 Multiprocessor and multicomputer are types of parallel computers. The fundamental difference between them is that a multiprocessor is a solitary computer containing several processors interconnected with the common computing resources such as memory and I/O devices. On the contrary, the multicomputer is constructed by interconnecting multiple autonomous computers through a network and each autonomous system has its own computing resource.
Multiprocessor and multicomputer are types of parallel computers. The fundamental difference between them is that a multiprocessor is a solitary computer containing several processors interconnected with the common computing resources such as memory and I/O devices. On the contrary, the multicomputer is constructed by interconnecting multiple autonomous computers through a network and each autonomous system has its own computing resource.
Content: Multiprocessor Vs Multicomputer
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Multiprocessor | Multicomputer |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Multiple processors in a single computer. | Interlinked multiple autonomous computers. |
| Memory attached to the processing elements | Single shared | Multiple distributed |
| Communication between processing elements | Mandatory | Not necessary |
| Type of network | Dynamic network | Static network |
| Example | Sequent symmetry S-81 | Message passing multicomputer |
Definition of Multiprocessor
Multiprocessor is a computer used for processing and executes isolated instruction streams residing in a single address space. A wide range of multiprocessors are the shared memory devices, built by linking various processors to one or more memory banks with the help of a bus or switch.
There are three models comes under a multiprocessor
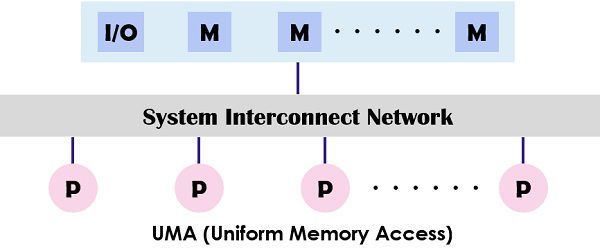
- UMA (Uniform Memory Access) model: This model shares physical memory in a uniform way between the processors where all the processors have an even access time to all memory words.
- NUMA (Non-Uniform Memory Access) model: It can be considered as the shared memory multiprocessor only where the access time can vary regarding the location of the memory word. There are two variants of NUMA model.
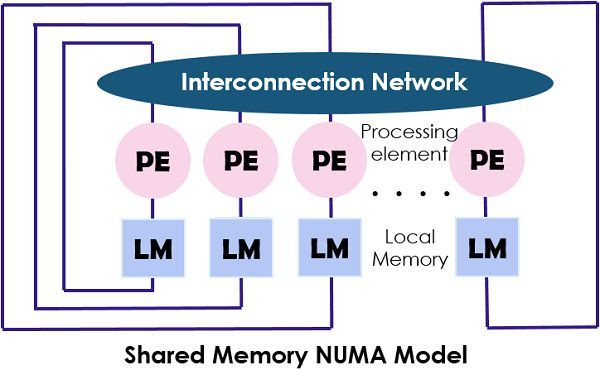 One is in which the shared memory is physically distributed to all Processing elements while in the other model uses shared memory in the multiprocessor system.
One is in which the shared memory is physically distributed to all Processing elements while in the other model uses shared memory in the multiprocessor system.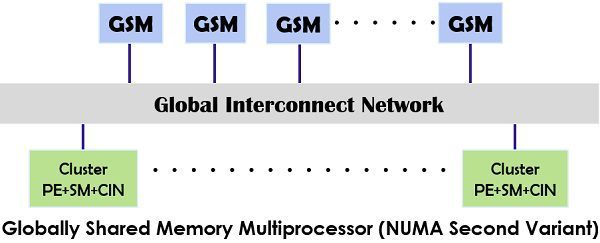
- COMA (Cache-Only Memory Architecture) model: This model is composed by the combination of multiprocessor and cache memory. It changes distributed memory into caches and is an exceptional case of NUMA. It lacks the use of the memory hierarchy, and global address space is made up of combining all the caches.
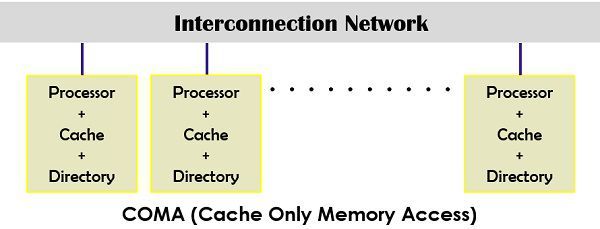
Definition of Multicomputer
Multicomputer are the computers where the processors can carry out separate instruction streams and have their own individual memory. These are not capable of accessing the other memories attached to other processors. Most of the multicomputers are the distinct memory machines made by linking nodes (where each node includes a microprocessor and some memory).
The NORMA model is based on multicomputers. NORMA stands for No-Remote Memory Access where multiple autonomous nodes containing a processor, local memory, linked disks and I/O peripherals communicates through passing messages instead of direct communication.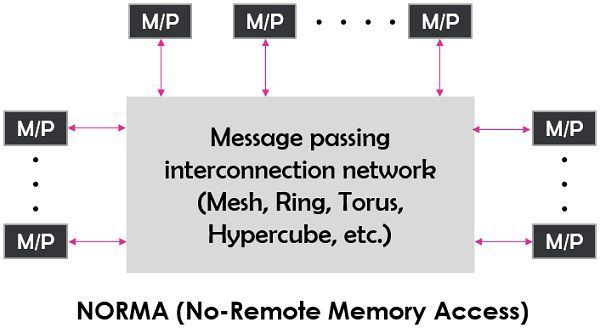
Key Differences Between Multiprocessor and Multicomputer
- Multiprocessor is a single computer in which many processors exist. As against, multicomputer has multiple autonomous computers.
- There are many processing elements are used in the multiprocessor but they do not have their private individual memories instead it shares a single memory. In contrast, multicomputer has several processing elements along with its own memory and I/O resources, rather than sharing the memory it implements the distributed memory.
- Multiprocessor model needs proper communication between the processing elements and memory for the effective allocation of resources. Contrariwise, there is no interaction between the processing elements and memory resources is required.
- Multiprocessors use a dynamic network in which the communication links can be rearranged by setting the active switching unit of the system. On the contrary, the multicomputer employs static network where the connection of switching units is fixed and determined by direct point-to-point connections.
- The microprocessor is referred to as the tightly coupled systems while multicomputer is known as loosely coupled systems.
Conclusion
The Multiprocessor and multicomputer are the types of parallel computers where the multiprocessor has numerous processing elements using shared memory. Conversely, in multicomputer various autonomous computers are connected with each other and have their own distributed memory.
Monika says
Great content…..
Mazia Yameen says
Excellent… well content
petrus says
extremely charming