 Memory is a large array of bytes, where each byte has its own address. The memory allocation can be classified into two methods contiguous memory allocation and non-contiguous memory allocation. The major difference between Contiguous and Noncontiguous memory allocation is that the contiguous memory allocation assigns the consecutive blocks of memory to a process requesting for memory.
Memory is a large array of bytes, where each byte has its own address. The memory allocation can be classified into two methods contiguous memory allocation and non-contiguous memory allocation. The major difference between Contiguous and Noncontiguous memory allocation is that the contiguous memory allocation assigns the consecutive blocks of memory to a process requesting for memory.
On the contrary, the noncontiguous memory allocation assigns the separate memory blocks at a different location in memory space in a nonconsecutive manner to a process requesting for memory.
We will discuss some more differences between contiguous and non-contiguous memory allocation with the help of comparison chart shown below.
Content: Contiguous Vs Noncontiguous Memory Allocation
Comparison Chart
| Basis the Comparison | Contiguous Memory Allocation | Noncontiguous Memory Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Allocates consecutive blocks of memory to a process. | Allocates separate blocks of memory to a process. |
| Overheads | Contiguous memory allocation does not have the overhead of address translation while execution of a process. | Noncontiguous memory allocation has overhead of address translation while execution of a process. |
| Execution rate | A process executes fatser in contiguous memory allocation | A process executes quite slower comparatively in noncontiguous memory allocation. |
| Solution | The memory space must be divided into the fixed-sized partition and each partition is allocated to a single process only. | Divide the process into several blocks and place them in different parts of the memory according to the availability of memory space available. |
| Table | A table is maintained by operating system which maintains the list of available and occupied partition in the memory space | A table has to be maintained for each process that carries the base addresses of each block which has been acquired by a process in memory. |
Definition of Contiguous Memory Allocation
The operating system and the user’s processes both must be accommodated in the main memory. Hence the main memory is divided into two partitions: at one partition the operating system resides and at other the user processes reside. In usual conditions, the several user processes must reside in the memory at the same time, and therefore, it is important to consider the allocation of memory to the processes.
The Contiguous memory allocation is one of the methods of memory allocation. In contiguous memory allocation, when a process requests for the memory, a single contiguous section of memory blocks is assigned to the process according to its requirement.
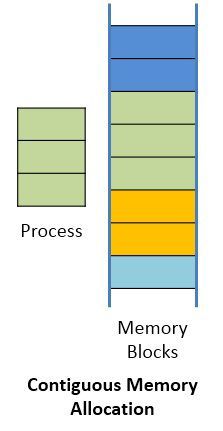 The contiguous memory allocation can be achieved by dividing the memory into the fixed-sized partition and allocate each partition to a single process only. But this will cause the degree of multiprogramming, bounding to the number of fixed partition done in the memory.
The contiguous memory allocation can be achieved by dividing the memory into the fixed-sized partition and allocate each partition to a single process only. But this will cause the degree of multiprogramming, bounding to the number of fixed partition done in the memory.
The contiguous memory allocation also leads to the internal fragmentation. Like, if a fixed sized memory block allocated to a process is slightly larger than its requirement then the left over memory space in the block is called internal fragmentation. When the process residing in the partition terminates the partition becomes available for the another process.
In the variable partitioning scheme, the operating system maintains a table which indicates, which partition of the memory is free and which occupied by the processes. The contiguous memory allocation fastens the execution of a process by reducing the overheads of address translation.
Definition Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation
The Non-contiguous memory allocation allows a process to acquire the several memory blocks at the different location in the memory according to its requirement. The noncontiguous memory allocation also reduces the memory wastage caused due to internal and external fragmentation. As it utilizes the memory holes, created during internal and external fragmentation.
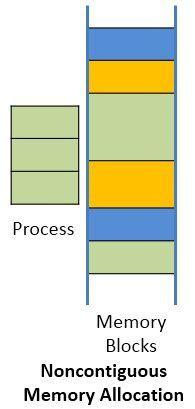
Paging and segmentation are the two ways which allow a process’s physical address space to be non-contiguous. In non-contiguous memory allocation, the process is divided into blocks (pages or segments) which are placed into the different area of memory space according to the availability of the memory.
The noncontiguous memory allocation has an advantage of reducing memory wastage but, but it increases the overheads of address translation. As the parts of the process are placed in a different location in memory, it slows the execution of the memory because time is consumed in address translation.
Here, the operating system needs to maintain the table for each process which contains the base address of the each block which is acquired by the process in memory space.
Key Differences Between Contiguous and Noncontiguous Memory Allocation
- The basic difference between contiguous and noncontiguous memory allocation is that contiguous allocation allocates one single contiguous block of memory to the process whereas, the noncontiguous allocation divides the process into several blocks and place them in the different address space of the memory i.e. in a noncontiguous manner.
- In contiguous memory allocation, the process is stored in contiguous memory space; so there is no overhead of address translation during execution. But in noncontiguous memory allocation, there is an overhead of address translation while the process execution, as the process blocks are spread in the memory space.
- Process stored in contiguous memory executes faster in comparison to process stored in noncontiguous memory space.
- The solution for contiguous memory allocation is to divide the memory space into the fixed-sized partition and allocate a partition to a single process only. On the other hands, in noncontigous memory allocation, a process is divided into several blocks and each block is placed at different places in memory according to the availability of the memory.
- In contiguous memory allocation, operating system has to maintain a table which indicates which partition is available for the process and which is occupied by the process. In noncontiguous memory allocation, a table is maintained for each process which indicates the base address of each block of the process placed in the memory space.
Conclusion
Contiguous memory allocation does not create any overheads and fastens the execution speed of the process but increases memory wastage. In turn noncontiguous memory allocation creates overheads of address translation, reduces execution speed of a process but, increases memory utilization. So there are pros and cons of both allocation methods.
Riya says
best answer.
prashant says
its very beneficial..
Jeffry says
This the best solution I got so far
Vivek says
You are doing good job well done.
And thanks for this.
Jyoti says
Excellent
Thanks for its solution
Shalini Sharma says
It’s really very helpful to understand memory management and it’s related topics…thank you, mam…
Jinoy says
Easy to understand the main difference between them