 RGB and CMYK are the colour models which provides an abstract numeric system for defining the colours with the help of three or four major numbers to show the primary colours. The fundamental difference between RGB and CMYK colour modes is that the number of channels contained by RGB is three. On the contrary, the CMYK model has four component colours.
RGB and CMYK are the colour models which provides an abstract numeric system for defining the colours with the help of three or four major numbers to show the primary colours. The fundamental difference between RGB and CMYK colour modes is that the number of channels contained by RGB is three. On the contrary, the CMYK model has four component colours.
The RGB expands to Red, Green and Blue while CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow) are the complements of the red, green and blue. Both of the colour modes can possibly produce the other colours present in a different colour model, in simple terms red, green and blue can be formed by changing the intensities of the CMYK colours. Similarly, CMYK colours can be produced used in RGB colours.
Content: RGB Vs CMYK
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | RGB | CMYK |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Additive color model | Substractive color model |
| Application | Employed in computer displays and web graphics | Used as printing material |
| Make use of | Light | Ink |
| Mechanism involved | Transmission of light | Reflection of light |
| Contains | Red+Green+Blue=White | Cyan+Magenta+Yellow=Black |
| Size of the file | Smaller | Larger |
Definition of RGB
RGB colour model is the most prevalently used additive type of colour model in computer graphics. It specifies Red, Green and Blue components of the colours which are capable of producing a wide variety of colours by adding the different intensities of Red, Green and Blue colour. By adding full intensities of Red, Green and Blue, we get the white colour and black colour if none of them are present. Furthermore, if the intensities of RGB colour is equal, then the colour it produces is grey (i.e., Shade of the colour will be between black and white).
Representation
In order to represent the RGB colour model, we can use the three axes in which each is assigned to one of the axes. The cube shown in the below-given figure is capable of illustrating all of the colours present in an RGB system. If the value of the Blue is 0, the lower face of the cube will have varying shades of black, green, red and yellow. Similarly, when the value of red is 1, the front right face contains the varying shades of red, yellow, magenta and white.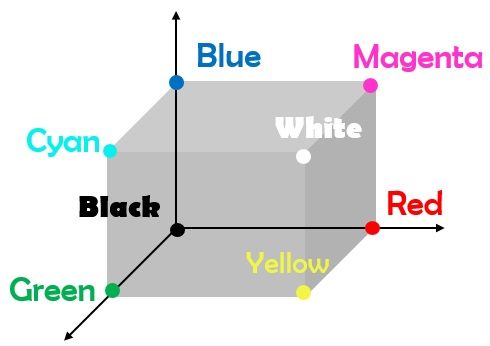
Application
Adding all colours of full intensity in RGB creates white light which means all the light is transmitted back to the eye. These additive colours are mainly employed for lighting, video and monitors. For example, the colours in LCD monitors are produced when the emitted light is passed through the red, green and blue filters.
Definition of CMYK
The CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and K for Black) model is just inverse of the RGB model. This model is subtractive in nature. The subtractive model is expressed by the fact that the more it adds the colour, the more colour will be subtracted from the white. Therefore, if none of the CMYK colour is present the resulting colour is white, but if all the CMYK colours exist at their fullest intensities, then it produces a black. However, by adding the equal intensities of each colour, the shades of grey can be generated.
Representation
The below-given diagram shows how the CMYK colour model can be represented and the relationship between the RGB and CMYK. So, in the RGB cube, the opposite edges of the cube represent the colours cyan, magenta and yellow.
Application
This model works by the light-absorbing property of ink printed on the paper. In this mechanism, when the white light hits the semi-transparent ink, some portion of the spectrum is absorbed while the other portion is reflected back to your eyes. Theoretically, the full intensity of these colours (cyan(C), magenta(M) and Yellow(Y)) pigments must be mixed to absorb all colour and generate black. Due to this reason, these are known as subtractive colours. Although, all printing inks have a tiny amount of impurities causing the produced colour to be muddy brown. So, these are must be combined with the black ink to create a denser black colour.
In the CMYK model, we use k to identify black colour to circumvent the confusion with blue colour. The colours in the CMYK model is used for reproducing the various colours by combining these inks, and this is referred to as four-colour-process printing.
Key Differences Between RGB and CMYK
- RGB colour model is known as the additive model because these colours produce a brighter outcome when added with light. Conversely, CMYK is a subtractive model where we begin with the white sheet of paper, and for getting the dark result, you need to add more ink to it.
- The RGB model is mainly implemented in the display monitors for generating various colours. In contrast, CMYK is utilized in printing material majorly.
- In the RGB model, the light is used for changing the produced colour intensity. On the contrary, in CMYK model uses ink for altering the colour intensity.
- By adding the RGB colours, the white colour is generated while the addition of CMYK colours produces a black colour.
- There is a straightforward relationship between the additive and the subtractive colour. To represent this in an additive system we can consider the creation of the colours by mixing them such as the yellow colour is produced by combining red and green light. As against, in the subtractive system, the yellow colour is generated due to the subtraction of blue colour from the white light.
- The RGB model helps in operating the tasks at a higher speed and consumes less memory space (file size is smaller) as compared to the CMYK model.
Conclusion
The two-colour models RGB and CMYK works better for the intended applications such as RGB is good for displaying colours on the display devices used red, green and blue light. On the other hand, CMYK (Cyan, Magenta and Yellow) is good for the printing ink as they work entirely inversely to the monitors. However, the RGB colour range (i.e. gamut) is more extensive than the CMYK.
shiran nandasena says
very good