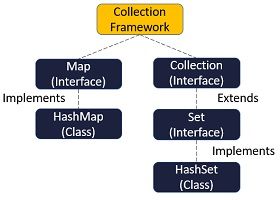
 HashMap and HashSet are the classes that implement the interfaces of the Java collection framework. The class HashMap implements from the Map interface, whereas HashSet implements from the Set interface.
HashMap and HashSet are the classes that implement the interfaces of the Java collection framework. The class HashMap implements from the Map interface, whereas HashSet implements from the Set interface.
HashMap is a data structure in Java that maps a key to a value. In HashMap, each key must be unique; however, duplicate values are allowed.
HashSet is a data structure in Java that stores a set of unique values. It strictly does not allow duplicate values.
In this content, we will be discussing the difference between these two Java collection framework classes. We will even learn to decide for which scenario you must use HashMap and for which you must use HashSet.
Content: HashMap Vs HashSet
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | HashMap | HashSet |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Implements Map interface | Implements Set interface |
| Used | Used to store elements in Key-Value pair | Used to store unique objects |
| Duplication | Keys must be unique; duplicate values are allowed | Duplicate values are not allowed |
| Null Value | There can be single Null Keys and multiple Null values | There can only be a single Null value |
| Insertion Method | put() method is used to insert elements into HashMap | add() method is used to insert elements in HashSet |
| Element Retrieval | Retrieving elements from HashMap is faster | Retrieving elements from HashSet is slower |
| Example | {101 -> “Jim”, 102 -> “Sam”, 103 -> “Anne”, 104 -> “Sam”, 105 -> “Neve”} This HashMap maps roll-number to names | {101, 102, 103, 104, 105} This HashSet contains a unique set of values |
What is HashMap?
HashMap is a generic Java class that implements the Java Collection Framework Map interface. It uses a hash table to store elements in the map, which uses the hashing mechanism internally.
Each element of the HashMap is a pair of keys and values. The keys of maps must be unique though duplicate associated values are allowed.
The class is declared as:
class HashMap<K, V>
K defines the type of the key, and V defines the type of the associated value. The HashMap class extends the AbstractMap class and implements the Map interface. So, it uses the methods they define and eventually does not define the method of its own.
The time complexity for the method get() and put() remains constant, i.e. O(1), even for the large collection.
- get() – it is used to retrieve the value associated with the particular key provided to the method as a parameter.
- put() – it is used to map a specific value to a specific key in the map.
- contains() – it is used to check whether HashMap contains a particular key.
- remove() – used to remove the mapping of the particular key from HashMap.
- size() – used to check the size of the HashMap, i.e., the number of key-value pair.
The code below creates a HashMap that maps students’ names to their marks.
import java.util.HashMap;
class HashMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating a hash map
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// Put elements to the map
map.put("John", 280);
map.put("Smith", 123);
map.put("Jane", 378);
map.put("Tod", 292);
map.put("Ralph", 198);
//print all elements
System.out.println(map);
//Size of map
System.out.println("Size of the map is:" + map.size());
//iterate map using set-view
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> set : map.entryset()) {
System.out.print(set.getKey() + ": ");
System.out.println(set.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
// Search using contain method
If(map.contains(“Smith”)){
System.out.println(map contains Smith);
// Modify John marks to 300
Integer marks = map.get("John");
map.put("John", marks + 20);
System.out.println("John updated marks are: " + map.get("John"));
// Delete
map.remove(“Jane”)
System.out.println(map);
}
}
The output for the following code is :
{Smith=123, Ralph=198, Jane=378, John=280, Tod=292}
Size of the map is:5
Jane: 378
John: 280
Tod: 292
Smith: 123
Ralph: 198
map contains Smith
John updated marks are: 300
What is HashSet?
HashSet is a generic class in Java that implements the Set interface. The class uses a hash table for storing the elements to create a collection where each element is unique. The HashSet strictly does not allow duplicates in the set. We declare this class as:
class HashSet<E>
E defines the type of object that the set will contain.
The mechanism hash table uses to store elements is hashing. The hashing function accepts a key and generates a unique value that we refer to as hash code. The value of this hash code is used as an index where the data associated with the key is stored.
- add() – used to add elements to the HashSet.
- contains() – used to check whether the HashSet contains particular or not.
- remove() – used to remove an element from HashSet.
- size() – used to check the size of the HashSet.
Now let us understand the concept of the HashSet with the help of code.
import java.util.HashSet;
class HashSetExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating a hash set
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
// Adding elements to the hash set.
set.add("101");
set.add("102");
set.add("103");
set.add("104");
set.add("105");
//print all elements
System.out.println(set);
// Check Size
System.out.println(“size of set is: ”+ set.size());
// Search using contain method
If(set.contains(104)){
System.out.println(set contains 104);
// Delete
Set.remove(102)
System.out.println(set);
}
}
}
The output first displays all the elements of the HashSet -> set. Then it displays the size of the set. Next, it displays the result of the method set.contains(104). Finally, it displays all the elements of the set after executing the method set.remove(102).
[104, 102, 105, 101, 103] Size of set is: 5 Set contains 104 [105, 104, 101, 103]
Key Differences Between HashMap and HashSet
- HashMap implements the Map interface, whereas HashSet implements the Set interface of the Java Collection Framework.
- We use HashMap to store elements where each element is a key-value pair. However, we use HashSet to store unique elements only.
- Elements of HashMap do not allow duplicate keys, but it allows duplicate values. On the other hand, elements of HashSet must be unique.
- In HashMap, the collection can have a single Null Key and may have multiple Null values. However, a HashSet collection can have a single Null value.
- To insert an element into the HashMap, we use put() method. On the contrary, to insert an element to the HashSet, we use add() method.
- Retrieving an element from HashMap is faster than HashSet, as the values are associated with the unique key. On the other hand, the elements of the HashSet are used to calculate the hash code, which may come out the same for two elements.
Similarities Between HashMap and HashSet
- HashMap and HashSet are the classes that implement the interfaces that are part of the Java Collection Framework.
- Both use a hash table to store elements.
- Performance complexity of both these classes is O(1).
- HashMap and HashSet do not guarantee the order of the stored elements. It is not mandatory that the order in which you add the elements in both the iterator will read them in the same order.
- We use an iterator to traverse both HashMap and HashSet.
- Both of them do not define any new method of their own and only use the methods provided by their superclasses and interfaces.
Conclusion
HashMap and HashSet are both types of collections but of different kinds. HashSet is a collection of unique elements. HashSet is a collection of unique elements. HashMap is a collection of elements where each element is a pair of keys and values.
Leave a Reply