 SRAM and DRAM are the modes of integrated-circuit RAM where SRAM uses transistors and latches in construction while DRAM uses capacitors and transistors. These can be differentiated in many ways, such as SRAM is comparatively faster than DRAM; hence SRAM is used for cache memory while DRAM is used for main memory.
SRAM and DRAM are the modes of integrated-circuit RAM where SRAM uses transistors and latches in construction while DRAM uses capacitors and transistors. These can be differentiated in many ways, such as SRAM is comparatively faster than DRAM; hence SRAM is used for cache memory while DRAM is used for main memory.
RAM (Random Access Memory) is a kind of memory which needs constant power to retain the data in it, once the power supply is disrupted the data will be lost, that’s why it is known as volatile memory. Reading and writing in RAM is easy and rapid and accomplished through electrical signals.
Content: SRAM Vs DRAM
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | SRAM | DRAM |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Size | Small | Large |
| Cost | Expensive | Cheap |
| Used in | Cache memory | Main memory |
| Density | Less dense | Highly dense |
| Construction | Complex and uses transistors and latches. | Simple and uses capacitors and very few transistors. |
| Single block of memory requires | 6 transistors | Only one transistor. |
| Charge leakage property | Not present | Present hence require power refresh circuitry |
| Power consumption | Low | High |
Definition of SRAM
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) is made up of CMOS technology and uses six transistors. Its construction is comprised of two cross-coupled inverters to store data (binary) similar to flip-flops and extra two transistors for access control. It is relatively faster than other RAM types such as DRAM. It consumes less power. SRAM can hold the data as long as power is supplied to it.
Working of SRAM for an individual cell:
To generate stable logic state, four transistors (T1, T2, T3, T4) are organized in a cross-connected way. For generating logic state 1, node C1 is high, and C2 is low; in this state, T1 and T4 are off, and T2 and T3 are on. For logic state 0, junction C1 is low, and C2 is high; in the given state T1 and T4 are on, and T2 and T3 are off. Both states are stable until the direct current (dc) voltage is applied. 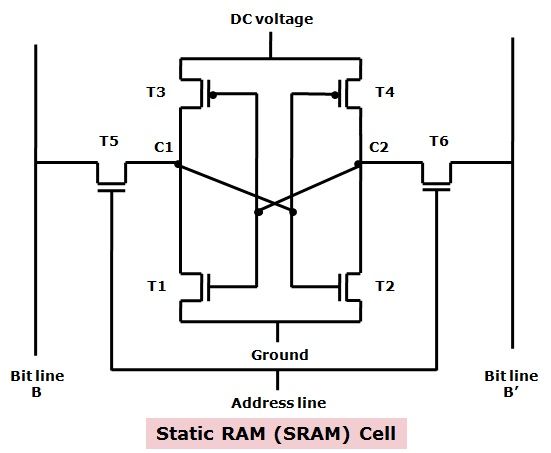 The SRAM address line is operated for opening and closing the switch and to control the T5 and T6 transistors permitting to read and write. For read operation the signal is applied to these address line then T5 and T6 gets on, and the bit value is read from line B. For the write operation, the signal is employed to B bit line, and its complement is applied to B’.
The SRAM address line is operated for opening and closing the switch and to control the T5 and T6 transistors permitting to read and write. For read operation the signal is applied to these address line then T5 and T6 gets on, and the bit value is read from line B. For the write operation, the signal is employed to B bit line, and its complement is applied to B’.
Definition of DRAM
DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) is also a type of RAM which is constructed using capacitors and few transistors. The capacitor is used for storing the data where bit value 1 signifies that the capacitor is charged and a bit value 0 means that capacitor is discharged. Capacitor tends to discharge, which result in leaking of charges.
The dynamic term indicates that the charges are continuously leaking even in the presence of continuous supplied power that is the reason it consumes more power. To retain data for a long time, it needs to be repeatedly refreshed which requires additional refresh circuitry. Due to leaking charge DRAM loses data even if power is switched on. DRAM is available in the higher amount of capacity and is less expensive. It requires only a single transistor for the single block of memory.
Working of typical DRAM cell:
At the time of reading and writing the bit value from the cell, the address line is activated. The transistor present in the circuitry behaves as a switch that is closed (allowing current to flow) if a voltage is applied to the address line and open (no current flows) if no voltage is applied to the address line. For the write operation, a voltage signal is employed to the bit line where high voltage shows 1, and low voltage indicates 0. A signal is then used to the address line which enables transferring of the charge to the capacitor.
When the address line is chosen for executing read operation, the transistor turns on and the charge stored on the capacitor is supplied out onto a bit line and to a sense amplifier. 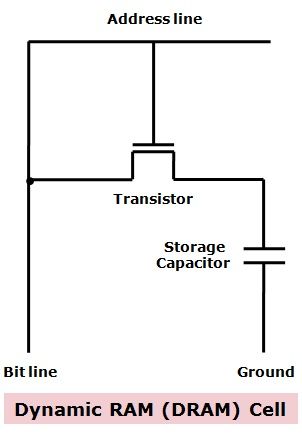 The sense amplifier specifies whether the cell contains a logic 1 or logic 2 by comparing the capacitor voltage to a reference value. The reading of the cell results in discharging of the capacitor, which must be restored to complete the operation. Even though a DRAM is basically an analog device and used to store the single bit (i.e., 0,1).
The sense amplifier specifies whether the cell contains a logic 1 or logic 2 by comparing the capacitor voltage to a reference value. The reading of the cell results in discharging of the capacitor, which must be restored to complete the operation. Even though a DRAM is basically an analog device and used to store the single bit (i.e., 0,1).
Key Differences Between SRAM and DRAM
- SRAM is an on-chip memory whose access time is small while DRAM is an off-chip memory which has a large access time. Therefore SRAM is faster than DRAM.
- DRAM is available in larger storage capacity while SRAM is of smaller size.
- SRAM is expensive whereas DRAM is cheap.
- The cache memory is an application of SRAM. In contrast, DRAM is used in main memory.
- DRAM is highly dense. As against, SRAM is rarer.
- The construction of SRAM is complex due to the usage of a large number of transistors. On the contrary, DRAM is simple to design and implement.
- In SRAM a single block of memory requires six transistors whereas DRAM needs just one transistor for a single block of memory.
- DRAM is named as dynamic, because it uses capacitor which produces leakage current due to the dielectric used inside the capacitor to separate the conductive plates is not a perfect insulator hence require power refresh circuitry. On the other hand, there is no issue of charge leakage in the SRAM.
- Power consumption is higher in DRAM than SRAM. SRAM operates on the principle of changing the direction of current through switches whereas DRAM works on holding the charges.
Conclusion
DRAM is descendent of SRAM. DRAM is devised to overcome the disadvantages of SRAM; designers have reduced the memory elements used in one bit of memory which significantly reduced the DRAM cost and increased the storage area. But, DRAM is slow and consumes more power than SRAM, it needs to be refreshed frequently in few milliseconds to retain the charges.
Sowmya Singh says
information provided on computer organisation… Very useful…
pranesh says
It is very useful..thank you so much…
Abhay says
Thank you for the info
JOHNATHAN says
Perfectly written…
Jagveer Singh says
I liked this information. All information provided is organized in an easy way.
piyush tripathi says
Thank you, ma’am.
Sanjay Yadav says
Good one. . .
Mansvi says
Thank you!! It was really helpful.
Raj says
Very good article.
Piyush Genwa says
Very well written
Jeet says
Thank you so much, Easy to understand.
Binh Thanh Nguyen says
Thanks, nice post
Redeem Grimm says
Who’s here learning on quarantine,? Very informative. Thanks a lot.
Jayamala says
Information provided is very good and easy to understand
Wen says
I never get any good answer for SRAM. But here I get it!
Sam says
Thanks….Good information
Daevor says
Thank you. I learnt a lot from this article.
Dalmiro says
CS student from Spain. Best explanation I found so far. Short and precise. Thank you for publishing this.
Ayesha Asad says
VERY HELPFULL ,thank you