 Keys are the essential elements of any relational database. It identifies each tuple in a relation uniquely. Keys are also used to establish the relationship among the tables in a schema. In this article, we will discuss two basic keys of any database that is super key and candidate key.
Keys are the essential elements of any relational database. It identifies each tuple in a relation uniquely. Keys are also used to establish the relationship among the tables in a schema. In this article, we will discuss two basic keys of any database that is super key and candidate key.
Every candidate key is a super key but, every super key may or may not be a candidate key. There many other distinguishing factors between super key and candidate key, which I have briefly discussed in the comparison chart below.
Content: Super Key Vs Candidate Key
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Super Key | Candidate Key |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | A single attribute or a set of attributes that uniquely identifies all attributes in a relation is super key. | A proper subset of a super key, which is also a super key is a candidate key. |
| One in other | It is not compulsory that all super keys will be candidate keys. | All candidate keys are super keys. |
| Selection | The set of super keys forms the base for selection of candidate keys. | The set of candidate keys form the base for selection of a single primary key. |
| Count | There are comparatively more super keys in a relation. | There are comparatively less candidate keys in a relation. |
Definition of Super key
A super key is a basic key of any relation. It is defined as a key that can identify all other attributes in a relation. Super key can be a single attribute or a set of attributes. Two entities do not have the same values for the attributes that compose a super key. There is at least one or more that one super keys in a relation.
A minimal super key is also called candidate key. So we can say some of the super keys get verified for being a candidate key. We will see later how a superkey is checked to become a candidate key.
Let us take a relation R (A, B, C, D, E, F); we have following dependencies for a relation R, and we have checked each for being super key.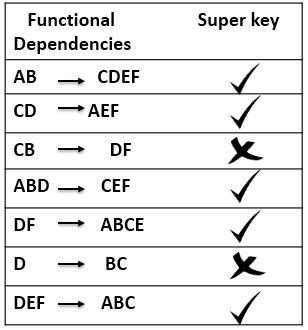 Using key, AB we are able to identify rest of the attributes of the table i.e. CDEF. Similarly, using keys CD, ABD, DF, and DEF we can identify remaining attributes of the table R. So all these are super keys.
Using key, AB we are able to identify rest of the attributes of the table i.e. CDEF. Similarly, using keys CD, ABD, DF, and DEF we can identify remaining attributes of the table R. So all these are super keys.
But using a key CB we can only find values for attribute D and F, we can not find the value for attributes A and E. Hence, CB is not a super key. Same is the case with key D we can not find the values of all attributes in a table using key D. So, D is not a super key.
Definition of Candidate Key
A super key that is a proper subset of another super key of the same relation is called a minimal super key. The minimal super key is called Candidate key. Like super key, a candidate key also identifies each tuple in a table uniquely. A candidate key’s attribute can accept NULL value.
One of the candidate keys is chosen as primary key by DBA. Provided, that the key attribute values must be unique and does not contain NULL. The attributes of Candidate key is called prime attributes.
In above example, we have found the Super keys for relation R. Now, let us check all the super keys for being Candidate key.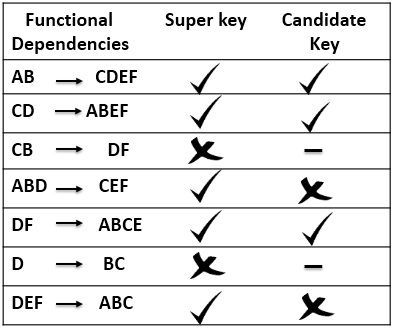 Super key AB is a proper subset of super key ABD. So, when a minimal super key AB alone, is capable of identifying all attributes in a table, then we do not need bigger key ABD. Hence, super key AB is a candidate key while ABD will only be super key.
Super key AB is a proper subset of super key ABD. So, when a minimal super key AB alone, is capable of identifying all attributes in a table, then we do not need bigger key ABD. Hence, super key AB is a candidate key while ABD will only be super key.
Similarly, a super key DF is also a proper subset of super key DEF. So, when DF is alone capable of identifying all attributes in a relation why do we need DEF. Hence, super key DF becomes a candidate key while DEF is only a super key.
The super key CD is not a proper subset of any other super key. So, we can say CD is a minimal super key that identifies all attributes in a relation. Hence, CD is a candidate key.
Whereas key CB and D are not super key so, they can not be the candidate key even. Viewing above table you can conclude that each candidate key is a super key but the inverse is not true.
Key Differences Between Super Key and Candidate Key
- A single attribute or a set of attributes that can uniquely identify all attributes of a particular relation is called Super key. On the other hands, a super key that is a proper subset of another super key is called candidate key.
- All candidate keys are super keys but the inverse is not true.
- The set of super keys is verified to find candidate keys whereas, the set of the candidate keys is verified to select a single primary key.
- Super keys are comparatively more in number than candidate keys.
Conclusion
Super key is a basic key of any relation. They must be plotted first before recognizing other keys for the relation as they form the base for other keys. Candidate key are important as it helps in recognizing the most important key of any relation that is a primary key.
sourabha says
can you provide refrence of these difference