 Routing is the mechanism of transferring information from a source to destination across an internetwork. The distance vector routing and link state routing are the two of routing algorithms, categorised depending on the way the routing tables are updated.
Routing is the mechanism of transferring information from a source to destination across an internetwork. The distance vector routing and link state routing are the two of routing algorithms, categorised depending on the way the routing tables are updated.
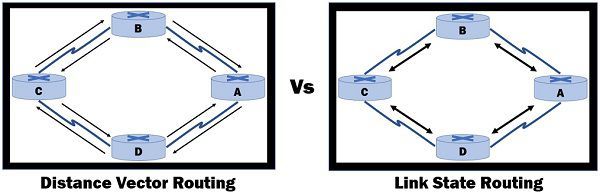
The prior difference between Distance vector and link state routing is that in distance vector routing the router share the knowledge of the entire autonomous system whereas in link state routing the router share the knowledge of only their neighbour routers in the autonomous system.
Content: Distance Vector Routing Vs Link State Routing
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Distance vector routing | Link state routing |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Bellman ford | Dijsktra |
| Network view | Topology information from the neighbour point of view | Complete information on the network topology |
| Best path calculation | Based on the least number of hops | Based on the cost |
| Updates | Full routing table | Link state updates |
| Updates frequency | Periodic updates | Triggered updates |
| CPU and memory | Low utilisation | Intensive |
| Simplicity | High simplicity | Requires a trained network administrator |
| Convergence time | Moderate | Fast |
| Updates | On broadcast | On multicast |
| Hierarchical structure | No | Yes |
| Intermediate Nodes | No | Yes |
Definition of Distance Vector Routing
In distance vector routing, a router need not know the entire path to every network segment; it only requires to know the direction or vector in which to send the packet. The technique determines the direction (vector) and distance (hop count) to any network in the internetwork.
Distance vector routing algorithms periodically send all or parts of their routing table to their adjacent neighbours. The routers running a distance vector routing protocol will automatically send periodic updates even if there are no changes in the network.
A router can verify all the known routes and alters its local routing table on the basis of the updated information received from neighbouring routing. This process is referred to as “routing by rumour” because the routing information that a router has of the network topology is based on the perspective of the routing table of the neighbour router.
RIP and IGRP is a commonly used distance vector protocol that uses hop counts or its routing metrics.
Definition of Link State Routing
In link-state routing, each router attempt to construct its own internal map of the network topology. At the initial stage of start-up, when a router becomes active, it sends the messages into the network and collects the information from the routers to which it is directly connected. It also provides information about whether the link to reach the router is active or not. This information is used by other routers to build a map of network topology. Then the router uses the map to choose the best path.
The link state routing protocols respond swiftly to the network changes. It sends triggered updates when a network change occurs and sends periodic updates at long time intervals such as 30 minutes. If the link alters state, the device detected the alteration generates and propagate an update message regarding that link to all routers. Then each router takes a copy of the update message and update its routing table and forwards the message to all neighbouring router.
This flooding of the update message is needed to ensure that all routers update their database before creating an update routing table that reflects the new technology. OSPF protocol is the example link state routing.
Key Differences Between Distance Vector Routing and Link State Routing
- Bellman-Ford algorithm is used for performing distance vector routing whereas Dijsktra is used for performing the link state routing.
- In distance vector routing the routers receive the topological information from the neighbour point of view. On the contrary, in link state routing the router receive complete information on the network topology.
- Distance vector routing calculates the best route based on the distance (fewest number of hops). As against, Link state routing calculates the best route on the basis of least cost.
- Link state routing updates only the link state while Distance vector routing updates full routing table.
- The frequency of update in both routing technique is different distance vector update periodically whereas link state update frequency employs triggered updates.
- The utilization of CPU and memory in distance vector routing is lower than the link state routing.
- The distance vector routing is simple to implement and manage. In contrast, the link state routing is complex and requires trained network administrator.
- The convergence time in distance vector routing is slow, and it usually suffers from count to infinity problem. Conversely, the convergence time in link state routing is fast, and it is more reliable.
- Distance vector doesn’t have hierarchical structure while in link state routing the nodes can have a hierarchical structure.
Conclusion
In distance vector routing the routing share, the information of the entire autonomous system and the information is shared only with neighbours. On the other hand, in link state routing the routers share the knowledge only about their neighbours and the information is shared with all routers.
Waheedullah says
Hi
I found it the most helpful web,
Really thanks.
Sk Naser Mahammad says
Really helpful.
Thanks Tech Differences.
Evans says
Well explained!!
KA Paul says
Impressive.
Okoth says
Thank for your helpful tutorials God bless you
Mary Kate says
Very nice content.
Abdallah says
Fully functional comparison Chart
arun says
well explained
very useful and effective website…
Susanta says
Thanks for this informative suggestion
Ritik says
Thanks for the detailed explanation…..
Herman Jansson says
The author has covered all the parts of the topic.
Thank you….