 DSL and ADSL are the technologies adopted by telecom companies to facilitate faster data transmission. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a set of technologies, among which ADSL is one.
DSL and ADSL are the technologies adopted by telecom companies to facilitate faster data transmission. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a set of technologies, among which ADSL is one.
Although ADSL is a subset of DSL technologies we will try to identify some of the differences between these two. We will also be discussing about both techniques in detail.
Content: DSL Vs ADSL
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | DSL | ADSL |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | DSL has equal uploading and downloading speed. | Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line |
| Speed | DSL has equal uploading and downloading speed. | ADSL has different uploading and downloading speed. |
| Technologies | DSL is a set of technologies. | ADSL is one of the technologies from DSL family. |
| Classification | ADSL, VDSL, HDSL, and SDSL | No further classification |
What is DSL?
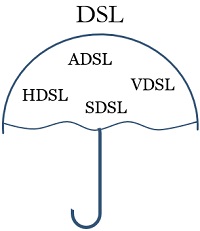
DSL is short for Digital Subscriber Line. It is a technology that reuses the existing infrastructure of telephone lines for the transmission of digital data. DSL is not a single technology instead, it is a set of technology that includes ADSL, VDSL, HDSL, and SDSL.
With the help of the figure below you can understand how a DSL connection is established over a telephone line to transmit data between the user and the internet.
DSL Modem
The DSL modem is a device connected to your computer on one side and on the other side to the telephone line over which it transmits data.
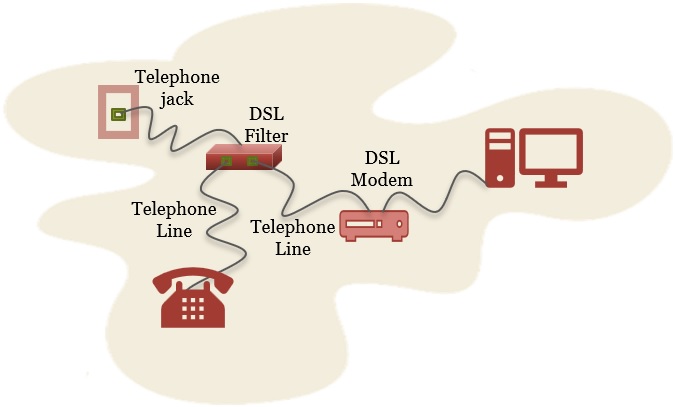
Your computer generates digital data which cannot be transmitted over the telephone line in the digital format. Thus the DSL modem converts the digital data into analog that we can transmit over the telephone line.
It is also responsible to convert the analog data that is coming from the telephone line into digital data. As the computer cannot process the analog data.
We all know that modem is short for modulator and demodulator. So, it is a device that can convert between digital and analog data.
What is ADSL?
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) is a DSL technology. The designers of ADSL have divided the available bandwidth unevenly. This leads to different uploading and downloading speeds. This is why we refer to it as asymmetric.
ADSL technology provides a higher downloading speed i.e. transmission of data from the internet to the user. It provides lower uploading speed i.e. transmission of data from user to the internet.
This scenario goes well with the residential users, who most of the time download stuff from the internet. But ADSL is not good for business users as they require large bandwidth in both directions.
Like DSL, ADSL uses the existing infrastructure of telephone lines. The telephone line uses a twisted-pair cable that is capable of handling bandwidths up to 1.1 MHz. But there is a filter installed at the end of these telephone lines. This filter limits the bandwidth up to 4 kHz which is suitable for voice communication.
Now if we remove this filter we will be able to use this entire 1.1 MHz of bandwidth for both data and voice communication.
However, 1.1 MHz is just a theoretical bandwidth. There are many factors that affect the bandwidth such as distance between the user and the switching office of the telephone company, size and quality of the cable used, etc.
ADSL Broadband
Broadband with ADSL technique exploits this 1.1 MHz of bandwidth provided by the twisted pair using the frequency division multiplexing i.e. FDM. The bandwidth of 1.1 MHz is divided as you can see in the figure below:
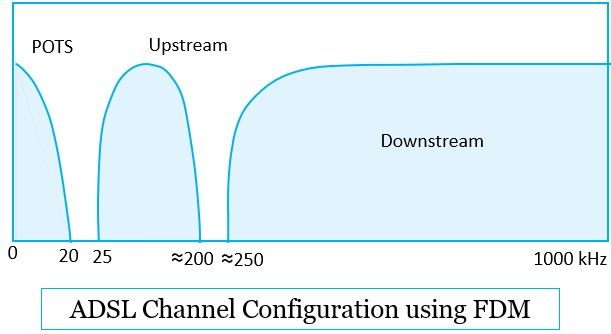
- ADSL keeps the lowest 25 kHz for voice transmission. We refer to this as POTS i.e. plain old telephone service. Although the voice is transmitted only within the bandwidth of 0 to 4 kHz. And rest of the bandwidth up to 25 kHz is left to prevent crosstalk between the data and the voice channel.
- Further FDM, divides the rest of the bandwidth into two streams i.e. smaller upstream and larger downstream.
- FDM can also be applied within the upstream and downstream. There it can split a single bit stream into multiple parallel bit streams. Each bit stream here can then be carried in a separate frequency band.
Echo Cancellation
You can even use echo cancellation to exploit the rest of the bandwidth into upstream and downstream. In this case, the upstream band overlaps the lower portion of the downstream band.
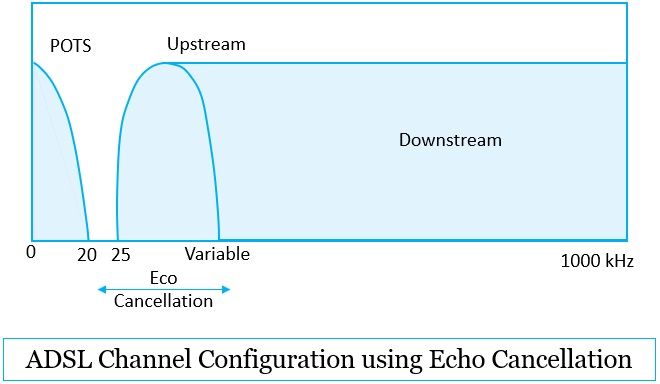
However, this overlapping leads to two advantages over the two distinct frequency bands for upstream and downstream:
- We all are aware, that the higher is frequency, the greater are the chances of attenuation. But with eco cancellation, most of the downstream bandwidth lies in the good part of the spectrum.
- Echo cancellation facilitates us with the benefit of extending upstream bandwidth upwards without running downstream.
The echo cancellation technique must be implemented at both ends of the stream. The asymmetric digital subscriber line can be deployed up to a range of 5.5 km depending on the diameter of the cable.
Key Differences Between DSL and ADSL
- DSL is short for Digital Subscriber Line. However, ADSL is Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line.
- DSL technology has equal uploading and downloading speeds. On the other hand, ADSL technology has a higher downloading speed and lower uploading speed.
- DSL is a set of technologies whereas ADSL is a DSL technology.
- The set of technologies offered by DSL is ADSL, VDSL, HDSL, and SDSL. ASDL is further not classified into any new technologies.
Conclusion
In this content, we have discussed the differences between two technologies DSL and ADSL. Here DSL is a broader term for technologies that use telephone line for data transmission. The other technologies that DSL offers are ADSL, VDSL, HDSL and SDSL.
Leave a Reply