 The point-to-point and Multipoint are two types of line configuration. Both of them describes a method to connect two or more communication devices in a link. The main difference between point-to-point and multipoint connection is that in a point-to-point connection the link is only between two devices i.e. a sender and a receiver.
The point-to-point and Multipoint are two types of line configuration. Both of them describes a method to connect two or more communication devices in a link. The main difference between point-to-point and multipoint connection is that in a point-to-point connection the link is only between two devices i.e. a sender and a receiver.
On the other hand, in a multipoint connection, the link is between a sender and multiple receivers. Lets us study further the difference between point-to-point and multipoint connection with the help of comparison chart shown below.
Content: Point-to-Point Vs Multipoint
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Point-to-Point | Multipoint |
|---|---|---|
| Link | There is dedicated link between two devices. | The link is shared between more than two devices. |
| Channel Capacity | The channel's entire capacity is reserved for the two connected devices. | The channel's capacity is shared temporarily among the devices connected to the link. |
| Transmitter and Receiver | There is a single transmitter and a single receiver. | There is a single transmitter and multiple receivers. |
| Example | Frame relay, T-carrier, X.25, etc. | Frame relay, token ring, Ethernet, ATM, etc. |
Definition of Point-to-Point Connection
The point-to-point is a kind of line configuration which describes the method to connect two communication devices in a link. The point-to-point connection is a unicast connection. There is a dedicated link between an individual pair of sender and receiver. The capacity of the entire channel is reserved only for the transmission of the packet between the sender and receiver.
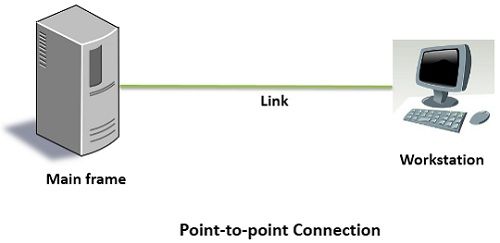 If the network is made up of point-to-point connections, then the packet will have to travel through many intermediate devices. The link between the multiple intermediate devices may be of different length. So, in point-to-point network finding the smallest distance to reach the receiver is most important.
If the network is made up of point-to-point connections, then the packet will have to travel through many intermediate devices. The link between the multiple intermediate devices may be of different length. So, in point-to-point network finding the smallest distance to reach the receiver is most important.
Definition of Multipoint Connection
The multipoint connection is a connection established between more than two devices. The multipoint connection is also called multidrop line configuration. In multipoint connection, a single link is shared by multiple devices. So, it can be said that the channel capacity is shared temporarily by every device connecting to the link. If devices are using the link turn by turn, then it is said to be time shared line configuration.
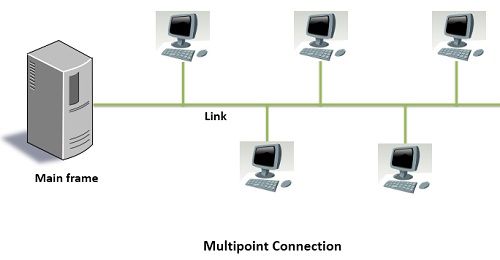 In the figure above, you can see that the five workstations share the common link between the main frame and the workstations. The multipoint networks are also called “Broadcast network”.
In the figure above, you can see that the five workstations share the common link between the main frame and the workstations. The multipoint networks are also called “Broadcast network”.
In a broadcast network, the packet transmitted by the sender is received and processed by every device on the link. But, by the address field in the packet, the receiver determines whether the packet belongs to it or not, if not, it discards the packet. If packet belongs to the receiver then keeps the packet and respond to the sender accordingly.
Key Differences Between Point-to-Point and Multipoint Connection
- When there is a single dedicated link only between two devices, it is a point-to-point connection whereas, if a single link is shared by more than two devices then it is said to be a multipoint connection.
- In multipoint connection, the channel capacity is shared temporarily by the devices in connection. On the other hand, in a point-to-point connection, the entire channel capacity is reserved only for the two devices in the connection.
- In point-to-point connection, there can only be a single transmitter and a single receiver. On the other hand, in multipoint connection, there is a single transmitter, and there can be multiple receivers.
Similarities
The point-to-point and multipoint both are the types of line configuration, that refers the technique to connect two or more communication devices.
Conclusion
If you want to send your data to the multiple receivers, using point to point connection will create more overhead, instead using multipoint connection will be more helpful.
ibrahima says
well done .perfect
RAHUL says
Thank you…Mam
It helped me so much.
Akanksha sachan says
Please tell me Difference between broadcast and point to point network
Deodatus kahwa says
Well done keep it up but can you develop References
compuetcargo says
great content to see …