 There are three modes of transmission simplex, half duplex, and full duplex. Transmission mode describes the direction, of flow of signal between two connected devices. The main difference between simplex, half duplex, and full duplex is that in a simplex mode of transmission the communication is unidirectional whereas, in the half-duplex mode of transmission the communication is two directional but the channel is alternately used by the both the connected device.
There are three modes of transmission simplex, half duplex, and full duplex. Transmission mode describes the direction, of flow of signal between two connected devices. The main difference between simplex, half duplex, and full duplex is that in a simplex mode of transmission the communication is unidirectional whereas, in the half-duplex mode of transmission the communication is two directional but the channel is alternately used by the both the connected device.
On the other hand, in the full duplex mode of transmission, the communication is bi-directional, and the channel is used by both the connected device simultaneously. Let us study the difference between simplex, half duplex, and full duplex with the help of comparison chart shown below.
Content: Simplex, Half Duplex, and Full Duplex
Comparison chart
| Basis for Comparison | Simplex | Half Duplex | Full Duplex |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direction of Communication | Communication is unidirectional. | Communication is two-directional but, one at a time. | Communication is two directional and done simultaneously. |
| Send/Receive | A sender can send data but, can not receive. | A sender can send as well as receive the data but one at a time. | A sender can send as well as receive the data simultaneously. |
| Performance | The half duplex and full duplex yields better performance than the Simplex. | The full duplex mode yields higher performance than half duplex. | Full duplex has better performance as it doubles the utilization of bandwidth. |
| Example | Keyboard and monitor. | Walkie-Talkies. | Telephone. |
Definition of Simplex
In a simplex transmission mode, the communication between sender and receiver occur only in one direction. That means only the sender can transmit the data, and receiver can only receive the data. The receiver can not reply in reverse to the sender. Simplex is like a one-way road in which the traffic travels only in one direction, no vehicle from opposite direction is allowed to enter. The entire channel capacity is only utilized by the sender.
 You can better understand the simplex transmission mode with an example of keyboard and monitor. The Keyboard can only transmit the input to the monitor, and the monitor can only receive the input and display it on the screen. The monitor can not transmit any information back to the keyboard.
You can better understand the simplex transmission mode with an example of keyboard and monitor. The Keyboard can only transmit the input to the monitor, and the monitor can only receive the input and display it on the screen. The monitor can not transmit any information back to the keyboard.
Definition of Half Duplex
In a half-duplex transmission mode, the communication between sender and receiver occurs in both the directions but, one at a time. The sender and receiver both can transmit and receive the information but, only one is allowed to transmit at a time.
Half duplex is still a one way road, in which a vehicle traveling in opposite direction of the traffic has to wait till the road is empty. The entire channel capacity is utilized by the transmitter, transmitting at that particular time.
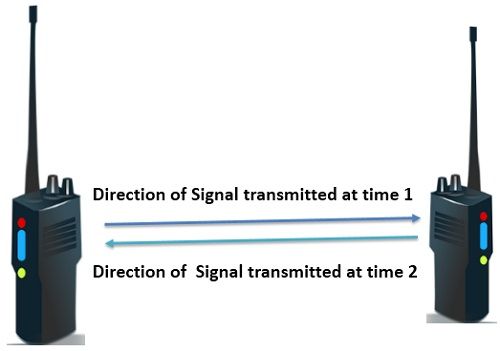 Half duplex can be understood with an example of walkie-talkies. As the speaker at both the end of walkie-talkies can speak but they have to speak one by one. Both can not speak simultaneously.
Half duplex can be understood with an example of walkie-talkies. As the speaker at both the end of walkie-talkies can speak but they have to speak one by one. Both can not speak simultaneously.
Definition of Full Duplex
In a full duplex transmission mode, the communication between sender and receiver can occur simultaneously. Sender and receiver both can transmit and receive simultaneously at the same time. The full duplex transmission mode is like a two way road in which traffic can flow in both the direction at the same time. The entire capacity of the channel is shared by both the transmitted signal traveling in opposite direction.
Sharing of the channel capacity can be achieved in two different ways. First, either you physically separate the link in two parts one for sending and other for receiving. Second, or you let the capacity of a channel to be shared by the two signals traveling in opposite direction.
 Full duplex can be understood best, with an example of a telephone. When two people communicate over a telephone both are free to speak and listen at the same time.
Full duplex can be understood best, with an example of a telephone. When two people communicate over a telephone both are free to speak and listen at the same time.
Key Differences Between Simplex, Half Duplex and Full Duplex
- In a Simplex mode of transmission, the signal can be sent only in one direction; hence, it is unidirectional. On the other hand, in half duplex, both the sender and receiver can transmit the signal but, only one at a time, whereas, in full duplex, the sender and receiver can transmit the signal simultaneously at the same time.
- In a simplex mode of transmission, only one of the two devices on the link can transmit the signal, and the other can only receive but can not send back the signal in reverse. In a half duplex mode, both the devices connected on the link can transmit the signal but only one device can transmit at a time. In a full-duplex mode, both the device on the link can transmit simultaneously.
- The performance of full duplex is better than half duplex and simplex because it better utilizes the bandwidth, as compared to half duplex and simplex.
- If we take the example of keyboard and monitor, it is observed that keyboard inputs the command and monitor displays it, monitor never reply back to the keyboard; hence, it is an example of the simplex transmission mode. In a walkie-talkie, only one person can communicate at a time so; it represents an example of half duplex mode of transmission. In a telephone, both the person on the either side of a telephone can communicate parallelly at the same time; hence, it represents an example of a full-duplex mode of transmission.
Conclusion
The full duplex transmission modes offer the better performance and also increases the throughput of the bandwidth.
Anu says
Awesome and main points included in the comparision chart of related topic…best and correct key points to gain knowledge!
kanha says
awesome post mam.
Joshua says
Thanks for the quick article. Helped me to understand the differences a little better. I’ll mention just for kicks that I found a really easy to understand example is a car radio station. It uses simplex, so you can hear it but not transmit.
Mayank deep says
ONLY DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SIMPLEX MODE AND FGULL DUPLEX MODE .