 The prior difference between the holography and photography is that holography intends to form three-dimensional images while the photography generally generates two-dimensional images of a three-dimensional object.
The prior difference between the holography and photography is that holography intends to form three-dimensional images while the photography generally generates two-dimensional images of a three-dimensional object.
However, the creation of the images in both of the techniques is different where holography uses the interference of light between the reference beam and light reflected from the object. On the other hand, the photography makes use of photographic film on which the light gets incident after reflecting from an object. The formation of the image takes place because of the chemical reaction between the light and the chemically coated film.
Content: Holography Vs Photography
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Holography | Photography |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Generates a three-dimensional image | Creates a two-dimensional image |
| Mechanism | Interference of the light | Chemical reaction between the light and the film |
| Light source | Should be monochromatic and coherent | Any light source could be useful |
| Reconstruction of the image | Requires a small piece of a hologram | Needs the negative of the photograph |
| Each point includes | Light scattered from every point in the object | Light scattered from an individual point in the object |
| Viewing the image | From a wide-angle with the help of specific forms of illumination | Only a single view in a wide range of lighting conditions |
| Need for lens | Not required | Lens is required for focusing purpose |
| Information capacity | High | Low |
Definition of Holography
The holography is defined as the process of wave recording or method of recording optical images. It is a technique of creating ornate realities that look hyper-real. These are considered as the precise and indelible tracings of the real object or sometimes elaborate fakes also.
Dennis Gabor first introduced the term holography in 1947. Later, for inventing the three-dimensional lensless method of photography (i.e., holography), Gabor was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1971. The holography uses an interferometric technique where the phase of the light wave is recorded along with amplitude. The image that is recorded in the process is truly three-dimensional, which means that each distinct perspective of the image can be visualized by viewing the recorded image from different angles.
Holography basically performs two steps, the first step records holographic ‘photo’ with the help of the interference of light waves, while in the second step the object is reconstructed from the hologram by using diffraction of the light waves.
Formation of the hologram
There is a two-step process followed for constructing the holograms as mentioned above. In the first step, the object image is recorded on a photo plate. Recording occurs when photo plate is concomitantly exposed to coherent light of the wavelength same as the light coming from the object (object wave). The interference of the object wave and reference wave is recorded in the photographic plate, and this is called a hologram.
A hologram records the intensity variation along with the relative phases of the incoming light incident from different parts of the objects. It further stores the ‘depth’ to two-dimensional intensity; therefore, it is three dimensional.
When we expose this hologram to coherent light, the light gets diffracted, which produces a vivid three-dimensional image. The two processes are explained with the help of the diagrams shown below.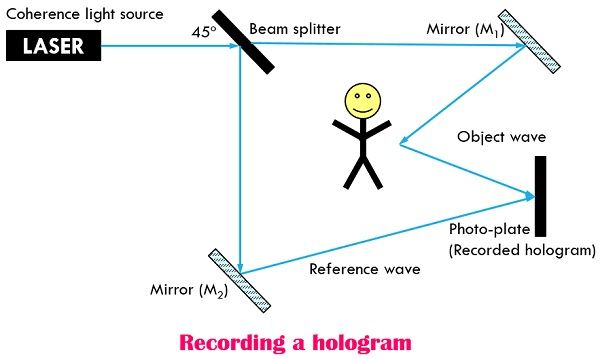
Here, the above-shown diagrams illustrate how a hologram is recorded where the object wave and reference wave are incident on the photo-plate and the interference patterns are recorded in it.
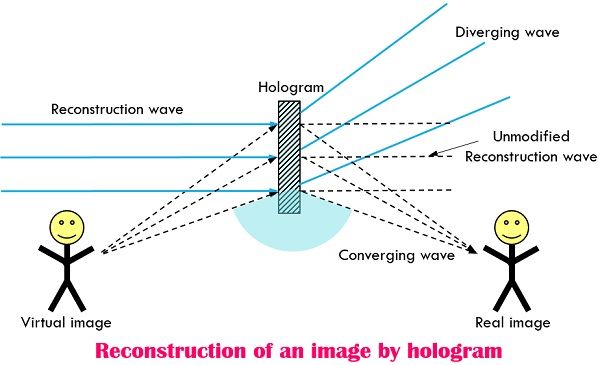
The above-given diagram demonstrates the reconstruction of an image by hologram where the diffraction of light produces converging and diverging beams and the converging beam constructs the real image.
Holography process is a combination of two stages recording and reconstruction, in the recording phase, the object is converted into a photographic record, and in the reconstruction phase, the object is transformed into an image. In a respective sense, the holography can be compared to a two-dimensional Fourier transforms where –
- Construction involves the interference of the object wave and reference wave.
- Reconstruction of the image is done by the diffraction of waves by the hologram.
Definition of Photography
Photography, on the contrary, is a two-dimensional image of the object having all three dimensions. It employs a lens system to focus the image on the photographic plate where only one plane is focused at a time, and remaining planes are out of focus. This is how three-dimensional articles are recorded in two dimensions.
A photograph records the light intensity distribution at the plane. The light-sensitive medium sense only the varying intensities, thus the phase distribution obtained at the plane of the photograph is lost. The recording of intensity distribution only of the scene in a photograph causes the loss of the three-dimensional element in the photograph. Therefore, in a photograph, the perspective of the image cannot be altered when viewed from different angles. It is also not possible to refocus the unfocussed parts of an image in a photograph.
Formation of the Photograph
The photograph is taken from a camera, which is fundamentally a light-proof housing that is comprised of a lens and light sensor. The camera includes an aperture to regulate the amount of light passing through the lens, a shutter to control the period of the exposure and type of viewfinder to frame the objects to be photographed.
In the early days, the size of the camera was quite large, and the light detector is a sensitized photographic plate. To create negative of an image, the plates are exposed and developed; then the negative is utilized to produce a positive contact print of precisely the same size. As the size of the photograph does not change, so the lenses are not tested rigorously, and the resulting print looks good in quality.
Key Differences Between Holography and Photography
- Holography uses interference and diffraction of light to produce a hologram. As against, in photography, the light reflected from the object strikes on the photographic film which is then reacted with the chemical coated over the film to create an image.
- A hologram records intensity in the interference pattern and phases of object wave concerning reference wave to create a 3D effect with vivid realism. In contrast, photograph stores the ordered arranged intensity (2D) pattern in a plane.
- Holography requires a monochromatic, coherent light source (i.e. laser) whereas photography does not need any special type of light source.
- The reconstruction of an image in the holography is easier and can be done with a small broken piece of the hologram. On the other hand, a photograph can not be constructed by its negative without the negative of a photograph; it is not possible to construct its original image.
- The process of recording an image is different in both of the techniques – holography and photography. In a photograph, every point of object pertains to a connected point in the image. While in a hologram all points of object pertain to each point of the hologram. Therefore, we can assume that in a photograph, there is one-to-one correlation whereas, in a hologram, the relation exists is one-to-all.
- A photograph can be of a single size, meaning that the during the reconstruction of the image by using negative the size of the photograph cannot be altered, but the size of the hologram can be changed.
- To capture a photograph, the lenses are required. Conversely, there is no use of lenses in holography.
- The information capacity of the hologram is larger than a photograph as it cannot superimpose multiple images, but a hologram could.
Conclusion
Holography and photography are different methods to produce 3D and 2D images, respectively, and both methods hold equal importance. Holography forms images that seem to be three-dimensional while photography results in the generation of two-dimensional photographs.
Leave a Reply