 The SAN and NAS are the information storage techniques which are often mixed with one another because of alike acronyms. These can be differentiated by the fact that SAN (Storage Area Network) shares the storage to the dedicated network whereas NAS (Network Attached Storage) share the storage over a shared network. SAN uses block storage. Conversely, NAS uses the file system.
The SAN and NAS are the information storage techniques which are often mixed with one another because of alike acronyms. These can be differentiated by the fact that SAN (Storage Area Network) shares the storage to the dedicated network whereas NAS (Network Attached Storage) share the storage over a shared network. SAN uses block storage. Conversely, NAS uses the file system.
These storage techniques were devised to fulfil the purpose of storing, protecting and managing the magnificent amount of information at organisations.
Content: SAN Vs NAS
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | SAN | NAS |
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Storage Area Network | Network Attached Storage |
| Device that can connect to the technology | Only the devices that are server class and has SCSI fibre channel. | Each device that connects to the LAN and can utilize NFS, CIFS or HTTP protocol would be able to connect to the NAS. |
| Identification of data | Identify data by disk block. | Addresses data by file name and byte offset. |
| Extent of information sharing | The sharing of file rely on the operating system. | It enables greater sharing especially among OS such as Unix and NT. |
| Management of file system | Servers | Head unit is responsible. |
| Protocols | SCSI, fibre channel or SATA. | File server, NFS or CIFS. |
| Backups and recovery | Block by block copying technique is used. | Files are used for backups and mirrors. |
| Cost and complexity | Expensive and more complex. | Cost effective and less complicated comparatively. |
Definition of SAN
SAN (Storage Area Network) transfer data between servers and storage devices with the help of fibre channel and switches. SAN allows the whole data to be merged at a single storage and shared over multiple servers. With this multiple organizations can connect geographically separated storage and servers. SAN is robust and secure communication technology.
Earlier SAN was implemented by combining hosts and storage that connect to the network through a hub and connecting device. The older configuration is known as Fibre channel arbitrated loop. It uses block storage where the data is stored in the volumes known as blocks.
The SAN was invented after the invention of DAS (Directly Attached Storage), where each host provided with a storage and it was not manageable, shareable and flexible enough. It runs on high-speed fibre channel where for the front end (SAN connectivity), fibre optics cable is used and for back-end (disk connectivity) copper cable is used and uses protocols such as FC and SCSI.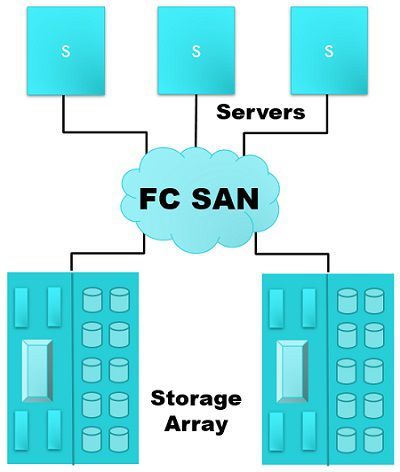
Components of SAN
SAN comprised of following components:
- All the fibre channel devices are called as node ports such as storage, hosts, and tape libraries. Each node could be either a source or a destination for another host.
- Cabling of the network is done using fibre optic cable and copper cable. To cover short distance copper cable used such as for backend connectivity.
- Hubs, switches and directors are the interconnect device adopted for the SAN.
- The large storage arrays are used for providing host access to the storage resources.
- The SAN management software is used to control the interfaces between storage arrays, interconnect devices and hosts.
Definition of NAS
NAS (Network Attached Storage) is a file-level storage technology provides a file sharing facility with the help of the local area network. It involves a shared network instead of dedicated, unlike SAN. The major advantage of NAS is that it excludes the need of using multiple servers through server consolidation. Using file storage rather than block storage is better when the user wants it to be cost-effective or low cost.
File storage offers a highly accessible centralized location for files. A real-time operating system often stripped down is dedicatedly used for NAS by using standard protocols. The NAS units are configured and controlled over the network, using a browser. In NAS the data is travelled in file data stream.
The file access requires an extra layer for processing host and translation between file access and block access as it is constructed on a higher abstraction layer. The consequence of the NAS processing is that it requires additional overhead which affects the processing speed or extra data transfer.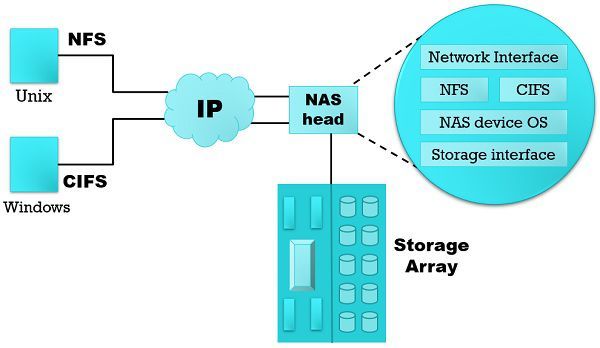
Components of NAS
- NAS head (CPU and memory).
- Network interface card that enables connectivity to the network.
- An optimized operating system which controls the functionality in NAS.
- Protocols for sharing files such as NFS and CIFS.
- Storage protocols like ATA, SCSI, or FC are utilized to connect and manage physical disk resources.
Key Differences Between SAN and NAS
- SAN connects to only those devices that have SCSI fibre channel and belong to the server class. In contrast, NAS can connect the devices that exist in a LAN and able to utilise protocol such NFS or CIFS.
- The data in SAN is recognized by dist block whereas in NAS it is addressed by file name and byte offset.
- Information is shared by a server-based operating system in SAN, that is why it relies on the operating system. As against, NAS allow higher sharing particularly among OS like Unix and NT.
- In SAN the file system is handled by servers, whereas in NAS the head unit controls file system.
- The protocols used in SAN are SCSI, fibre channel or SATA. On the contrary, NAS involves protocols such as NFS or CIFS.
- The backup and mirrors are made using blocks in SAN. Inversely, in NAS files are used to generate backup and mirror.
- SAN is costlier and complicated than NAS.
Advantages of SAN
- Provides flexibility and simplified storage administration.
- Servers are able to boot itself automatically from SAN.
- Faulty servers are easily and quickly replaced.
- Provision for effective disaster recovery processes.
- Provides better storage replication.
Advantages of NAS
- The single volume is shared among multiple hosts (clients).
- Provides fault tolerant system.
- Allows administrators to employ simple and low-cost load balancing.
Disadvantages of SAN
- Highly expensive.
- Management of SAN is difficult.
- Higher degree skills are required to maintain SAN.
Disadvantages of NAS
- Not supported by all applications.
- The backup solution is costlier than the storage system.
- Any contraction in local area network can slow down the storage access time.
Conclusion
SAN is suitable for transactional data or frequently changing data, and it provides high performance. On the other hand, NAS is suitable for shared file data and provides simplified access and management of shared files.
idiatan ramon idris says
thank you very much