 WiFi and Ethernet are networking technologies that allow multiple devices to connect to the network and access the Internet simultaneously. Though both technologies connect you to a network or the Internet, they differ in many ways. WiFi is wireless technology, whereas Ethernet is wired technology.
WiFi and Ethernet are networking technologies that allow multiple devices to connect to the network and access the Internet simultaneously. Though both technologies connect you to a network or the Internet, they differ in many ways. WiFi is wireless technology, whereas Ethernet is wired technology.
WiFi offers mobility to its user as there is a wireless transmission. On the other hand, Ethernet offers fast and secure access to the Internet. We will discuss these techniques in detail and their differences, so let’s start.
Content: WiFi and Ethernet
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | WiFi | Ethernet |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | It is a wireless connection to the network and the Internet | It is a wired connection to the network and the Internet |
| Speed | Comparatively Smaller | Faster |
| Security | Comparatively less secure | More secure |
| Reliability | Less reliable | More secure |
| Data Size | Inadequate to upload or download files with large data size | Capable of uploading and downloading a file with a large data size |
| Mobility | Offers mobility | Restrict mobility |
| Standard | Wireless LAN IEEE 802.11 | Wired LAN IEEE 802.3 |
What is WiFi?
WiFi is a short form for ‘Wireless Fidelity’, a wireless networking technology that we use to connect various communication devices. These devices are computers (desktops and laptops), mobile devices (smartphones and tabs) and other electronic devices (printers, CCTVs). WiFi allows these devices to exchange information with one another and also allows them to access the Internet.
Now you might be thinking about how WiFi connects devices in a wireless medium. Well, for this, the devices must have short-range radio transmitters and receivers, allowing them to send and receive the information.
WiFi is standard for wireless LAN, which we call IEEE 802.11. The basic motive behind the development of WiFi was that – a user should be able to walk into the WiFi-enabled premises and easily connect his devices to the Internet. But there were compatibility issues between the two connecting devices. It was like a device with a brand X radio transmitter and receiver that could not work within a Wi-Fi-enabled space with a brand Y base station.
So, there was a requirement to standardize the wireless networking technology, and the task was given to the IEEE committee, which already has a standard for the wired LAN, i.e. IEEE 802.3. This is how WiFi which is wireless LAN standard IEEE 802.11, came into existence.

Now, we know that a wireless medium device communicates using radio waves, which should be of a certain frequency.
What should be the frequency of WiFi?
IEEE 802.11 operates on an unlicensed frequency spectrum defined by ITU-R (e.g., 902-928 MHz, 2.4-2.5 GHz, 5.725-5.825 GHz) with certain limitations. The devices should restrict their transmit power so that other devices in the same space can operate.
The frequency of these radio waves is measured in gigahertz. The router emits radio waves at the speed of 2.5 to 5 Gigahertz per sec. The radio waves at 5 gigahertz per sec deliver the information faster over a shorter distance. However, the radio waves at 2.5 gigahertz per sec cover a farther distance but at a slower rate.
Knowing this much let us learn the working of WiFi.
How Does WiFi Works?
A WiFi network is made up of several clients (devices that want to access the Internet), a router and a modem. On one end, the modem is connected to the Internet through a wired medium. At the other end, the modem is connected to the router. We refer to the router as Access Point (AP) or base station.

So, to create a WiFi-enabled zone, we establish an access point that, on one end, is connected to the Internet via a modem. At the other end, to create a network, it emits radio waves that are broadcasted in your space. The clients enabled with the short-range radio transmitter and receiver access these broadcasted signals to connect themselves to the Internet.
To experience the best quality communication, ensure you are within the range of access points. The communication quality will fade as your range from the access point exceeds.
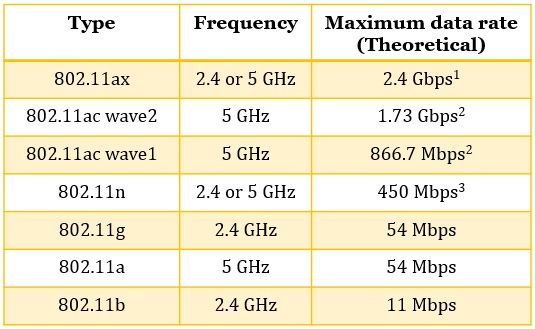
Types of WiFi
The WiFi technology can be classified on the basis frequency band they use. The table below describes the frequency each WiFi version uses and the speed offered by each version.
Advantages and Disadvantages of WiFi
Advantages
- WiFi technology increases your accessibility to the Internet, so you are rarely out of touch. Thus, increasing your availability.
- It increases flexibility – for example, in a Wi-Fi-enabled office, an employee can connect their device to the network from any corner of the office building.
- As the network requires the least infrastructure for connecting the user to the network, it is cost-efficient.
- WiFi technology allows companies to offer new services to their customers.
Disadvantages
- Being a wireless networking technology, WiFi is always prone to interference by other electronic devices and physical objects.
- WiFi is more prone to attacks as there is a wireless data transmission.
- Parameters such as interference from devices or physical objects effects transmission speed.
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet is a wired networking technology that we use to connect several devices in a network or the Internet. We use Ethernet to form wired LAN or WAN networks.
Ethernet uses Carrier Sensing Multiple Access/Collision Detection, i.e. CSMA/CD access control method that limits the connected system from accessing the physical resources available in the network.
Now that Ethernet is a wired networking technology, what kind of wires or cables does it use to connect the devices?
Mainly we use three types of ethernet cables:
- Coaxial cables
- Twisted pair cables
- Fibre optic cables
How Does Ethernet Work?
Ethernet is a wired networking technology, so whatever information has to be exchanged between the sender and receiver would be a wired transmission. Thus, here the information is divided into frames; this frame has required information for transmissions, such as the sender’s and receiver’s addresses. This information helps the routers route the frames through the network.
Now, as all the computers in LAN share a single connection then, there is a maximum chance of a collision. Thus, Ethernet uses an access control protocol CSMA/CD, i.e. carrier-sense multiple access collision detections. The CSMA /CD protocol ensures that if a computer in the network wants to send data, then the shared connection is free, and no other computer is accessing the link.
But this was the scene earlier; nowadays, every device has a private connection to the network through a switch or node. Now the Ethernet operates on a full duplex mode which makes separate channels for sending and receiving devices, thus avoiding any collision.
However, even if the collision occurs, the Ethernet do not have any error correction or detection method, and the frames rely on advanced protocols to determine and correct the errors.
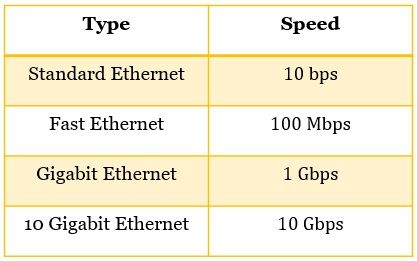
Types of Ethernet
Ethernet has evolved through four generations. So we can classify them into four types. The table below shows you the four different types of Etherent along with the speed they provide:
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ethernet
Advantages
- Ethernet provides a wired internet connection, so there are few chances of interference.
- With Ethernet you can easily achieve Internet speed upto 10 Gbps.
- Etherent is more secure as it is hard to intercept the Ethernet network.
- Ethernet is a reliable medium to connect your device to Internet.
Disadvantages
- Etherent restricts mobility to its users.
- If you want to expand the the network you need to expend more .
- Installation is quite complex as it involves lots of wires.
Key Differences Between WiFi and Ethernet
- WiFi is a wireless connection to a network or the Internet. On the other hand, Ethernet is a wired connection to a network or the Internet.
- As WiFi is a wireless connection to the Internet, it may face interference from other devices or physical objects, which hampers its speed, although the maximum WiFi speed is 700 Mbps. On the contrary, Ethernet is a wired connection to the Internet. Thus, there are fewer chances of any interference. However, it offers a speed of 10 Gbps.
- The Ethernet is much more secure than WiFi because any device that wants to interfere with the wired network must be physically connected to the network. While in a WiFi network, the data navigate to the access point through the air so it can be easily intercepted.
- WiFi is prone to interference from electrical devices and other physical objects, making it less reliable. On the other hand, in Ethernet, the entire network is formed using insulated cables, so there are fewer chances of interference due to other devices or any physical object; thus, it is more reliable.
- Ethernet has a greater bandwidth as compared to WiFi. So, with Ethernet, you can transmit large files and stream video with lower latency and faster data rate.
- When it comes to convenience, of course, WiFi is more convenient as compared to Ethernet as it offers mobility to its user.
- WiFi is a standard for wireless LAN, i.e. IEEE 802.11. However, Ethernet is a standard for wired LAN, i.e. IEEE 802.3.
Conclusion
WiFi and Ethernet offer you a connection to a network or the Internet, but they differ in many ways. We have discussed the maximum possible ways in which they differ. However, if you want a better speed or you want to upload large files or stream videos, then you can go for the Ethernet. But, Ethernet restricts your mobility. While WiFi offers mobility to users who want to connect their device to a network or the Internet.
Leave a Reply