 Data is raw, unanalyzed, unorganised, unrelated, uninterrupted material which is used to derive information, after analyzation. On the other hand, Information is perceivable, interpreted as a message in a particular manner, which provides meaning to data.
Data is raw, unanalyzed, unorganised, unrelated, uninterrupted material which is used to derive information, after analyzation. On the other hand, Information is perceivable, interpreted as a message in a particular manner, which provides meaning to data.
Data doesn’t interpret anything as it is a meaningless entity, while information is meaningful and relevant as well. Data and Information are different common terms which we frequently use, although there is a general interchangeability between these terms. So, our primary goal is to clarify the essential difference between Data and Information.
Content: Data Vs Information
Comparison Chart
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | DATA | INFORMATION |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Data is unrefined facts and figures and utilized as input for the computer system. | Information is the output of processed data. |
| Characteristics | Data is a individual unit which contains raw material and doesn't carry any meaning. | Information is the product and group of data which collectively carry a logical meaning. |
| Dependence | It doesn't depend on Information. | It relies on Data. |
| Peculiarity | Vague | Specific. |
| Measuring Unit | Measured in bits and bytes. | Measured in meaningful units like time, quantity, etc. |
Definition of Data
Data is distinguishable information that is arranged in a particular format. Data word stems from a singular Latin word, Datum; its original meaning is “something given”. We have been using this word since 1600’s, and data turn into the plural of datum.
Data can adopt multiple forms like numbers, letters, set of characters, image, graphic, etc. If we talk about Computers, data is represented in 0’s and 1’s patterns which can be interpreted to represent a value or fact. Measuring units of data are Bit, Nibble, Byte, kB (kilobytes), MB (Megabytes), GB (Gigabytes), TB (Terabytes), PT (Petabyte), EB (Exabyte), ZB (Zettabytes), YT (Yottabytes), etc.
To store data, earlier punched cards were used, which were then replaced by magnetic tapes and hard disks.
There are two variants of data, Qualitative and Quantitative.
- Qualitative Data emerges when the categories present in data are distinctly separated under an observation and expressed through natural language.
- Quantitative Data is the numerical quantification which includes the counts and measurements and can be expressed in terms of numbers.
Data deteriorates as time passes.
Definition of Information
Information is what you get after processing data. Data and facts can be analysed or used as an effort to gain knowledge and infer on a conclusion. In other words, accurate, systematize, understandable, relevant, and timely data is Information.
Information is an older word that we have been using since 1300’s and have a French and English origin. It is derived from the verb “informare” which means to inform and inform is interpreted as to form and develop an idea.
Information = Data + Meaning
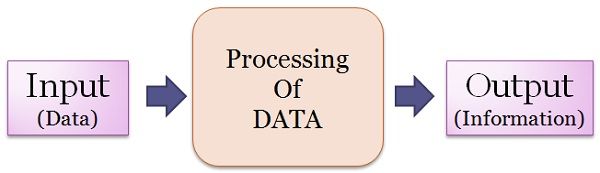
Unlike data, Information is a meaningful value, fact and figure which could derive something useful.
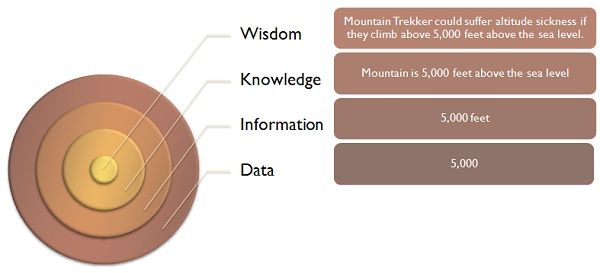
Let us take an example “5000” is data but if we add feet in it i.e. “5000 feet” it becomes information. If we keep on adding elements, it will reach the higher level of intelligence hierarchy as shown in the diagram.
- Information is critical in a sense.
- There are various encoding techniques for interpretation and transmission of information.
- Information encryption is used for increasing the security during transmission and storage also.
Key Differences Between Data and Information
- Data is a single unit which contains raw facts and figures. In contrast, Information is the collection of useful data,which is able to provide knowledge or insight about particular manner.
- Information is derived from the data and hence, data does not rely upon information, but information does.
- Data is used as Input, which needs to be processed and organized in a particular fashion to generate output, i.e. information.
- Data couldn’t specify anything; there is no relation exists between chunks of data while Information is specific and there exists a correlation.
- Data has no real meaning whereas Information carries certain meaning.
Conclusion
Data and Information, both the terms we use are a part of intelligence hierarchy and differ in the way that Data is not meaningful, but Information which is formed by the processed data is meaningful in context.
atul panddey says
The data is concise, and the way you have described is so good. I got the difference now….
Anuj says
Such a great article. This helps me a lot. It’s very informative. And once again thank you so much.