 Telnet and SSH are the general purpose client server application program and uses remote terminal service which allows a user at one site to interact with a remote time-sharing system at another site as if the user’s keyboard and a display connected directly to the remote machine.
Telnet and SSH are the general purpose client server application program and uses remote terminal service which allows a user at one site to interact with a remote time-sharing system at another site as if the user’s keyboard and a display connected directly to the remote machine.
The main difference between Telnet and SSH is that the Telnet is conventional protocol whereas SSH is the replacement for Telnet protocol and also SSH have enhanced features.
Content: Telnet Vs SSH
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Telnet | SSH |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Less secured | Highly secured |
| Uses port number | 23 | 22 |
| Data format | Telnet transfers the data in plain text. | Encrypted format is used to send data and also uses a secure channel. |
| Authentication | No privileges are provided for users authentication. | Uses public key encryption for authentication. |
| Suitability of network | Private networks are recommended. | Suitable for Public networks. |
| Vulnerabilities | Vulnerable to security attacks. | SSH has overcome many security issues of telnet. |
| Bandwidth Usage | Low | High |
Definition of Telnet
TELNET is a client-server program that permits the user to retrieve any application program on a remote computer. The function of a telnet is to provide the services to the user on the remote computer and transferring the result to the local computer. TELNET is an acronym for TErminal NETwork. TELNET facilitates the establishment of the connection to a remote system in a manner that the local terminal resembles to be a terminal at the remote system.
Remote Login
Whenever a user intends to access an application program or utility placed on a remote machine, then user performs Remote Login. Here the TELNET client server program is utilized. The user enters the keystrokes to the terminal driver, which is then accepted as characters by the local operating system.
However, characters are not interpreted. The characters are transmitted to TELNET client and converted into a universal character group refer to as Network Virtual Terminal characters. Then these characters are delivered to the local TCP/IP stack.
The text and commands in NVT format move through the internet and reaches the TCP/IP stack at the remote machine. After transferring the characters to the operating system, it is then passed to the TELNET server, which alters the characters to the corresponding intelligible characters translated by the remote computer.
The characters are moved to the terminal driver as it is not intended to accept characters from a TELNET server. The solution is to add a piece of software known as a pseudo terminal driver which behaves as the characters are transmitted from the terminal. At last, the operating system moves the characters to the appropriate application program.
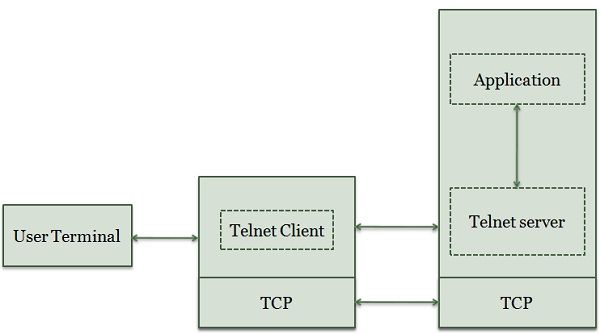
Telnet Protocol Model
Although TELNET is widely used and is not as complex as some remote terminal protocols. Usually, TELNET client software permits the user to describe a remote machine either by the giving its domain name or IP address.
The three type of basic services that TELNET offers are:
- It determines a virtual network terminal that renders a standard interface to remote systems.
- It provides a set of standard options and includes a mechanism that permits the client and server to transact options.
- It allows an arbitrary program to become a client or either end can negotiate options.
Definition of SSH
SSH (Secure SHell) is a network protocol which provides a substitution for vulnerable remote login and command execution provision, such as telnet, rlogin and rsh. It encrypts traffic in both directions, preventing traffic, sniffing and password theft. SSH also gives multiple supplementary features like compression, public key authentication, Authentication of the server, port forwarding, X11 forwarding, file transfer.
SSH also provides remote command execution. When you log in, a pseudo-terminal is assigned to your session and your session, will remain open until you explicitly log out or is terminated from the server end. This protocol supports functionalities like Secure command-shell, secure file transfer and port forwarding.
- Secure Command Shell: It allows a user to view the contents of directories, edit files and access custom database applications remotely.
- Secure file transfer: It acts as a subsystem of the secure shell protocol. Essentially, Secure file transfer protocol is a separate protocol layered over the SSH protocol to handle the transfer of a file.
- Port forwarding: It is also known as tunnelling, which provides the basic security for the TCP/IP application.
Key Differences Between Telnet and SSH
- Telnet and SSH both serve the same purpose and provides the connectivity to the remote server but Telnet is conventional protocol, although it is still in use in the various application. SSH is the replacement for Telnet and has some enhanced features too.
- Telnet doesn’t provide any security mechanism whereas SSH is more secure and provides security measures.
- In Telnet transmits data in plain text that is the reason it is vulnerable to security attacks. On the other hand, SSH uses encryption for transmitted data and security breach does not likely occur. SSH can withstand eavesdropping, man in the middle and insertion/ replay attacks.
- Telnet doesn’t provide authentication facility while SSH provides user authentication.
- Telnet works with a private network. In contrast, SSH works with a public network.
- Telnet communicates via port number 23 over TCP/IP. As against, SSH uses port number 22 for communication.
Conclusion
The SSH protocol is a somewhat better replacement for Telnet as SSH has security measures. While Telnet does not provide much security although still in use.
Leave a Reply