 Hue and saturation are properties of the colour. The main difference between them is that the hue is the purest form of the colour whereas saturation is the degree of brightness and dullness of a hue. Generally, the colour are measured in the range of 0 to 360 degrees where red lies in 0, green at 120 and blue at 240.
Hue and saturation are properties of the colour. The main difference between them is that the hue is the purest form of the colour whereas saturation is the degree of brightness and dullness of a hue. Generally, the colour are measured in the range of 0 to 360 degrees where red lies in 0, green at 120 and blue at 240.
Now, most of the colour wheels work in degrees where angles in the colour wheel are measured, but in the case of computers, the concept is quite modified where everything exists in binary numbers. To save the colour in the computer’s memory, a byte is used which falls a little bit short as it can scale from 0 to 255. So, only 240 values are used to store the hue in which the RGB (Red, Green, Blue) colours are allocated in the difference of 80 such as red at the 0 lowest frequency of the colour, 80 at green and 160 at blue (highest frequency of the colour).
Content: Hue and Saturation
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Hue | Saturation |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Represent the colour type | Degree of vividness |
| Alternative names | Dominant frequency | Purity |
| Identified by | Observing the difference between white light and red or green light. | Measuring the amount of grey mixed in the pure colour. |
Definition of Hue
Before understanding hue we must understand the science behind the colours, the human eye is able to see. The white light emitted by any source such as the sun and a light bulb is comprised of all the frequencies within the visible range. When white light strikes an object, it absorbs an amount of light while reflecting back some frequencies. The group of frequencies reflected from the object identified and perceived as the colour of that object.
So, if the low frequencies are superior in the reflected light, the object is described as red and considered as the dominant frequency at the red end of the spectrum. This dominant frequency is known as hue or in a simple way the colour.
Hue is the part of the chromaticity of the colour. The three chief hues in light are red, green and blue. This is the reason the television and computer radiators and other electronic colour visual displays trio of red, green and blue phosphors to create all electrically communicated colours. Hue is basically a single value that represents a colour of something and usually measured in degrees as mentioned above. It contains the colours like red, orange, yellow, green, blue, purple and magenta back to red. However, magenta and pink are not really any frequency of light. This can be proved by a rainbow, it starts with red and then other colours but does not contain magenta and pink as these are not the real frequencies which human can see.
Definition of Saturation
Saturation is determined as the purity of the colour, and how far the colour is from grey. If the colour contains more greyness, then it has the lower level of saturation. For example, in red, the high saturation presents the deepest red while low saturation colour is closer to grey as shown in the diagram below.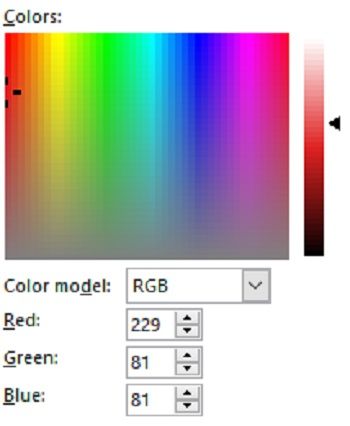
Furthermore, saturation can also be interpreted as the dominance of hue in the colour. In the hue wheel, the outermost edge contains the pure hue, as we go inward in the wheel to the centre containing grey the hue gradually decreases and saturation also lowers. It corresponds to a physical property referred to as excitation property, where the percentage of the luminance mixed with the dominant or pure colour is measured. In the other way, it can be represented as shown below: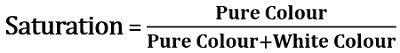
This concept is limited to the light having the identifiable dominant wavelength because there are also some lights whose wavelength cannot be identified. It mainly links the physical concept of the light and the perpetual classification of the colour.
Key Differences Between Hue and Saturation
- Hue is the fundamental property of light which helps in distinguishing the different colours from each other. Conversely, the saturation describes how much the colour is at the provided hue or the degree of vividness (i.e., brightness or luminance).
- To measure hue the degree of the angle is used to measure while saturation is generally measured in percentage.
- Hue is detected by measuring the difference between white light and other colour of light. As against, saturation is measured by the amount of grey amalgamated in the hue.
Conclusion
Hue and saturation are the inclinations of the line which is described by the position of the RGB vector over the line. Hue is the property of colour which separates the white light from the red and green light. On the other hand, saturation is the amount of luminance blended with the pure component of the colour.
Leave a Reply