 Bluetooth and Wifi provide wireless communication and uses radio signals for doing so. The main difference between Bluetooth and Wifi is the purpose behind its designing. Bluetooth is essentially used to connect short-range devices for sharing data while Wifi provides high-speed internet access.
Bluetooth and Wifi provide wireless communication and uses radio signals for doing so. The main difference between Bluetooth and Wifi is the purpose behind its designing. Bluetooth is essentially used to connect short-range devices for sharing data while Wifi provides high-speed internet access.
Another difference between Bluetooth and Wifi is that limited number of devices have provision to connect with other devices in Bluetooth. On the other hand, Wifi provides access to more number of users.
Bluetooth is used when speed is not our concern and low bandwidth is allocated to it. Wifi provides high bandwidth as the speed of internet is an important factor.
Content: Bluetooth Vs Wifi
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Bluetooth | Wifi |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | Low | High |
| Hardware requirement | Bluetooth adapter on all the devices connecting with each other. | Wireless adapter on all the devices of the network and a wireless router. |
| Ease of Use | Fairly simple to use and switching between devices is easier. | It is more complex and requires configuration of hardware and software. |
| Range | 10 meters | 100 meters |
| Security | Less secure comparatively | Security features are better. Still, there are some risks. |
| Power consumption | Low | High |
| Frequency range | 2.400 GHz and 2.483 GHz | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz |
| Flexibility | Supports limited number of user | It provides support for a large number of users |
| Modulation techniques | GFSK (Gaussian frequency shift keying) | OFDM (Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) and QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) |
Definition of Bluetooth
Bluetooth is an open specification (universal) for short-range wireless voice and data communications. Inventors of Bluetooth are Ericsson, Nokia, IBM, Toshiba and Intel formed a Special Internet Group (SIG) to expand the concept and to develop a standard under IEEE 802.15 WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network).
Bluetooth is the first widespread technology for a short-range ad-hoc network that is designed for combined voice and data application. Compared with Wifi, Bluetooth has a reduced data rate. However, it has an embedded mechanism to assist the application. Bluetooth is inexpensive personal area ad-hoc network operating in unlicensed lands and owned by the user.
Bluetooth SIG involves three applications based scenario
- Cable replacement
- Ad-hoc personal network
- Integrated Access Points (APs) for data/voice.
Overall Architecture
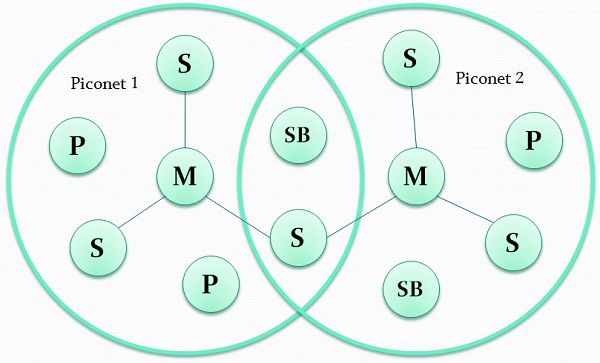
Bluetooth topology is referred to as a scattered ad-hoc topology. It defines a small cell called Piconet which is a collection of devices connected in an ad-hoc fashion.
There are four states
- M(Master): It can manage seven concurrent and up to 200 active slaves in the piconet.
- S(Slave): Terminals which can take part in more than one piconet.
- SB(Stand by): Waiting to join the piconet later meanwhile retaining its MAC address in it.
- P(Parked/hold): Waiting to adhere to the piconet later and releases its MAC address.
 Physical connection
Physical connection
The FHSS (frequency hopping spread spectrum) modem is utilized in the physical connection of the Bluetooth with a nominal antenna power of 0 dBm(10 m coverage) and alternately operated at 20 dBm(100 m coverage). Bluetooth hopping rate is 1600 hops/second. Bluetooth allocates a specific frequency- hopping format for each piconet.
Connection management
The connection establishment in Bluetooth has two phases- Inquiry, page and connection. Active devices are allocated a 3 bit AMA (Active Member Address), Parked devices are assigned an 8-bit PMA (Parked Member Address), Standby devices do not need an address.
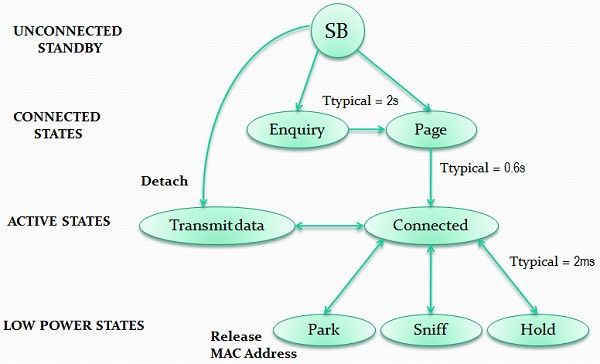
- Sniff State: Slaves listens to the piconet at minimized rates.
- Hold state: Slave stops ACL (Asynchronous Connection Less) transmission but can exchange SCO (Synchronous Connection Oriented) packets.
- Park state: Slave releases its AMA.
- Page state: AMA is assigned (becomes master).
- Connected state: Listen, transmit and receive.
- Standby state: Listen periodically.
- Inquiry state: To discover what other devices are out there.
Security
Bluetooth offers usage security and information confidentiality. It uses a 128 bit long random number, 48-bit MAC address of the device and two keys – Authentication (128 bits) and Encryption (8 to 128 bits). Three modes of operation are non-secure, service level and link level.
Definition of Wifi
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) is the name given by the Wi-Fi Alliance to the IEEE 802.11 suite of standards. 802.11 defined the initial standard for wireless local area networks (WLANs), IEEE specifications are wireless standards that define an interface which uses are as the medium for transmitting and receiving signals between a wireless client and a station or access point, as well as among wireless clients.
The aim of the 802.11 standards was to develop a MAC and PHY layer for wireless connectivity for permanent, portable and mobile stations inside a local area.
IEEE 802.11 standard involves the following special features –
- It provides asynchronous and time-bounded delivery facility.
- It supports continuity of service within extended areas via distribution system.
Requirements of IEEE 802.11
- Single MAC is supporting multiple PHYs’.
- Mechanisms to allow multiple overlapping networks in the same area.
- Provisions to manage the interface from other ISM based radios and microwave oven.
- Mechanisms to manage “hidden” terminal.
- Options to support time-bounded services.
- Provision to handle privacy and access security.
Reference Architecture
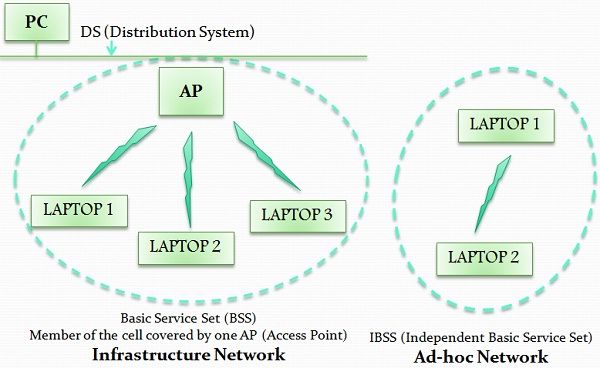
There are two operations models or topologies defined in IEEE 802.11-
- Infrastructure mod: In this mode, the wireless network comprises of minimum one access point (AP) which is generally linked to the wired network infrastructure and a collection of the wireless end station. Access controls encryption on the network and may bridge or route the wireless traffic to a wired ethernet network (or internet).
- Ad- hoc mode: In this mode, multiple 802.11 wireless stations interact directly with each other in the absence of an access point or any connection to a wired network. It is also called independent Basic service set (IBSS) or a peer-to-peer mode.
Security
IEEE 802.11 has provisions for authentication and privacy. Two types of authentication supported by IEEE 802.11 are-
- Open system authentication: Default authentication scheme. The request frame sends the authentication algorithm ID for an open system. The response time sends the results of the request.
- Shared Key authentication: It provides a greater amount of security. The request frame carries the authentication frames ID for the shared key using a 40-bit secret code that is shared between itself and IP. The 2nd station sends a challenge text of 128 bytes. The 1st station sends encrypted text as a response. The 2nd station sends authentication results.
Privacy is maintained in IEEE 802.11 by WEP(wired equivalent privacy) specification. A key sequence is constructed by a pseudorandom generator and 40-bit secret key where the key sequence is simply an XOR-ed with the plain-text message.
Key Differences Between Bluetooth and Wifi
- Bandwidth requirement is low in Bluetooth whereas it is high in case of Wifi.
- For connection establishment, through Bluetooth, a device would require Bluetooth adapter. On the other hand, for using Wifi devices require wireless adapter and router.
- Bluetooth is simple to use and switching between devices is easier while Wifi technology is kind of complicated and requires configuration of hardware and software.
- The radio signal range provided by Bluetooth is 10 meters while it is 100 meters in case of Wifi.
- Frequency range along which Bluetooth devices are supported is 2.4 GHz and 2.483 GHz. On the contrary, in Wifi the frequency range is 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
- Power consumption is low in Bluetooth, while it is high in Wifi.
- Bluetooth is less secure as compared to Wifi and uses encryption and authentication keys. In contrast, Wifi has better security, although still there are some security issues. Wifi uses WEP (Wired Equivalency Privacy) and WPA (Wifi Protected Access).
Conclusion
Bluetooth and Wifi, both technologies were invented in order to enable wireless communication between the various devices. Although both has different purposes, has their relative advantages and disadvantages.
Basically, Bluetooth considered as short distance wireless communication while Wifi provides more privileges and long range, large number of users and cost effective way to connect to internet.
Rosered says
It is clarifying all the differences between wifi and Bluetooth.
Kay says
Great article. I was interested in the basics of WIFI and Bluetooth and kept getting confused.
I have read a lot about EMR coming from these devices and wanted to know what frequencies they operated on.
Now I get it. Thank you.
Eric says
Clear and concise.
Thank you
Jack Delang says
good article, it cleared my all doubts.
Arnold says
It’s a wonderful website….
Reza says
Thank you, it was the best article I’ve read comparing these two technologies
Muhammad Sabir says
Really good, with concise and clearly mentioned difference between these two technologies. Well done.
Frado says
wow easy to understand and straight to the point. also the way the work is presented is perfect