 CIDR and VLSM are the terms explicitly used at the time of designing a network where CIDR is used for merging the routes in order to decrease the routing information carried by the core routers. On the contrary, VLSM facilitates in optimizing the available address space.
CIDR and VLSM are the terms explicitly used at the time of designing a network where CIDR is used for merging the routes in order to decrease the routing information carried by the core routers. On the contrary, VLSM facilitates in optimizing the available address space.
CIDR is just opposite of VLSM, where it describes rules for referencing set of networks with a single route statement. Conversely, VLSM defines rules for subdividing the networks.
Content: CIDR and VLSM
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | CIDR | VLSM |
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Classless Interdomain Routing | Variable Length Subnet Masking |
| Basic | Enable routers to group routes together | Facilitates in optimizing the available address space |
| Uses the concept of | Supernetting | Subnetting |
| Supported by | BGP and OSPF | RIPv2, OSPF, EIGRP, IS-IS and BGP |
Definition of CIDR
Before understanding the CIDR, we must understand what prefix routing is. It means to allocate a set of classful networks, expressed by a single network address. Prefix masks shows a set of TCP/IP network addresses using the technique of address or subnet mask. The aggregation of classful networks specifies the old structure of Class A, B, C addressing, or classful addressing. However, this classful addressing would not useful at the time of establishing connectivity between organizations through the internet. Therefore, for aggregating these classful networks and connecting the organizations through the network, the concept used is known as Interdomain Routing.
CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) does not use the ides of class-based networks, as we know that classful addressing had the limitation where the public IP addresses were lesser than the demand of the people for the public addresses (For using the internet). Initially, it was designed to enable ISPs to hand out the smaller or larger blocks of IP addresses instead of a class. It is also known as route summarization.
Definition of VLSM
VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking) is a technique of assigning the host space of distinct size between the networks through distributing a network into several subnetworks. It was basically designed to provide more flexibility for configuring a network using different masks.
In other words, the Variable Length Subnet Masking or VLSM is the technique of applying multiple subnet mask to a provided class of addresses over a routed system. This was not possible before as the previously designed protocols like RIPv1 would not support subnet mask of advertised networks in their routing updates. As an outcome, they are unable to learn the existence of more than one mask length.
The classless routing protocols like OSPF, RIPv2, EIGRP, IS-IS and BGP make the implementation of VLSM possible by incorporating the subnet mask for the networks that are advertised in the routing updates. Previously, the use of networks were limited to only/26 masks throughout the system.
Example of CIDR
The below-given diagram shows the use of CIDR.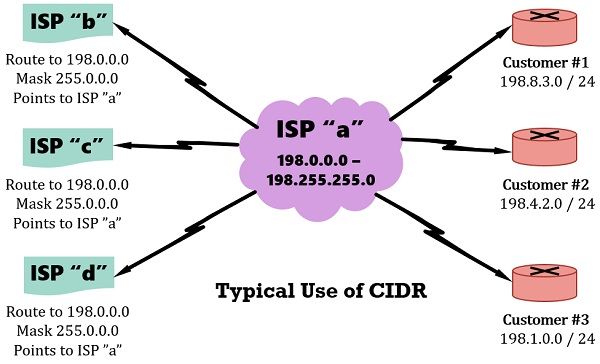 For example, ISP “a” owns a Class C networks 198.0.0.0 by 198.255.255.0. When no CIDR is used, all the other ISPs’ routing tables would be having a distinct route to each of the 2^16 Class C networks that begin with 198. But when CIDR is implemented the other ISPs’ routers have a unique route to the 198.0.0.0/8, as shown in the diagram. Alternatively, it contains a route to all hosts in which the IP address starts with 198. However, more than 2.09 million Class C networks alone exist, but CIDR has promoted internet routers shorten their routing tables to a more manageable size.
For example, ISP “a” owns a Class C networks 198.0.0.0 by 198.255.255.0. When no CIDR is used, all the other ISPs’ routing tables would be having a distinct route to each of the 2^16 Class C networks that begin with 198. But when CIDR is implemented the other ISPs’ routers have a unique route to the 198.0.0.0/8, as shown in the diagram. Alternatively, it contains a route to all hosts in which the IP address starts with 198. However, more than 2.09 million Class C networks alone exist, but CIDR has promoted internet routers shorten their routing tables to a more manageable size.
A routing protocol that interchanges the mask, as well as the subnet/network number, helps in obtaining the classless view of the number. Let’s assume, 198.0.0.0/8 defines a group of addresses whose first 8 bits are to decimal 198. Now, the work of the ISP “a” is to advertise this certain route to the remaining ISPs, who requires the only route to the IP address 198.0.0.0/8. The ISP “a” is aware of which Class C networks are at which customer sites.
Example of VLSM
Let’s take an example of a university which has several departments with different computing needs, such as engineering department needs 75 hosts, management department needs 50, similarly arts department with 25 and medical science department with 20. Here, we are taking regular class C address space – 192.168.1.0. If we employ fixed subnetting in the above example, the 255 host addresses will be divided into 4 subnets of 62 hosts. Therefore, the engineering department will experience a shortage of IP addresses while medical science department would get IP addresses in abundance.
So, resolve this issue VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking) is used, the 255 addresses are first divided into two parts each having 126 hosts. One subnet will be allotted to the engineering department. The other subnet is divided into two sub-subnets each having 62 hosts, among which one is assigned to the management department. Similarly, the sub-subnet with 62 hosts is further split to generate two sub-sub-subnets containing 30-30 hosts each which covers the remaining two departments.
Key Differences Between CIDR and VLSM
- The CIDR is the summarization of the subnets back to the classes. As against, VLSM permits you to apply variable subnet masks to the same class address space.
- CIDR uses suppernetting which refers to the aggregation of the network in a single address. On the contrary, VLSM employs the concept of the subnetting which is nothing but the subdivision of one network into multiple subaddresses.
- The protocols that assist CIDR are BGP and OSPF. Whereas, VLSM is implemented through RIPv2, OSPF, IGRP, and BGP.
Merits of CIDR
- Reduces the size of the routing table.
- Generates less overhead with respect to network traffic, CPU and memory.
- Provides flexibility in designing, addressing the networks.
Merits of VLSM
- Effective utilization of the address space.
- It is capable of hierarchical addressing.
- Reduces the size of the routing tables.
Conclusion
The CIDR allows to aggregate several networks in a single address, and this is done with the help of a routing table entry which expresses the aggregation of the network. In contrast, the VLSM helps in creating a hierarchy of subnets holding distinct sizes from an IP address space.
Leave a Reply