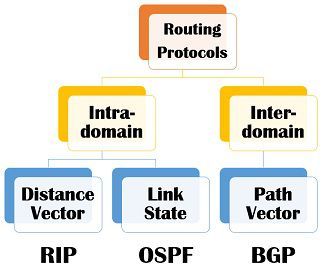
 The major difference between OSPF and BGP is that the OSPF is an intradomain routing protocol while BGP is the interdomain routing protocol. The OSPF protocol uses link state routing. On the other hand, BGP protocol uses path vector routing.
The major difference between OSPF and BGP is that the OSPF is an intradomain routing protocol while BGP is the interdomain routing protocol. The OSPF protocol uses link state routing. On the other hand, BGP protocol uses path vector routing.
The routing operations performed inside an autonomous system is known as intradomain routing or interior gateway routing and when the routing is performed between two autonomous systems, it is referred to as interdomain routing or exterior gateway routing. An autonomous system is a combination of networks and router which is controlled by single administration.
Content: OSPF Vs BGP
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | OSPF | BGP |
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Open Shortest Path First | Border Gateway Protocol |
| Gateway Protocol | OSPF is an internal gateway protocol | BGP is an external gateway protocol |
| Implementation | Easy to implement | Complex to implement |
| Convergence | Fast | Slow |
| Design | Hierarchical network possible | Meshed |
| Need of device resources | Memory and CPU Intensive | Scaling is better in BGP although it relies on the size of the routing table. |
| Size of the networks | Used on primarily smaller scale network which could be administered centrally. | Mostly used on large scale networks such as the internet. |
| Function | Fastest route is preferred over shortest. | Best path is determined for the datagram. |
| Algorithm Used | Dijkstra algorithm | Best path algorithm |
| Protocol | IP | TCP |
| Works on | Protocol number 89 | Port number 179 |
| Type | Link State | Path Vector |
Definition of OSPF
The Open Shortest Path First is an interior gateway protocol. The Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) working group formed to design an IGP based on Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to use it in the Internet Protocol networks. It uses link state routing. The OSPF was created because of the limitations of the RIP; RIP protocol had limited capability of serving large heterogeneous internetworks. OSPF is a link state routing which can operate within a hierarchy. The top level and largest entity in the hierarchy is the autonomous system. OSPF call to the routers within the hierarchical area for sending the link state advertisements.
OSPF allows various authentication schemes and every exchange within the routers need to be authenticated. The purpose of authentication is to permit the only authorized routers to advertise the routing information. The separate routes are calculated to a single destination based on HOP count and high throughput for each type of service. When a number of equal-cost routes exist to the destination, it performs load balancing where the traffic is distributed equally.
In OSPF the set of networks are grouped in a self-contained Area. An area hides its topology from the remaining autonomous system and from other areas also. This information hiding reduces the routing traffic. To distinguish the acquired information within the network (internal sources) from the information obtained from an outside router (external sources), the distinct message formats are used in OSPF.
The Area partitioning builds two distinct kinds of routing according to the source and the destination location in the network, and whether they present in the same area or different area. When the source and destination present in the same area it is known as intra-area routing and if the source and destination present in the different area it is referred to as inter-area routing.
Definition of BGP
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an external gateway protocol devised to exchange routing information for the Internet. By using an arbitrary topology, the BGP could connect any internetwork of autonomous systems. It just necessarily requires having at least one router at each autonomous system with the capability of running the BGP which must connect to at least one other autonomous system’s BGP router.
A BGP can manage a set of AS’s connected in any configuration such as full mesh, partial mesh, and also it can handle the changes that occur in the topology over time. The BGP system basically exchanges the network reachability information with other BGP systems and create graph of autonomous systems with the received reachability information at the BGP routers. The path vector routing mechanism is employed in the BGP systems because the distance vector routing and link state routing become intractable when the domain of the operation becomes large.
In path vector routing the router has the list of networks which can be reached with the path to reach each of them. It conserves network bandwidth and supports CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing). The BGP protocol does not have any information about what is happening inside an autonomous system and that a necessary prerequisite for an autonomous system. It has its own internal topology and chooses the routing protocols to determine the routes.
It is named as Border Gateway Protocol because in this a BGP router must communicate with a peer in another autonomous system usually which reside near the edge (border) of the autonomous system. This communication occurs when a pair of autonomous systems accepts to exchange the routing information and which involves the routers to become the BGP peers.
Key Differences Between OSPF and BGP
- The OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First whereas BGP expands to Border Gateway Protocol.
- OSPF is an Interior gateway routing protocol in which the routing operation is performed inside an autonomous system. On the other hand, the BGP is an Exterior gateway routing protocol which enables the routing operations to be performed between the two autonomous systems.
- OSPF is simple to employ while BGP is complex to implement.
- The time elapsed by a router takes to share and update the latest routing information is known as convergence. So, OSPF can achieve convergence by consuming less time. In contrast, the BGP has a slow convergence rate as compare to OSPF.
- The OSPF follows a hierarchical structure whereas BGP usually adopts mesh structure.
- OSPF requires intensive use of memory and CPU resources. As against, in BGP the need of device resources relies on the size of the routing table.
- BGP is more flexible and scalable than OSPF and used on a larger network, unlike OSPF.
- The primary objective of the OSPF is to determine the best route, i.e., fastest. Conversely BGP emphasizes on determining the best path.
- OSPF uses link state routing while BGP uses path vector routing.
Conclusion
The OSPF is an Interior gateway routing protocol while BGP is an exterior gateway routing protocol. The OSPF is based on the link state routing where each router sends the state of the neighbour router to every router present in the area. On the other hand, BGP is based on path vector routing where a router has a list of networks that can be reached with the path to reach each of them.
Nick says
Well done, very good article…..