the disk. , and the length and width of the pit are 0.8-3 and 0.5 microns respectively.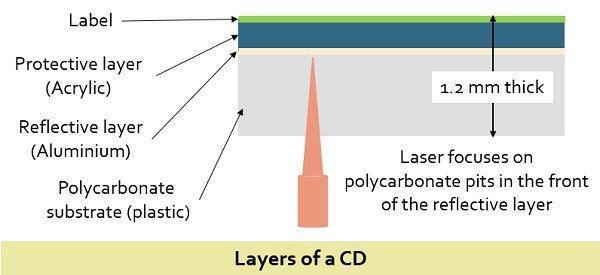
The stored bits are read through targetting the laser light on to the polycarbonate part of the spinning disk. Indented portion of the disk reflects back the light which is detected by the photodetector. There are several variations of the compact disc such as CD-R, CD-ROM, CD-RW.
Definition of DVD
The advent of DVD (Digital Versatile Disk) provided an alternative for the videotape used in VCR (Video Cassette Recorder) and CD-ROM used in PC as the DVD can acquire 7 times larger amount of the data relative to CD. It renders videos with excellent picture quality and random access. A DVD is built from the same material as the CD but the process and the layers are different, it is used from both of the sides such as two CDs are sticking together. It implements different techniques for the error correction i.e., RS-PC and recording code EFMPlus.
The reasons why it provides greater size than a CD are – dense packing of the bits, use of shorter wavelength laser and generation of the two-sided disc (data can be read from write to both the sides). To obtain the smaller spacing about 0.74 microns between the spiral tracks and the minimum distance of 0.4 microns between the pits a short wavelength laser is used. 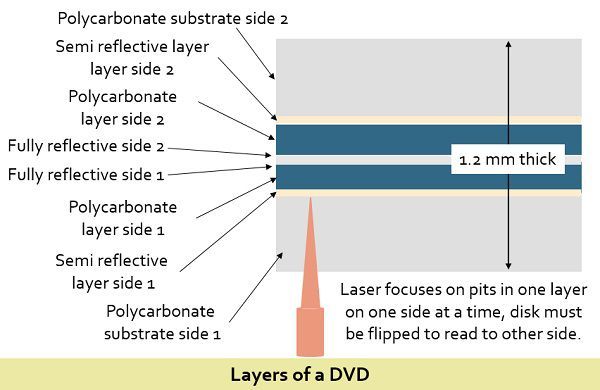 It also employs a dual layer of pits and lands on the standard layer and a semi-reflective layer on the top of the reflective layer. To read the content of the layers separately in a DVD the laser must be carefully focused. Similar to CD, DVD also has variants such as DVD-R, DVD-RW, etcetera.
It also employs a dual layer of pits and lands on the standard layer and a semi-reflective layer on the top of the reflective layer. To read the content of the layers separately in a DVD the laser must be carefully focused. Similar to CD, DVD also has variants such as DVD-R, DVD-RW, etcetera.
Key Differences Between CD and DVD
- A compact disk can hold up to 700 MB of data while a digital versatile disk can hold a maximum 17 GB of data.
- As the DVD can acquire a larger size, it is more prevalently used than a CD.
- The metal layer used for recording is placed beneath the labelling side in the CD. In contrast, in DVD this metal layer is situated in the centre of the disk.
- The layers of pits and land on a CD can be only one whereas in DVD it can be two.
- A CD contains the spacing of 1.6 micrometres between spiral tracks and 0.834 micrometres between the pits on the disc. On the other hand, the spiral loops in DVD are 0.74 micrometres apart and the distance between the pits is 0.4 micrometres.
- The error correcting codes used in CD are CIRC and EFMP. As against, DVD uses distinct error correction techniques which involves RS-PC and EFMPlus.
- The removal of the adhesive label of a CD can cause the severe damage to the CD. On the contrary, when the adhesive label of the DVD is removed, the imbalance in spin is caused.
Conclusion
The CD and DVD are the optical recording medium where CD was devised as an audio storage format while DVD is used as the universal storage format. The latter technology DVD can hold data about 7 times more than CD and its format efficiency is also 32% greater than a CD.
Masseb says
It’s been beneficial for me. It was an assignment for me to search for the difference between the CD and the DVD. Now it will be straightforward to represent all this knowledge.
Jim Noel says
Can you convert OLD CD’s into an email format?