 VPN and DNS are the tools that let you access the geo-blocked contents. Although their basic work is different. The VPN provides secure communication between your device and the Internet. On the other hand, the DNS resolves the name of a remote host to its IP address.
VPN and DNS are the tools that let you access the geo-blocked contents. Although their basic work is different. The VPN provides secure communication between your device and the Internet. On the other hand, the DNS resolves the name of a remote host to its IP address.
Initially, we will discuss the differences between VPN and DNS with the help of the comparison. Further, we will discuss the terms VPN and DNS in detail along with the related queries.
Content: VPN Vs DNS
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | VPN (Virtual Private Network) | DNS (Domain Name System) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | VPN secures connection between the communicating hosts. | DNS helps users to access any remote host by its name. |
| Working | VPN encrypts your Internet traffic. | DNS converts name of remote host to its IP address. |
| Security | More secure | Less secure |
| Speed | VPN is comparatively slower. | Faster. |
| Bypass Firewall | VPN can bypass firewall. | DNS cannot bypass firewall. |
| Availability | VPN service or app is not available in all devices. | DNS service is available in almost all devices. |
| Set up | Setting up VPN is complex and it requires installation. | Setting up DNS is simple and it doesn’t require installation. |
| Cost | VPN services are expensive. | DNS services are cost friendly. |
What is VPN?
A virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technique that encrypts connection between your device and the network. This encrypted connection encrypts the data that you sent or receive so that the intruder or attacker is unable to read it.
Why to Use a VPN?
In order to retrieve some data over the internet, your device is directly connected to the webserver. This connection is transparent and all your activities are visible to the snoopers. Such as what are you surfing on the internet? What is your current location? And many more.
This provides an opportunity for the intruders and attackers to hack your system. From your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to companies that collect users’ data may put your privacy at risk as they can sell or monetize your data. They can even use your data for some malicious purpose.
Thus, we required a trusted tool that would protect the user’s privacy over the internet. A VPN encrypts the data that the user sends or receives, and the encrypted data becomes unreadable to the attacker, increasing the user’s privacy.
Does VPN change IP Address?
Each connection on the network is assigned a unique IP address that provides information related to your geographical location, and your Internet Service Provider (ISP). When you implement VPN to enhance your privacy it replaces your original IP address with the other IP address so that it appears like you are connecting from a different geographical location.
To change the IP address, you have to open the VPN app. In the app, you just have to select the new server location you want to connect. Now you will be able to surf with the new IP address.
How does VPN Work?
VPN technology is implemented on the router that connects your device to the network. To implement VPN, ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) protocol of IP sec is used in tunnel mode. This enables the router to encapsulate the datagram, including its header.
Let us discuss it working in brief with the help of the figure below:
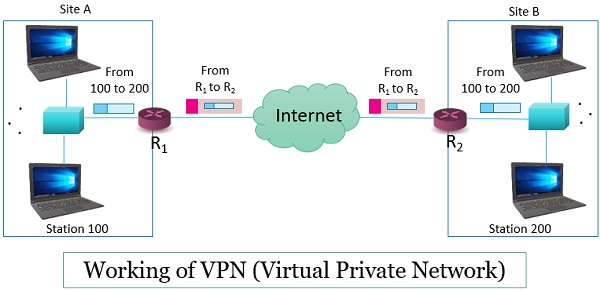
Consider that we have two sites A and B where a station 100 in site A has to send data to station 200 in site B. Site A is connected to the internet via router R1 and site B is connected to the internet via router R2.
Now, station 100 creates a datagram and sends it to the router R1. The router R1 further encapsulate the datagram including its header inside the ESP packet. The router R1 uses its own IP address as the source address and the IP address of router R2 as the destination address.
This encapsulated datagram is now passed through the Internet. No outsider can decipher the content of the datagram and not even the source and destination IP address.
When this encapsulated datagram reaches the router R2, it decapsulates the datagram it revealing its original destination address and thereby delivering it.
Why VPN is Slow?
The VPN enhances the security of data by encrypting (encapsulating) the data into the ESP packet. This process of encryption and decryption of the data adversely affects the internet speed slowing it down.
Can VPN Increase Internet Speed?
Under certain situations, VPN can boost your internet speed. Sometimes your ISPs slow down a certain type of internet traffic such as streaming entertainment services like amazon prime, Netflix etc.
Now when you are using the VPN service the ISP cannot see what kind of services the user is connecting with. Thus, it will not slow down the internet speed and improve it.
Can VPN be Hacked?
VPN provides safety to your device but it doesn’t make your device immune from hacking. VPN secures your device from the attack that requires to access your IP address.
But it may not protect you from an attack that doesn’t require to access your device’s IP address. Like, malware attacks, phishing attacks etc.
Although the high-quality VPN services imply a no-log policy. This directs the servers, the VPN runs on, to store a minimal amount of data that is necessary to connect to the internet. Each time you disconnect or change the server, the data gets deleted so even if the hacker attack it won’t get enough information to make any kind of advantage.
Do you need a VPN for Streaming?
The licensing agreement of streaming services such as Netflix, prime video, Disney+Hotstar, etc. varies from country to country. So, they have a common feature of geo-blocked content i.e. there may be some streaming content like a TV show, a movie or a web series that is restricted to your country.
VPN bypasses this restriction and allows you to watch these geo-blocked contents. The VPN provides a high level of encryption with many server locations that will allow watching a lot of geo-restricted content.
Although you may get caught and your account may get suspended, the chances are less.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of VPN
- The basic principle of a VPN is to secure your internet connection.
- VPN hides the crucial information that you enter on websites such as your account details, your login information etc.
- VPN prevents data throttling. After a user consumes a specific amount of data the ISP slow down his services. But when the user is using VPN the ISP is not even to detect how much data the user has consumed. Thus, ISP avoids throttling your data.
- VPN allows let you access the geo-blocked content on streaming services.
- A VPN doesn’t disclose your location to hackers by hiding your IP address.
- VPN allows you to expand your network.
Disadvantages of VPN
- As VPN performs the encryption on the data that you send or receive, it adversely affects the speed of the internet and reduces the internet speed.
- VPN protects you from attacks but it doesn’t make your device immune to attacks.
- To ensure more privacy you have to hire a higher level of VPN.
- VPN increases your data consumption.
- VPN doesn’t always bypass the restriction on geo-blocked content.
What is DNS & Why it is Used?
Usually, humans prefer to remember a site by its name instead of its numeric address. But a computer prefers to remember a site by its numeric IP address. Therefore, we require a system that can help humans to operate computers. This system must be able to map a name to its address and an address to its name.
Earlier each host would store the host file that has its remote computer names and their corresponding addresses. Any application or program in the host that needs to map a name to its address would consult this host file. The host update this host file periodically.
But the host file is so large that we cannot store it on each host. Thus, this host file is stored on a single centralized computer and the host that needs mapping would consult this centralized computer. But this would increase traffic on the internet.
So, in order to avoid the traffic, the information in the host file is divided into parts and these parts are stored on a different computer. In this case, the host that needs mapping would consult the nearest computer holding the required mapping information. This system is the Domain Name System (DNS).
A DNS Client is Called?
We refer to a DNS client as a resolver as it resolves the domain name to its IP address.
Working of DNS
Consider that a host wants to access the website techdifferences.com (name of file transfer server running on the remote host). Now in order to access this website, the TCP/IP protocol requires the IP address of this website or file transfer server. To retrieve the IP address of this website the host computer will perform the following steps.
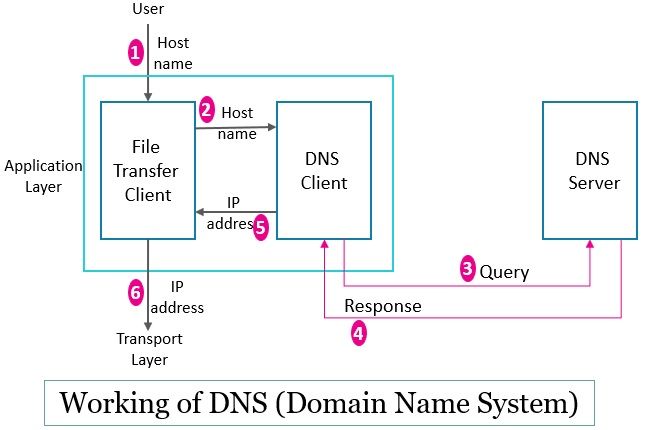
- The user will provide the name of the file transfer server to the file transfer client (FTP).
- The file transfer client will forward this name to the DNS client that knows the IP address of one nearest DNS server.
- DNS client would raise a query with the file transfer server name and send it to the DNS server.
- The DNS server will respond with the IP address of the file transfer server and forwards it to the DNS client.
- The DNS client further forwards the IP address of the file transfer server to the file transfer client.
- The file transfer client will now use this IP address to access the corresponding file transfer server with the name techdifferences.com.
Why does DNS use UDP?
Being the application layer protocol DNS has to use either of the two transport layer protocols i.e. UDP or TCP. This is because DNS requires some means to send DNS queries and receive DNS responses over the internet.
DNS used the UDP (user datagram protocol) over TCP for the following reasons.
- DNS requests are small and they get easily fit into UDP segments.
- UDP is faster hence it resolves the name to IP address faster.
What is DNS Flush?
Although each DNS record has a particular life span i.e. time-to-live (TTL). Still, we can manually delete these DNS entries from the system cache. So, the process of manually deleting the DNS entries is nothing but DNS flush. The deletion of the DNS entries is carried out using system-specific flush commands.
DNS flush is carried out for three specific reasons:
- To hide the search behaviour of the user.
- To prevent hackers from manipulating the DNS entries that might land you on fake websites.
- It even resolves technical problems.
Where DNS Server is Located?
Usually, the DNS servers are located at your ISP’s data centre.
Why Change DNS?
There is a handful of reasons to change your DNS:
- Service Speed
Opting for the third-party DNS server may faster your services as compared to the ISP’s default DNS server. The service speed also depends on how close the third-party DNS server is to your home. - Service Reliability
If your internet service seems to be unreliable, changing your DNS server will be an easy solution. - Improve Web-Filtering
Being a parent, you always want to control your child’s activity on the internet. Changing your DNS service to OpenDNS allows you to block certain categories of websites - Advanced Protection
Some DNS services allow you to block certain websites that are popular as phishing websites. - Access Geo-Blocked Content
Similar to VPN services, some DNS services also allow accessing the geo-blocked content. With some smart tricks and network tunnelling, the DNS server will make you look like you don’t belong to the blocked region.
Does DNS Affect Internet Speed?
DNS is not bound to improve your internet speed. Still, it can fasten up the time required to open up a webpage on your computer by resolving the domain name faster.
Does DNS Affect Ping?
No, the DNS does not affect the ping test it only improves the initial lookup of the website.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DNS
Advantages
- It prevents the user from memorizing the complex IP addresses.
- DNS systems are easy to use and configure.
Disadvantages
- DNS can undergo DNS attacks due to which the domain names resolve to false IP addresses.
- Troubleshooting is difficult in DNS.
Key Differences Between VPN and DNS
- The abbreviation of VPN is Virtual Private Network. On the other hand, an abbreviation of DNS is Domain System.
- VPN secures the communication between your device and the internet. DNS resolve the name of the remote host to its IP address.
- To provide privacy VPN encrypts the communication between the devices. On the other hand, DNS does not perform any kind of encryption.
- Due to encryption VPN is more secure if compared with DNS.
- VPN services can bypass the firewall. However, DNS cannot bypass any firewall.
- If we talk about the VPN service or app it is not available on all the devices. Whereas, DNS service is available on almost all communication devices.
- Setting up DNS is easy and it doesn’t require any kind of installation. On the other hand, setting up a VPN requires installation.
- VPN is expensive as compared to DNS.
Conclusion
So this is all about the VPN and DNS. You must have got answers to all your queries related to these services.
Leave a Reply