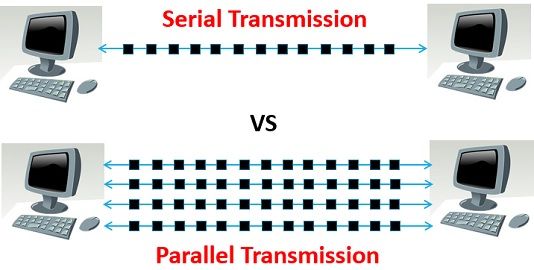
 For transferring data between computers, laptops, two methods are used, namely, Serial Transmission and Parallel Transmission. There are some similarities and dissimilarities between them. One of the primary difference is that; in Serial Transmission, data is sent bit by bit whereas, in Parallel Transmission a byte (8 bits) or character is sent at a time.
For transferring data between computers, laptops, two methods are used, namely, Serial Transmission and Parallel Transmission. There are some similarities and dissimilarities between them. One of the primary difference is that; in Serial Transmission, data is sent bit by bit whereas, in Parallel Transmission a byte (8 bits) or character is sent at a time.
The similarity is that both are used to connect and communicate with peripheral devices. Furthermore, the parallel transmission is time-sensitive, whereas serial transmission is not time-sensitive. Other differences are discussed below.
Content: Serial Vs Parallel Transmission
Comparison Chart
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | SERIAL TRANSMISSION | PARALLEL TRANSMISSION |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Data flows in bi-direction, bit by bit | Multiple lines are used to send data, i.e. 8 bits or 1 byte at a time |
| Cost | Economical | Expensive |
| Bits transferred at 1 clock pulse | 1 bit | 8 bits or 1 byte |
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Applications | Used for long-distance communication. E.g., Computer to computer | Short distance. E.g., computer to a printer |
| Number of communication channel required | Only one | N number of communication channels are needed |
| Need of converters | Required to convert the signals according to the need. | Not required |
Definition Of Serial Transmission
In Serial Transmission, data is sent bit by bit from one computer to another in bi-direction where each bit has its clock pulse rate. Eight bits are transferred at a time having a start and stop bit (usually known as a Parity bit), i.e. 0 and 1 respectively.
For transmitting data to a longer distance, serial data cables are used. However, the data transferred in the serial transmission is in proper order. It consists of a D-shaped 9 pin cable that connects the data in series. Serial Transmission has two subclasses synchronous and asynchronous. In asynchronous transmission, an extra bit is added to each byte so that the receiver is alert about the arrival of new data. Usually, 0 is a start bit, and 1 is the stop bit. In synchronous transmission, no extra bit is added rather the data transferred in the form of frames which contains multiple bytes.
Serial Transmission has two subclasses synchronous and asynchronous. In asynchronous transmission, an extra bit is added to each byte so that the receiver is alert about the arrival of new data. Usually, 0 is a start bit, and 1 is the stop bit. In synchronous transmission, no extra bit is added rather the data transferred in the form of frames which contains multiple bytes.
The serial transmission system would not be able to work without installing hardware at the sending and receiving. The hardware residing in the sending and receiving end is capable of converting the data from the parallel mode (used in the device) to the serial mode (used in the wires).
Definition Of Parallel Transmission
In Parallel Transmission, various bits are sent together simultaneously with a single clock pulse. It is a fast way to transmit as it uses many input/output lines for transferring the data.
Furthermore, it is advantageous because it conforms to the underlying hardware also, as the electronic devices like computer and communication hardware uses parallel circuitry internally. This is a reason the parallel interface complements the internal hardware well.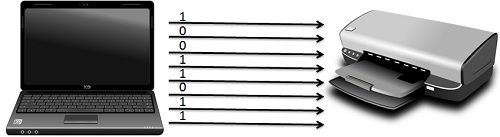 The installation and troubleshooting is easier in parallel transmission system due to its placement in a single physical cable. Parallel Transmission uses a 25 pin port having 17 signal lines and 8 ground lines. The 17 signal lines are further divided as
The installation and troubleshooting is easier in parallel transmission system due to its placement in a single physical cable. Parallel Transmission uses a 25 pin port having 17 signal lines and 8 ground lines. The 17 signal lines are further divided as
- 4 lines that initiate handshaking,
- Status lines used to communicate and notify errors and
- 8 to transfer data.
Despite the speed of the data, the parallel transmission has a limitation called skew where bits could travel in quite different speeds over the wires.
Key Differences Between Serial And Parallel Transmission
- Serial transmission requires a single line to communicate and transfer data whereas, parallel transmission requires multiple lines.
- Serial transmission is used for long-distance communication. As against, parallel transmission is used for the shorter distance.
- Error and noise are least in serial as compared to parallel transmission. Since one bit follows another in Serial Transmission whereas, in Parallel Transmission multiple bits are sent together.
- Parallel transmission is faster as the data is transmitted using multiples lines. On the contrary, in Serial transmission data flows through a single wire.
- Serial Transmission is full-duplex as the sender can send as well as receive the data. In contrast, Parallel Transmission is half-duplex since the data is either sent or received.
- The special types of converters are required in a serial transmission system to convert the data between the internal parallel form and serial form while there is no such requirement of converters in parallel transmission systems.
- Serial transmission cables are thinner, longer and economical in comparison with the Parallel Transmission cables.
- Serial Transmission is simple and reliable. Conversely, Parallel Transmission is unreliable and complicated.
Advantages
Serial transmission
- It is cost-effective
- It is appropriate for long-distance communication.
- More reliable
Parallel transmission
- Transmits data at a higher speed.
- Suits better for short-distance communication.
- Set of bits are transferred simultaneously.
Disadvantages
Serial transmission
- Data transmission rate is low.
- Throughput relies on the bit rate.
Parallel transmission
- It is a costly transmission system.
- In order to transmit the data over long ranges, the thickness of the wire has to be increased to diminish signal degradation.
- There are multiple communication channels required.
Conclusion
Both Serial and Parallel Transmission have their advantages and disadvantages, respectively. Parallel Transmission is used for a limited distance, provides higher speed.
On the other hand, Serial Transmission is reliable for transferring data to longer distance. Hence, we conclude that both serial and parallel are individually essential for transferring data.
Anju says
Very useful
autin says
this is helpful
Nancy says
Very useful.
Nuimrata says
good
Rui Simpson says
Thanks
Steve Ng says
very detailed explanation. Thank you!!!
Yathin Naik N S says
Thank you
sarkar says
help for my exam purpose
Saloni says
great job…very clear explanation…thank u..!!
King obey says
Very useful for my exam
Hassan says
Thank you for this article
saurav says
very clear explanation…thank you….!!