 Procedure-oriented Programming(POP) and Object-oriented programming(OOP) both are the programming approaches, which uses high-level language for programming. A program can be written in both the languages, but if the task is highly complex, OOP operates well as compared to POP. In POP, the ‘data security’ is at risk as data freely moves in the program, as well as, ‘code reusability’ is not achieved which makes the programming lengthy, and hard to understand.
Procedure-oriented Programming(POP) and Object-oriented programming(OOP) both are the programming approaches, which uses high-level language for programming. A program can be written in both the languages, but if the task is highly complex, OOP operates well as compared to POP. In POP, the ‘data security’ is at risk as data freely moves in the program, as well as, ‘code reusability’ is not achieved which makes the programming lengthy, and hard to understand.
Large programs lead to more bugs, and it increases the time of debugging. All these flaws lead to a new approach, namely “object-oriented programming”. In object-oriented programming’s primary concern is given on ‘data security’; it binds the data closely to the functions which operate on it.
It also resolves the problem of ‘code reusability’, as if a class is created, its multiple instances(objects) can be created which reuses the members and member functions defined by a class. There are some other differences which can be explained with the help of a comparison chart.
Content: OOP Vs POP
Comparison Chart
| Basis For comparison | POP | OOP |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Procedure/Structure oriented . | Object oriented. |
| Approach | Top-down. | Bottom-up. |
| Basis | Main focus is on "how to get the task done" i.e. on the procedure or structure of a program . | Main focus is on 'data security'. Hence, only objects are permitted to access the entities of a class. |
| Division | Large program is divided into units called functions. | Entire program is divided into objects. |
| Entity accessing mode | No access specifier observed. | Access specifier are "public", "private", "protected". |
| Overloading or Polymorphism | Neither it overload functions nor operators. | It overloads functions, constructors, and operators. |
| Inheritance | Their is no provision of inheritance. | Inheritance achieved in three modes public private and protected. |
| Data hiding & security | There is no proper way of hiding the data, so data is insecure | Data is hidden in three modes public, private, and protected. hence data security increases. |
| Data sharing | Global data is shared among the functions in the program. | Data is shared among the objects through the member functions. |
| Friend functions or friend classes | No concept of friend function. | Classes or function can become a friend of another class with the keyword "friend". Note: "friend" keyword is used only in c++ |
| Virtual classes or virtual function | No concept of virtual classes . | Concept of virtual function appear during inheritance. |
| Example | C, VB, FORTRAN, Pascal | C++, JAVA, VB.NET, C#.NET. |
Definition of Object-oriented programming(OOP)
OOP’s chief concern is to hide the data from non-member functions of a class, which it treats like “critical information”. Data is closely tied to the member functions of a class, which operates on it. It doesn’t allow any non-member function to modify the data inside it. Objects interact with each other through member functions to access their data.
OOP is developed on the basic concept of “object”, “classes”, “data encapsulation or abstraction”,” inheritance”, and “Polymorphism or overloading”. In OOP, programs can be divided into modules by partitioning data and functions, which further can be used as templates for creating new copies of modules, if required. Therefore, it is an approach that facilitates in modularizing programs by constructing a partitioned memory area for data and functions.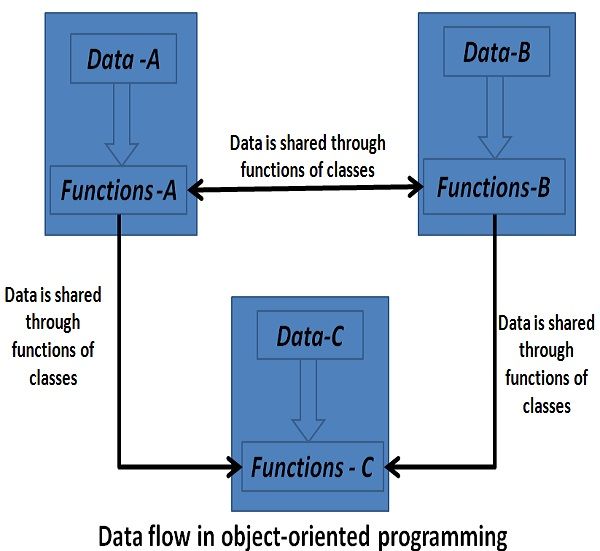
Object-Oriented Concepts
- Objects: It is considered as a variable of type class and an instance of a class.
- Class: It is a set of objects of similar type. A complete set of data and code of an object creates an user-defined data type by using a class.
- Data abstraction and encapsulation: Abstraction is nothing but a method of hiding background details and representing essential features. The encapsulation is a method of packing the data and functions into a single unit.
- Inheritance: Inheritance is a technique of acquiring features of objects from one class to the other class objects. In other words, it helps in deriving a new class from the existing one.
- Polymorphism: Polymorphism provides a method of creating multiple forms of a function by using a single function name.
- Dynamic binding: It specifies that the code associated with a particular procedure is not known until the moment of the call at run time.
- Message passing: This OOP concept enables interaction between different classes by transmitting and receiving information.
Definition of Procedure oriented programming(POP)
POP is a conventional way of programming. Procedural programming is where the primary focus is on getting the task done in sequential order. Flowchart organizes the flow of control of the program. If the program is extensive, it is structured in some small units called functions, which shares global data. Here, the concern of data security arises, as there is an unintentional change in the program by functions.
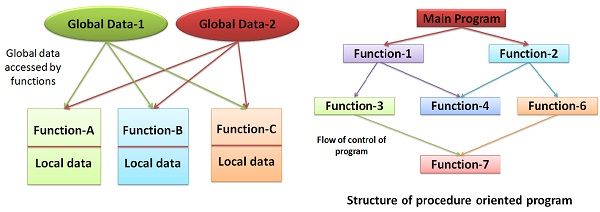
POP characteristics
- While designing a program, POP follows a top-down programming approach.
- Majority of the functions allows global data to be shared.
- It also divides larger programs into smaller parts called as functions.
- It allows a free data movement around the system from functions to functions.
- Data is transformed by the functions from one form to another.
- It gives importance to the concept of the functions.
Key Differences Between OOP and POP
- POP is procedure-oriented programming while OOP is object-oriented programming.
- The main focus of POP is on “how to get the task done” it follows the flow chart to get the task done. OOP’s main focus is on data security as only the objects of a class are allowed to access the attributes or function of a class.
- The functions are small units of the large programs or a sub-program that execute to get the main task done. In contrast, OOP attributes and functions of the class are divided among the objects.
- In POP, there is no specific accessing mode to access attributes or functions in the program. Conversely, in OOP there are three accessing modes “public”, “private”, “protected”, that are used as an accessing method to access attributes or functions.
- POP does not support the concept of Overloading/polymorphism. On the contrary, OOP supports Overloading/Polymorphism, which means using the same function name for performing different functions. We can overload functions, constructor, and operators in OOP.
- There is no concept of inheritance in POP whereas, OOP supports inheritance which allows using the attribute and functions of other class by inheriting it.
- POP is less secure as compared to OOP because in OOP the access specifier limits the access to attributes or functions which increase the security.
- In POP if some data is to be shared among all the functions in the program, it is declared globally outside all functions. While in OOP the data member of the class can be accessed through the member functions of the class.
- In POP there is no concept of the friend function. As against, in OOP there is a concept of friend function which is not the member of the class, but because it is friend member it can access the data member and member functions of the class.
- There is no concept of virtual classes in POP whereas in OOP, the virtual functions support polymorphism.
Advantages
POP (Procedure Oriented Programming)
- Provides an ability to reuse the same code at various places.
- Facilitates in tracking the program flow.
- Capable of constructing modules.
OOP (Object Oriented Programming)
- Objects help in task partitioning in the project.
- Secure programs can be built using data hiding.
- It can potentially map the objects.
- Enables the categorization of the objects into various classes.
- Object-oriented systems can be upgraded effortlessly.
- Redundant codes can be eliminated using inheritance.
- Codes can be extended using reusability.
- Greater modularity can be achieved.
- Data abstraction increases reliability.
- Flexible due to the dynamic binding concept.
- Decouples the essential specification from its implementation by using information hiding.
Disadvantages
POP (Procedure Oriented Programming)
- Global data are vulnerable.
- Data can move freely within a program
- It is tough to verify the data position.
- Functions are action-oriented.
- Functions are not capable of relating to the elements of the problem.
- Real-world problems cannot be modelled.
- Parts of code are interdependent.
- One application code cannot be used in other application.
- Data is transferred by using the functions.
OOP (Object Oriented Programming)
- It requires more resources.
- Dynamic behaviour of objects requires RAM storage.
- Detection and debugging is harder in complex applications when the message passing is performed.
- Inheritance makes their classes tightly coupled, which affects the reusability of objects.
Conclusion
The flaws of POP arises the need for OOP. OOP corrects the flaws of POP by introducing the concept of “object” and “classes”. It enhances the data security and automatic initialization & clear-up of objects. OOP makes it possible to create multiple instances of the object without any interference.
nabin says
it’s a really nice article. this article clear all confusion about pop vs oop. thank you
Ameen says
Well presented, Thank you.
kotresh says
Thanks for the article, Good for beginners
Amitesh says
This is nice article
It is very helpful
Mahesh says
Good
Boddireddy Charishma says
very nice
A says
It’s really helpful to me.
Thanks a lot.
Mr.Professional says
Nice explanation in simple words
A. Sridhar says
Helpful article. Thanks a lot.
Gopal Jain says
this article is very helpful to understand the difference between pop and oops
Monika says
Nice information
sai sanchit says
it is a gratifying article…..
Rajat Bisht says
everything is explained in detail
MEERABAI says
very useful
Hsu Yee Htet says
I can clearly understand all the concepts of OOP and POP
Samir T says
Simple and clear with diagrams, thanks alot