 Pure ALOHA and Slotted ALOHA both are the Random Access Protocols, that are implemented on the Medium Access Control (MAC) layer, a sublayer of Data Link Layer. The purpose of the ALOHA protocol is to determine that which competing station must get the next chance of accessing the multi-access channel at MAC layer.
Pure ALOHA and Slotted ALOHA both are the Random Access Protocols, that are implemented on the Medium Access Control (MAC) layer, a sublayer of Data Link Layer. The purpose of the ALOHA protocol is to determine that which competing station must get the next chance of accessing the multi-access channel at MAC layer.
The main difference between Pure ALOHA and Slotted ALOHA is that the time in Pure Aloha is continuous whereas, the time in Slotted ALOHA is discrete. Let us discuss the other differences between Pure ALOHA and Slotted ALOHA in the comparison chart.
Content: Pure ALOHA Vs Slotted ALOHA
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Pure ALOHA | Slotted ALOHA |
|---|---|---|
| Introduced | Introduced by Norman Abramson and his associates at the University of Hawaii in 1970. | Introduced by Roberts in 1972. |
| Frame Transmission | The user can transmit the data frame whenever the station has the data to be transmitted. | The user has to wait till the next time slot start, to transmit the data frame. |
| Time | In Pure ALOHA the time is continuous. | In Slotted ALOHA the time is discrete. |
| Successful Transmission | The probability of successful transmission of the data frame is: S= G* e^-2G | The probability of successful transmission of the data frame is: S= G*e^-G |
| Synchronization | The time is not globally synchronized. | The time here is globally synchronized. |
| Throughput | The maximum throughput occurs at G = 1/2 which is 18%. | The maximum throughput occurs at G = 1 which is 37%. |
Definition Of Pure ALOHA
Pure ALOHA is introduced by Norman Abramson and his associates at the University of Hawaii in early 1970. The Pure ALOHA just allows every station to transmit the data whenever they have the data to be sent. When every station transmits the data without checking whether the channel is free or not there is always the possibility of the collision of data frames. If the acknowledgment arrived for the received frame, then it is ok or else if the two frames collide (Overlap), they are damaged.
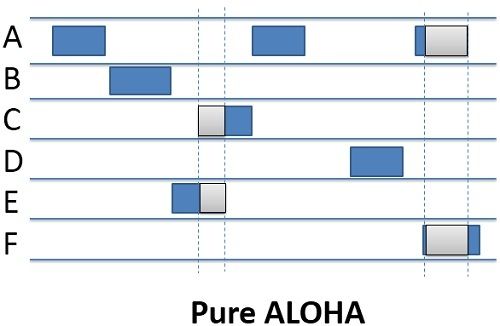 If a frame is damaged, then the stations wait for a random amount of type and retransmits the frame till it transmits successfully. The waiting time of the each station must be random and it must not be same just to avoid the collision of the frames again and again.
If a frame is damaged, then the stations wait for a random amount of type and retransmits the frame till it transmits successfully. The waiting time of the each station must be random and it must not be same just to avoid the collision of the frames again and again.
The throughput of the Pure ALOHA is maximized when the frames are of uniform length. The formula to calculate the throughput of the Pure ALOHA is S-=G*e^-2G, the throughput is maximum when G=1/2 which is 18% of the total transmitted data frames.
Definition Of Slotted ALOHA
After the pure ALOHA in 1970, Roberts introduced an another method to improve the capacity of the Pure ALOHA which is called Slotted ALOHA. He proposed to divide the time into discrete intervals called time slots. Each time slot corresponds to the length of the frame.
In contrast to the Pure ALOHA, Slotted ALOHA does not allow to transmit the data whenever the station has the data to be send. The Slotted ALOHA makes the station to wait till the next time slot begins and allow each data frame to be transmitted in the new time slot.
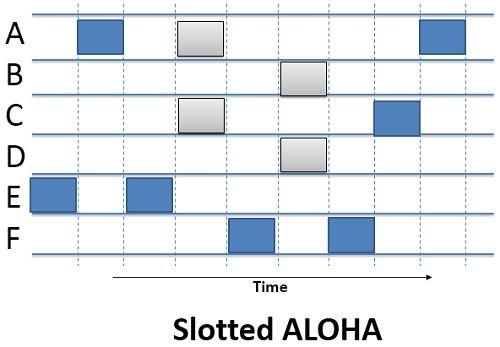 Synchronization can be achieved in Slotted ALOHA with the help of a special station that emits a pip at the beginning of every time slot as a clock does. The formula to calculate the throughput of the Slotted ALOHA is S=G*e^-G, the throughput is maximum when G=1 which is 37% of the total transmitted data frames. In Slotted ALOHA, 37% of the time slot is empty, 37% successes and 26% collision.
Synchronization can be achieved in Slotted ALOHA with the help of a special station that emits a pip at the beginning of every time slot as a clock does. The formula to calculate the throughput of the Slotted ALOHA is S=G*e^-G, the throughput is maximum when G=1 which is 37% of the total transmitted data frames. In Slotted ALOHA, 37% of the time slot is empty, 37% successes and 26% collision.
Key Differences Between Pure ALOHA and Slotted ALOHA
- Pure ALOHA was introduced by Norman and his associates at the university of Hawaii in 1970. On the other hand, Slotted ALOHA was introduced by Roberts in 1972.
- In pure ALOHA, whenever a station has data to send it transmits it without waiting whereas, in slotted ALOHA a user wait till the next time slot beings to transmit the data.
- In pure ALOHA the time is continuous whereas, in Slotted ALOHA the time is discrete and divided into slots.
- In pure ALOHA the probability of successful transmission is S=G*e^-2G. On the other hand, in slotted ALOHA the probability of successful transmission is S=G*e^-G.
- The time of sender and receiver in pure ALOHA is not globally synchronized whereas, the time of sender and receiver in slotted ALOHA is globally synchronized.
- The maximum throughput occurs at G=1/2 which is 18 % whereas, the maximum throughput occurs at G=1 which is 37%.
Conclusion
The Slotted ALOHA is somewhat better than the Pure ALOHA. As the probability of collision is less in Slotted ALOHA as compared to Pure ALOHA because the station waits for the next time slot to begin which let the frame in a previous time slot to pass and avoids the collision between the frames.
Mahi says
It is very helpful article. I really appreciate and like your blog.
sai says
It is very nice and simple. It is very useful also.
Hao3network says
Yes
tinashe says
thank you so much. it was easy to understand and it was fully explained
Chaus S P says
It is very simple and easy to understand. It is a very helpful article.
abhishek basu says
It is really good article. Thank you.
subuhi says
It is very easy and understandable
Harsh says
Very informative
zinabu Teka says
I liked it. Go a head!
GOH JIAN HUI . says
Thank you so much
Aston Muk says
Thanks
very Nice and Simple to follow
lucia liao says
thanks a lot!
easy to understand~
Alabhaya Tandon says
Awesomely Explained
Very Useful
Thank you
Trends Follow says
Thank you for sharing