 The word ‘identifier’ clearly defines itself; an identifier is a name given to an entity, which distinctly identifies an entity in a program at the time of its execution. Variable is also an identifier; its name uniquely identifies itself in a program.
The word ‘identifier’ clearly defines itself; an identifier is a name given to an entity, which distinctly identifies an entity in a program at the time of its execution. Variable is also an identifier; its name uniquely identifies itself in a program.
Here, the fundamental difference between an identifier and variable is that an identifier is a “name given to entity” in a program whereas, a variable is a “name given to memory location”, that is used to hold value, which may get modified during program execution.
Furthermore, the name given to a variable, function, class, structure, that is in the source code of the program is an identifier. As against, a variable is a name associated with the memory cell whose value can be altered in a program. The number of characters can be more in the identifier as compared to a variable.
Content: Identifier Vs Variable
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Identifier | Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Use | Identifier is used to name a variable, function, class, structure, union etc. | Variable is used to name a memory location, which holds a value. |
| Purpose | Created to give a unique name to an entity. | Allots a unique name to a particular memory location. |
| Range | All identifiers are not variable. | All variables names are identifier. |
| Example | int a; or int a(){ // } | int a; or float a; // |
Definition of Identifier
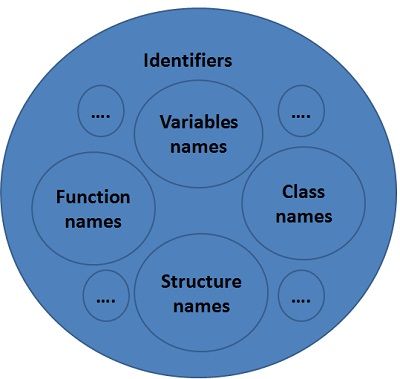
The name we use to call a particular entity in a program, which is not a keyword is called “identifier“. Identifier particularly names a ‘variable, function, structure, enum, class etc’. An identifier distinctly identifies an entity in a program while its execution. Two identifiers cannot have the same name in a program.
Example
Let’s understand it with an example.
float area;
Here ‘float’ is a ‘keyword’, and ‘area’ is an ‘identifier’. The identifier ‘area’ is a name given to a ‘variable’ which will store a float value. Now if ‘area’ weren’t a variable, but a function, then
float area(){
}
Here, ‘area’ is still an identifier, but this time, the identifier ‘area’ is a name given to a ‘function’. We have discussed the rules for naming an identifier in our previous article difference between keyword and identifier; you can go through it to understand it in a better way.
Definition of Variable
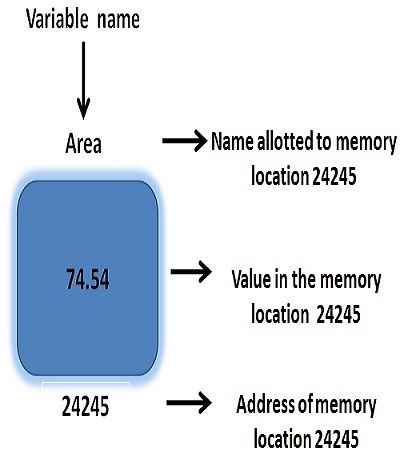
Variable is a “name given to a distinct memory location”. This named memory location contains a value which may be modified while the program gets executed. In C, a variable must be declared at the beginning of a program whereas, in C++, a variable could be declared anywhere in a program.
Types of Variables
Variables can be ‘local’, ‘global’ or ‘reference’ .
- Local variables are declared inside a function
- Global variables are declared outside a function.
- Reference variables are those which provide an “alternate name” for the previously defined variable.
If a variable is referenced to another variable, both the variables can be used alternately to represent that variable. If a variable accepts the value of an argument in a function, these variables are called ‘formal parameter’.
Rules for creating a Variable
- It can contain any combination of the alphabets, digits or underscores.
- Some compilers permit only variable having the length up to 247 characters. However, programmers prefer to use up to 31 characters length for a variable as this is convenient for them.
- The initial character of a variable name should be an alphabet or underscore as it is an identifier some of the rules are similar.
- Use of commas and blanks is not permitted within a variable name.
- None of the special symbols except ‘underscore’ can be used in a variable name.
Declaration of a variable
//type vaiable_name; int add;
A list of variables of the same type can be created at an instance, separated by a comma.
//type variable_list; int a, b, c;
In C++ variables could be initialized at runtime; it is referred to as ‘dynamic initialization’.
Example
float area = 3.14*rad*rad;
This statement would initialize the variable ‘area’ at runtime.
Key Differences Between Identifier and Variable
- Both an identifier and a variable are the names allotted by users to a particular entity in a program. The identifier is only used to identify an entity uniquely in a program at the time of execution. On the contrary, a variable is a name given to a memory location, that is used to hold a value.
- Variable is only a kind of identifier; other kinds of identifiers are function names, class names, structure names, etcetera. So it can be said that all variables are identifiers whereas, vice versa is not true.
- The number of characters in an identifier can be greater than that of a variable.
Conclusion
As identifier and variable names are user-defined names, it should be taken care that no two identifiers or no two variable names in a program should be the same. It will create a problem of ambiguity in a program.
Harshi says
Useful one
Balaji T says
Thanks a lot, and Very useful information.
Deus says
Very well understood,am beginner