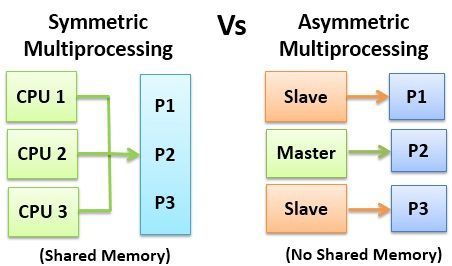
 There are two types of multiprocessing, Symmetric Multiprocessing and Asymmetric Multiprocessing. Multiprocessing system has more than one processor and they can execute multiple process simultaneously. In Symmetric Multiprocessing, processors shares the same memory. In Asymmetric Multiprocessing there is a one master processor that controls the data structure of the system.
There are two types of multiprocessing, Symmetric Multiprocessing and Asymmetric Multiprocessing. Multiprocessing system has more than one processor and they can execute multiple process simultaneously. In Symmetric Multiprocessing, processors shares the same memory. In Asymmetric Multiprocessing there is a one master processor that controls the data structure of the system.
The primary difference between Symmetric and Asymmetric Multiprocessing is that in Symmetric Multiprocessing all the processor in the system run tasks in OS. But, in Asymmetric Multiprocessing only the master processor run task in OS.
You can differentiate Symmetric Multiprocessor and Asymmetric Multiprocessor on some other points they are discussed in the comparison chart shown below.
Content: Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Multiprocessing
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Symmetric Multiprocessing | Asymmetric Multiprocessing |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Each processor run the tasks in Operating System. | Only Master processor run the tasks of Operating System. |
| Process | Processor takes processes from a common ready queue, or there may be a private ready queue for each processor. | Master processor assign processes to the slave processors, or they have some predefined processes. |
| Architecture | All processor in Symmetric Multiprocessing has the same architecture. | All processor in Asymmetric Multiprocessing may have same or different architecture. |
| Communication | All processors communicate with another processor by a shared memory. | Processors need not communicate as they are controlled by the master processor. |
| Failure | If a processor fails, the computing capacity of the system reduces. | If a master processor fails, a slave is turned to the master processor to continue the execution. If a slave processor fails, its task is switched to other processors. |
| Ease | Symmetric Multiprocessor is complex as all the processors need to be synchronized to maintain the load balance. | Asymmetric Multiprocessor is simple as master processor access the data structure. |
Definition of Symmetric Multiprocessing
Symmetric Multiprocessing is one in which all the processor run the tasks in the operating system. It has no master-slave relationship like asymmetric multiprocessing. All the processors here, communicate using the shared memory.
The processors start executing the processes from the common ready queue. Each processor may also have its own private queue of ready processes to get executed. It must be taken care by the scheduler that no two processors execute the same process.
Symmetric Multiprocessing has proper load balancing, better fault tolerance and also reduces the chance of CPU bottleneck. It is complex as the memory is shared among all the processors. In Symmetric Multiprocessing, a processor failure results in reduced computing capacity.
Definition of Asymmetric Multiprocessing
Asymmetric Multiprocessing has the master-slave relationship among the processors. There is one master processor that controls remaining slave processor. The master processor allots processes to slave processor, or they may have some predefined task to perform.
The master processor controls the data structure. The scheduling of processes, I/O processing and other system activities are controlled by the master processor.
In case a master processor fails, one processor among the slave processor is made the master processor to continue the execution. In case if a slave processor fails, the other slave processor take over its job. Asymmetric Multiprocessing is simple as there only one processor that is controlling data structure and all the activities in the system.
Key Differences Between Symmetric and Asymmetric Multiprocessing
- The most distinguishable point between symmetric and asymmetric multiprocessing is that the tasks in OS are handled only by the master processor in Asymmetric Multiprocessing. On the other hand, all the processors in symmetric multiprocessing run the tasks in OS.
- In symmetric multiprocessing, each processor may have its own private queue of ready processes, or they can take processes from a common ready queue. But, in asymmetric multiprocessing, master processor assigns processes to the slave processors.
- All the processor in Symmetric Multiprocessing has the same architecture. But the structure of processors in asymmetric multiprocessor may differ.
- Processors in symmetric multiprocessing communicate with each other by the shared memory. However, the processors in Asymmetric Multiprocessing need not to communicate with each other as they are controlled by the master processor.
- In case, the master processor fails, a slave processor is turned to master processor to continue the execution. But, if a processor in symmetric multiprocessing fails, the computing capacity of the system is reduced.
- Asymmetric Multiprocessor is simple as only master processor accesses the data structure whereas, symmetric multiprocessor is complex as all the processors need to work in synchronisation.
Conclusion
Multiprocessors increase the speed of the system, as one can execute multiple processes simultaneously. Asymmetric multiprocessing is simple, only one processor (master) can access the data structure. While Symmetric Multiprocessing is complex as the data structure is shared among all the processors and all the processor need to work in synchronization.
Toby says
thank you for your wisdom mam please give me more my teacher is bad.
Jack Markman says
nicely written.
Carolyn matuli says
Thanks a lot for the comprehensive explanation
Muazam Yar Mughal says
It is just amazing and nicely written by you.
Hassan Murtaza says
Thank You, Madam, it is really helpful to understand these overlapping concepts.
koti says
Thank You, Madam, it is really helpful to understand these overlapping concepts.
Seiko Santana says
When the master processor fails, will it crash the system?