 We used to come up with the terms file and folder on a very frequent base, and these are the common terms in the computer field. A file in computer resembles a typed document that could be available on the someone’s desk or inside a filing cabinet, practically. On the other hand, a folder is quite more than a container used to store files.
We used to come up with the terms file and folder on a very frequent base, and these are the common terms in the computer field. A file in computer resembles a typed document that could be available on the someone’s desk or inside a filing cabinet, practically. On the other hand, a folder is quite more than a container used to store files.
It would not be practically possible to put several hundred or thousands of paper files on a desk, as when you need a particular file from those papers it is next to impossible find it. So, that is the reason we store paper files in folders inside a filing cabinet. To make a file easily searchable, it must be organized into logical groups. In computers, the concept of file and folder functions exactly the same.
Content: File Vs Folder
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | File | Folder |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Collection of data | A place to store a group of related files and folders |
| Extensions | Files can have extensions. | Folders does not have any extensions. |
| Space consumption | There is a specific size of a file. | Folder does not consume space in the memory. |
| Organizations | Serial, sequential, indexed sequential and direct file organizations. | Single directory per user and multiple directory per user organization. |
| Can contain other same entity | No | Yes |
Definition of File
When we want to store the data in a computer system, the os provides an entity known as the file. A File can be defined as a set of related data or information that can be stored in secondary storage media. There are several types of file exists, according to the data stored in that file and it is distinguished by the file extensions.
For example, a file can be data file or a program file where data file can contain data and information in the form of numeric, alphanumeric or binary numbers. In the same way, a file containing the program code and can be executed too is a program file.
Properties of a File
- Name: The file name is used to distinguish the files from one and another. We access a file using its name, however there are different rules for naming a file in different operating systems.
- Extension: What is the type of the file whether it is text, document, image, video, audio or any other type, an extension is used to specify the type of the file.
- Date and time: The additional information stored by a file along with its data is the date and time of its creation or alteration.
- Length: The length of a file is expressed in terms of the total byte content, which is also stored by the file.
- Protection attributes: To identify which type of file access is given to the user, the file protection attributes are used such as read-only, archive, hidden, etcetera.
Operations performed over a file
There are several operations possible on a file, some of them are enlisted below:
- Read: This operation reads the information that is stored in the file.
- Write: We use this operation to add some new data or information in the existing file.
- Rename: For altering the name of the file, we use rename operation.
- Copy: Copy operation, creates a duplicate of the file simultaneously keeping the original file.
- Sort: This operation arranges the contents of the file in some specific order.
- Move: It transports a file from one position to the other.
- Delete: It removes a file.
- Modify: This operation is used for changing the contents of a file.
Categories of data files
The data files are mainly classified according to the manner in which the application program utilizes them. The data file categories are transaction files, master files, output files, report files and backup files.
File organization
The other crucial aspect of a file is how these are organized. File organization handles the physical organization of the data records in a file. The organization highly relies on data retrieval and the nature of storage. The general methods of file organization are shown below:
- Serial file organization: It stores the records serially one after the other, no certain logical sequence is used. However, these are arranged in a chronological order based on when the records were created.
- Sequential file organization: In this organization, the records are stored in some certain order concerning a given field of the record. This field might be a key field or a non-key field of the file.
- Index file sequential organization: In this type of organization the records are physically arranged according to the search key in the file. Additionally, it also maintains the primary index of the file.
- Direct or random file organization: It helps in accessing the records of a file in a direct manner with the help of a special process on the search key of the file. It finds the location of the record swiftly.
Definition of Folder
A folder is used to encapsulate a group of other folders and files and categorize them under the same heading. One can create any number of folders, and each folder can have multiple entries according to the number of files created where each file hold a position in a directory (i.e. folder). Similarly, when a file is deleted from the folder, entry is deleted from the folder automatically. The folder facilitates in storing files in some logical sequence separately so that the searching of a file is easier.
Structure of a folder
All the advanced operating system uses a hierarchical or inverted tree-like directory (folder) structure. In this structure, there is a root folder which can be comprised of files and subfolders, those subfolders can have more files and subfolders and so on.
Let’s understand this with the diagram shown below.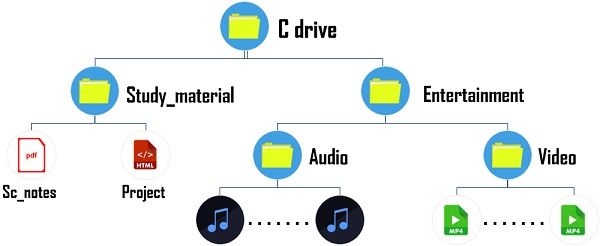 In the example, there is a root folder of C drive which has subfolders named as Study_material and Entertainment. The subfolder Study_material contains files,i.e., Sc_notes and Project. Similarly, subfolder entertainment accommodates two more sub-sub-folders, namely audio and video, which contains music and video files.
In the example, there is a root folder of C drive which has subfolders named as Study_material and Entertainment. The subfolder Study_material contains files,i.e., Sc_notes and Project. Similarly, subfolder entertainment accommodates two more sub-sub-folders, namely audio and video, which contains music and video files.
Key Differences Between File and Folder
- A file is a collection of data in some specific form while the folder is a subdivision of a drive and the location where files and other folders can be stored.
- Folders do not have any extension and inbuilt icon. Conversely, the file extension and icon changes with respect to the file type and the file application. However, the folder icon can also be changed manually according to user preferences.
- A file size can range from several bytes to gigabytes or larger than that based on the amount of data it stores. In contrast, there is no size of a folder.
- The various types of organization of the files are serial, sequential, indexed sequential and direct file organization. On the other hand, the folder does not have multiple organizations; it just follows a hierarchical approach.
- A folder can accommodate several files and folders, but a file can never contain a file or folder inside it.
Conclusion
The file and folder are completely distinct terms and can never be used interchangeably. A File contains data, whereas Folder is an entity that creates logical division of a drive and contains files and folders in it.
Leave a Reply