 A network is formed when two or more devices connect to share data or resources. A large network may need to be subdivided for efficient frame delivery or the traffic management. Bridges or switches are used to connect these subdivided segments of networks. In a long way, the terms bridge and switch are use interchangeably. Bridge and switch both provide the same functionality but the switch does it with greater efficiency.
A network is formed when two or more devices connect to share data or resources. A large network may need to be subdivided for efficient frame delivery or the traffic management. Bridges or switches are used to connect these subdivided segments of networks. In a long way, the terms bridge and switch are use interchangeably. Bridge and switch both provide the same functionality but the switch does it with greater efficiency.
A bridge connects smaller network segments to form a large network, and it also relays frame from one LAN to another LAN. On the other hand, the switch connects more network segments as compared to the bridges. This is a basic difference between bridge and switch. Let us compare the differences between the bridge and switch with the help of comparison chart shown below.
Content: Bridge Vs Switch
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Bridge | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | A bridge can connect fewer LAN. | A switch can connect more networks compared to the bridge. |
| Buffer | Bridges do not have buffers. | Switch has a buffer for each link connected to it. |
| Types | Simple bridge, multiport bridge and transparent bridge. | Store-and-forward switch and cut-through switch. |
| Error | Bridges do not perform error checking. | Switches perform error checking. |
Definition of Bridge
Bridge is a networking device used to connect the network segments of a large network. Bridge operates at two level i.e. physical layer and data link layer. Being a physical layer device, it regenerates the signal it receives. Here, it acts as a repeater.
The bridge being a data link layer device identifies the source and destination address of the frame it receives. It relays the frames between two separated LANs. On the other hands, the bridge also has the logic of filtering the traffic (separating the traffic of each network segment).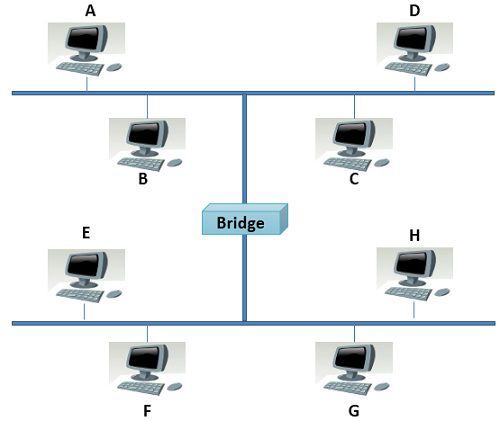 Bridge’s filtering capability can be explained with an example. You can observe the figure above, a bridge has joined two network segments. Now when station A sends a packet to station F, the packet arrives at the bridge. The bridge identifies that the intended recipient F is in the lower segment of the network. So, the bridge allows the packet to cross into the lower segment where the packet is received by the station F.
Bridge’s filtering capability can be explained with an example. You can observe the figure above, a bridge has joined two network segments. Now when station A sends a packet to station F, the packet arrives at the bridge. The bridge identifies that the intended recipient F is in the lower segment of the network. So, the bridge allows the packet to cross into the lower segment where the packet is received by the station F.
When the station A sends a packet to station C, the packet arrives at the bridge. As the station A and C are in the same segment, the bridge blocks the packet from crossing into the lower segment and relays the frame to station C.
Further, we will discuss the types of bridges. Simple Bridge is the most primitive bridge which links two network segments. It has a single table which contains the address of each station included in both the segment.
Multiport Bridge, it links more than two network segments. It has the number of tables equal to the number of network segments it connects. Each table contains the addresses of all the station reachable from the corresponding port. Transparent Bridge is a bridge whose existence is not known to the stations. If a transparent bridge is added or removed from the system, the stations are not required to be reconfigured again.
This is all about the bridges now let us move to the Switches which are similar to the bridges.
Definition of Switch
Whenever we talk about the switches we must specify the level at which the switch operates. We have two types of switches a two-layer switch and a three-layer switch. The two-layer switch operates on two layers i.e. physical and data link layer. A two-layer switch has similar functionality as that of a bridge but has faster forwarding capability and greater efficiency. On the other hands, a three-layer switch act as a router which receives, process and forwards the packet.
In this article, we are discussing two-layer switch which is similar to the multiport bridges. It can connect multiple network segments. A switch has a buffer for the each link connected to it. Here, the receiving link buffers store the packet and check for the outgoing link. If the outgoing link is free, switch sends the packet onto the outgoing link.
Switches are fabricated on two strategies that are store-and-forward and cut-through. The store-and-forward switch stores the frame in the receiving links buffer until the entire packet arrives. On the other hands, the cut-through switch forwards the packet as soon as the destination address of the frame is identified.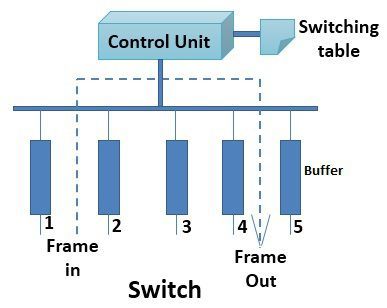 Every switch has a control unit and a switch table. The control unit process the frame to find the destination address of the frame and consults the switch table to find on which link the intended receiver is connected.
Every switch has a control unit and a switch table. The control unit process the frame to find the destination address of the frame and consults the switch table to find on which link the intended receiver is connected.
Key Differences Between Bridge and Switch
- Bridges generally connect fewer networks as compared to the switch.
- Switch has a buffer for each link connected to it which is missing in a buffer.
- Switch perform error checking which is not done in a buffer.
- Bridges are classified as a simple bridge, multiport bridge and transparent bridge. On the other hands, a switch can be classified as Store-and-forward switch and cut-through switch.
Conclusion
Bridges were introduced when the classic Ethernet was used hence they tend to join fewer networks. Switches are the modern bridges, and they tend to join comparatively more networks together and are more efficint than bridges.
Ameek Khan says
Your website is full of GREAT RESOURCES. I’m very thankful to you…..
Sathvik says
Great stuff… thanks!!!
chin2 says
very good explanation.
Dilsha Sandeepani says
One of the most valuable article you published. Thanks and good luck.
Akshay kumar says
Nice Article
Neil says
Very helpful info.
Can I make the Switch work as a bridge – in terms of blocking the traffic between A & C (above diagram) ?