 DES (Data Encryption Standard) and AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) both are the symmetric block cipher. AES was introduced to overcome the drawback of DES. As DES has a smaller key size which makes it less secure to overcome this triple DES was introduced but it turns out to be slower. Hence, later AES was introduced by the National Institute of Standard and Technology.
DES (Data Encryption Standard) and AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) both are the symmetric block cipher. AES was introduced to overcome the drawback of DES. As DES has a smaller key size which makes it less secure to overcome this triple DES was introduced but it turns out to be slower. Hence, later AES was introduced by the National Institute of Standard and Technology.
The basic difference between DES and AES is that in DES plaintext block is divided into two halves before the main algorithm starts whereas, in AES the entire block is processed to obtain the ciphertext.
Let us discuss some more differences between DES and AES with the help of the comparison chart shown below.
Content: DES Vs AES
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | DES (Data Encryption Standard) | AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | In DES the data block is divided into two halves. | In AES the entire data block is processed as a single matrix. |
| Principle | DES work on Feistel Cipher structure. | AES works on Substitution and Permutation Principle. |
| Plaintext | Plaintext is of 64 bits | Plaintext can be of 128,192, or 256 bits |
| Key size | DES in comparison to AES has smaller key size. | AES has larger key size as compared to DES. |
| Rounds | 16 rounds | 10 rounds for 128-bit algo 12 rounds for 192-bit algo 14 rounds for 256-bit algo |
| Rounds Names | Expansion Permutation, Xor, S-box, P-box, Xor and Swap. | Subbytes, Shiftrows, Mix columns, Addroundkeys. |
| Security | DES has a smaller key which is less secure. | AES has large secret key comparatively hence, more secure. |
| Speed | DES is comparatively slower. | AES is faster. |
Definition of DES (Data Encryption Standard)
Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a symmetric key block cipher that was adopted by National Institute of Standard and Technology in the year 1977. DES is based on the Feistel structure where the plaintext is divided into two halves. DES takes input as 64-bit plain text and 56-bit key to produce 64-bit Ciphertext.
In the figure below you can see the encryption of plaintext using DES. Initially, the 64-bit plaintext undergoes initial permutation which rearranges the bits to get 64-bit permuted input. Now this 64 bit permuted input is divided into two halves i.e. 32-bit left portion and 32-bit right portion. Both this portion undergoes sixteen rounds where each round follows the same functions. After completion of sixteen rounds, final permutation is done, and the 64-bit ciphertext is obtained.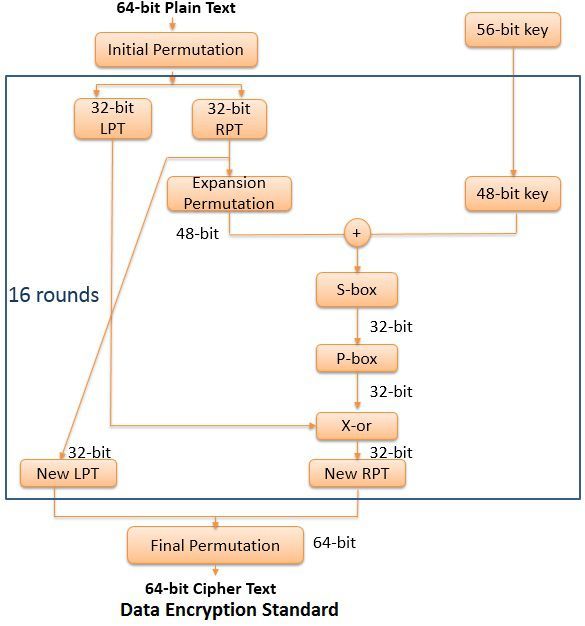 Each round contains following functions:
Each round contains following functions:
- Expansion Permutation: Here the 32-bit right portion is expanded to form 48-bit right portion.
- Xor: The 48-bit right portion is Xor with 48-bit subkey obtained from the 56-bit key, which results in the 48-bit output.
- S-box: The 48-bit output obtained by Xor step is reduced to 32 bit again.
- P-box: Here the 32-bit result obtained from S-box is again permuted, which result in 32-bit permuted output.
Definition of AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is also a symmetric key block cipher. AES was published in 2001 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. AES was introduced to replace DES as DES uses very small cipher key and the algorithm was quite slower.
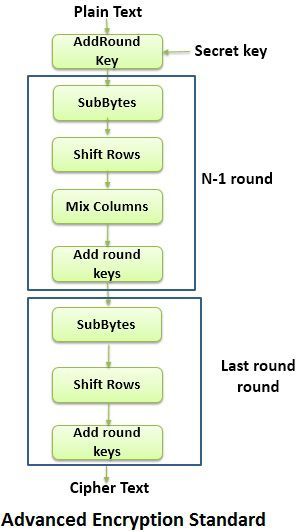 AES algorithm takes 128-bit plaintext and 128-bit secret key which together forms a 128-bit block which is depicted as 4 X 4 square matrix. This 4 X 4 square matrix undergoes an initial transformation. This step is followed by the 10 rounds. Among which 9 round contain following stages:
AES algorithm takes 128-bit plaintext and 128-bit secret key which together forms a 128-bit block which is depicted as 4 X 4 square matrix. This 4 X 4 square matrix undergoes an initial transformation. This step is followed by the 10 rounds. Among which 9 round contain following stages:
- Subbytes: It uses S-box by which it performs byte by byte substitution of the entire block (matrix).
- Shift Rows: Rows of the matrix are shifted.
- Mix Columns: Columns are of the matrix are shuffled from right to left.
- Add round keys: Here, the Xor of the current block and the expanded key is performed.
And the last 10th round involves Subbytes, Shift Rows, and Add round keys stages only and provides 16 bytes (128-bit) ciphertext.
Key Differences Between DES and AES
- The basic difference between DES and AES is that the block in DES is divided into two halves before further processing whereas, in AES entire block is processed to obtain ciphertext.
- The DES algorithm works on the Feistel Cipher principle, and the AES algorithm works on substitution and permutation principle.
- The key size of DES is 56 bit which is comparatively smaller than AES which has 128,192, or 256-bit secret key.
- The rounds in DES include Expansion Permutation, Xor, S-box, P-box, Xor and Swap. On the other hands, rounds in AES include Subbytes, Shiftrows, Mix columns, Addroundkeys.
- DES is less secure than AES because of the small key size.
- AES is comparatively faster than DES.
Conclusion
DES is the older algorithm and AES is the advanced algorithm which is faster and more secure than DES.
Pushpanjali says
This is the best website which actually gives satisfied answer to my question.
marjan says
That’s very useful !
Rinchen says
This website enlighten my knowledge. Got what i needed and clear my doubt but no author(s)? Thanks