 Deadlock and Starvation both are the conditions where the processes requesting for a resource has been delayed for a long. Although deadlock and starvation both are different from each other in many aspects. Deadlock is a condition where no process proceeds for execution, and each waits for resources that have been acquired by the other processes.
Deadlock and Starvation both are the conditions where the processes requesting for a resource has been delayed for a long. Although deadlock and starvation both are different from each other in many aspects. Deadlock is a condition where no process proceeds for execution, and each waits for resources that have been acquired by the other processes.
On the other hands, in Starvation, process with high priorities continuously uses the resources preventing low priority process to acquire the resources. Let us discuss some more differences between deadlock and starvation with the help of comparison chart shown below.
Content: Deadlock Vs Starvation
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparsion | Deadlock | Starvation |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Deadlock is where no process proceeds, and get blocked. | Starvation is where low priority processes get blocked, and high priority process proceeds. |
| Arising condition | The occurrence of Mutual exclusion, Hold and wait, No preemption and Circular wait simultaneously. | Enforcement of priorities, uncontrolled resource management. |
| Other name | Circular wait. | Lifelock. |
| Resources | In deadlocked, requested resources are blocked by the other processes. | In starvation, the requested resources are continuously used by high priority processes. |
| Prevention | Avoiding mutual exclusion, hold and wait, and circular wait and allowing preemption. | Aging. |
Definition of Deadlock
Deadlock is a situation where the several processes in CPU compete for the finite number of resources available within the CPU. Here, each process holds a resource and wait to acquire a resource that is held by some other process. All the processes wait for resources in a circular fashion.
In the image below, you can see that Process P1 has acquired resource R2 that is requested by process P2 and Process P1 is requesting for resource R1 which is again held by R2. So process P1 and P2 form a deadlock.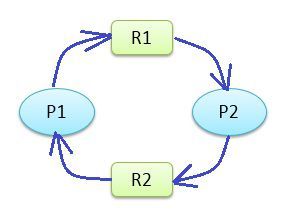 Deadlock is a common problem in multiprocessing operating systems, distributed systems, and also in parallel computing systems. There are four conditions which must occur simultaneously to raise the condition of deadlock, which are Mutual exclusion, Hold and waits, No preemption, and Circular wait.
Deadlock is a common problem in multiprocessing operating systems, distributed systems, and also in parallel computing systems. There are four conditions which must occur simultaneously to raise the condition of deadlock, which are Mutual exclusion, Hold and waits, No preemption, and Circular wait.
- Mutual exclusion: Only one process at a time can use a resource if other process requests the same resource, it has to wait till the process using resource releases it.
- Hold and Wait: A process must be holding a resource and waiting to acquire another resource that is held by some other process.
- No Preemption: The process holding the resources can not be preempted. The process holding the resource must release the resource voluntarily when it has completed its task.
- Circular wait: The process must wait for resources in a circular fashion. Suppose we have three processes {P0, P1, P2}. The P0 must wait for the resource held by P1; P1 must wait to acquire the resource held by process P2, and P2 must wait to acquire the process held by P0.
Although there are some applications that can detect the programs that may get deadlocked. But the operating system is never responsible for preventing the deadlocks. It is the responsibility of programmers to design deadlock free programs. It can be done by avoiding the above conditions which are necessary for deadlock occurrence
Definition of Starvation
Starvation can be defined as when a process request for a resource and that resource has been continuously used by the other processes then the requesting process faces starvation. In starvation, a process ready to execute waits for CPU to allocate the resource. But the process has to wait indefinitely as the other processes continuously block the requested resources.
The problem of starvation generally occurs in priority scheduling algorithm. In priority scheduling algorithm, the process with higher priority is always allocated the resource, preventing the lower priority process from getting the requested resource.
Aging can resolve the problem of starvation. Aging gradually increases the priority of the process that has been waiting long for the resources. Aging prevents a process with low priority to wait indefinitely for a resource.
Key Differences Between Deadlock and Starvation in OS
- In a deadlock, none of the processes proceeds for execution, each process get blocked waiting for the resources acquired by the another process. On the other hand, starvation is a condition where the processes that possess higher priority is allowed to acquire the resources continuously by preventing the low priority processes to acquire resources resulting in indefinite blocking of low priority processes.
- Deadlock arises when four conditions Mutual exclusion, Hold and wait, No preemption, and Circular wait occurs simultaneously. However, starvation occurs when process priorities have been enforced while allocating resources, or there is uncontrolled resource management in the system.
- Deadlock is often called by the name circular wait whereas, the starvation is called Lived lock.
- In Deadlock the resources are blocked by the process whereas, in starvation, the processes are continuously being used by the processes with high priorities.
- Deadlock can be prevented by the avoiding the conditions like mutual exclusion, Hold and wait, and circular wait and by allowing the preemption of the processes that are holding resources for a long time. On the other hand, Starvation can be prevented by aging.
Conclusion
Both Deadlock and Starvation delays the process execution by blocking it. On one hand where deadlock can cause processes to starve, and on the other hands starvation can get the processes out of the deadlock.
Rutuja says
Thank you so much for such great differences.
Rajesh Tanwar says
Your posts are really awesome…you deserve great love and respect from me…Thank you so much
Robert Kealeboga says
Your Hard Work is Highly Appreciated…
Ahmed Shihab says
Nice post…Appreciated.
data science course says
Thank you for creating this helpful site.