 The major difference between Array and Linked list regards to their structure. Arrays are index based data structure where each element associated with an index. On the other hand, Linked list relies on references where each node consists of the data and the references to the previous and next element.
The major difference between Array and Linked list regards to their structure. Arrays are index based data structure where each element associated with an index. On the other hand, Linked list relies on references where each node consists of the data and the references to the previous and next element.
Basically, an array is a set of similar data objects stored in sequential memory locations under a common heading or a variable name.
While a linked list is a data structure which contains a sequence of the elements where each element is linked to its next element. There are two fields in an element of linked list. One is Data field, and other is link field, Data field contains the actual value to be stored and processed. Furthermore, the link field holds the address of the next data item in the linked list. The address used to access a particular node is known as a pointer.
Another significant difference between an array and linked list is that Array has a fixed size and required to be declared prior, but Linked List is not restricted to size and expand and contract during execution.
Content: Array Vs Linked List
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Array | Linked list |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | It is a consistent set of a fixed number of data items. | It is an ordered set comprising a variable number of data items. |
| Size | Specified during declaration. | No need to specify; grow and shrink during execution. |
| Storage Allocation | Element location is allocated during compile time. | Element position is assigned during run time. |
| Order of the elements | Stored consecutively | Stored randomly |
| Accessing the element | Direct or randomly accessed, i.e., Specify the array index or subscript. | Sequentially accessed, i.e., Traverse starting from the first node in the list by the pointer. |
| Insertion and deletion of element | Slow relatively as shifting is required. | Easier, fast and efficient. |
| Searching | Binary search and linear search | linear search |
| Memory required | less | More |
| Memory Utilization | Ineffective | Efficient |
Definition of Array
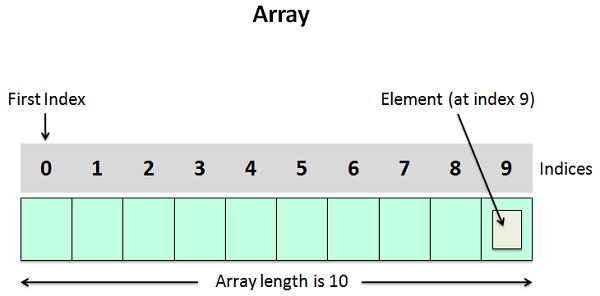
An array is defined as a set of a definite number of homogeneous elements or data items. It means an array can contain one type of data only, either all integers, all floating-point numbers, or all characters. Declaration of an array is as follows:
int a [10];
Where int specifies the data type or type elements array stores. “a” is the name of an array, and the number specified inside the square brackets is the number of elements an array can store, this is also called size or length of the array.
Points to Ponder
Let us look at some of the concepts to be remembered about arrays:
- The individual elements of an array can be accessed by describing the name of the array, followed by index or subscript (determining the location of the element in the array) inside the square brackets. For example, to retrieve 5th element of the array, we need to write a statement a[4].
- In any case the elements of an array will be stored in a consecutive memory location.
- The very first element of the array has index zero [0]. It means the first and last element will be specified as a[0], and a[9] respectively.
- The number of elements that can be stored in an array, i.e., the size of an array or its length is given by the following equation:
(upper bound-lower bound) + 1
For the above array, it would be (9-0) + 1 =10. Where 0 is the lower bound of the array, and 9 is the upper bound of the array. - Arrays can be read or written through the loop. If we read the one-dimensional array, it requires one loop for reading and other for writing (printing) the array, for example:
a. For reading an array
for ( i= 0; i <= 9; i++)
{ scanf ( “%d”, &a[ i ] ) ; }
b. For writing an array
for (i = 0 ; i <= 9 ; i++)
{printf ( “%d”, a[ i ] ) ; } - In the case of a 2-D array, it would require two loops and similarly n-dimensional array would need n loops.
Operations performed on arrays
- Creation of array
- Traversing an array
- Insertion of new elements
- Deletion of required elements.
- Modification of an element.
- Merging of arrays
Example
The following program illustrates the reading and writing of the array.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main ()
{
int a[10],i;
printf("Enter the array");
for ( i= 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
scanf ( "%d", &a[ i ] ) ;
}
printf( "Enter the array" );
for (i = 0 ; i <= 9 ; i++)
{
printf ( "%d\n", a[ i ] ) ;
}
getch ();
}
Definition of Linked List
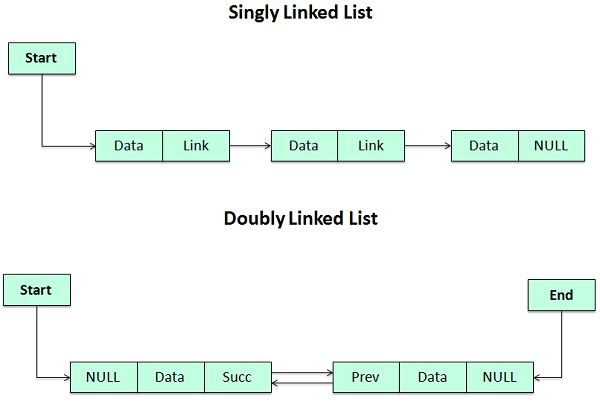
Linked list is a particular list of some data elements linked to one other. In this every element point to the next element which represents the logical ordering. Each element is called a node, which has two parts.
INFO part which stores the information and POINTER which points to the next element. As you know for storing address, we have a unique data structures in C called pointers. Hence the second field of the list must be a pointer type.
Types of linked lists are Singly-linked list, Doubly linked list, Circular linked list, Circular double linked list.
Operations performed on Linked List
- Creation
- Traversing
- Insertion
- Deletion
- Searching
- Concatenation
- Display
Example
The following snippet illustrates the creation of a linked list:
struct node
{
int num;
stuct node *next;
}
start = NULL;
void create()
{
typedef struct node NODE;
NODE *p, *q;
char choice;
first = NULL;
do
{
p = (NODE *) malloc (sizeof (NODE));
printf ("Enter the data item\n");
scanf ("%d", & p -> num);
if (p == NULL)
{
q = start;
while (q -> next ! = NULL)
{ q = q -> next
}
p -> next = q -> next;
q -> = p;
}
else
{
p -> next = start;
start = p;
}
printf ("Do you want to continue (type y or n) ? \n");
scanf ("%c", &choice) ;
}
while ((choice == 'y') || (choice == 'Y'));
}
Key Differences Between Array and Linked List
- An array is the data structure contains a collection of similar type data elements whereas the Linked list is considered as non-primitive data structure contains a collection of unordered linked elements known as nodes.
- In the array the elements belong to indexes, i.e., if you want to get into the fourth element you have to write the variable name with its index or location within the square bracket.
In a linked list though, you have to start from the head and work your way through until you get to the fourth element. - While accessing an element array is fast while Linked list takes linear time so, it is quite bit slower.
- Operations like insertion and deletion in arrays consume a lot of time. On the other hand, the performance of these operations in Linked lists is fast.
- Arrays are of fixed size. In contrast, Linked lists are dynamic and flexible and can expand and contract its size.
- In an array, memory is assigned during compile time while in a Linked list it is allocated during execution or runtime.
- Elements are stored consecutively in arrays whereas it is stored randomly in Linked lists.
- The requirement of memory is less due to actual data being stored within the index in the array. As against, there is a need for more memory in Linked Lists due to storage of additional next and previous referencing elements.
- In addition memory utilization is inefficient in the array. Conversely, memory utilization is efficient in the array.
Conclusion
Array and Linked lists are the types of data structures differ in their structure, accessing and manipulation methods, memory requirement and utilization. And have particular advantage and disadvantage over its implementation. Consequently, either one can be used as per need.
Akshau says
Good explanation
Shaik Ismail says
Thanks
zain says
nice definitions…
Supritha r gurlhosur says
Thanks for the information..
Supritha r gurlhosur says
Thank you
Surendranatha Reddy Chappidi says
good article
asnad ali says
your information is helping me in study thanks
anam naz says
very helpful thanks a lot
Jayakanth says
Nice
Jose says
Super clear!
suri babu kalla says
Thank you for helping me and also continue your work in this way…
Pokiya Jatin says
Thank you
Tapironte Crepuscolare says
Very well explained!
Dharani says
Good explanation